
Which structure among the following is used by parasites to draw food from their hosts?
(a)Rhizoids
(b)Haustoria
(c)Hyphae
(d)Capsids
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: This is a slender (or root-like structure) projection from the root of a parasitic plant or the hyphae of a parasitic fungus. This forms a vascular union between the plants.
Complete answer:
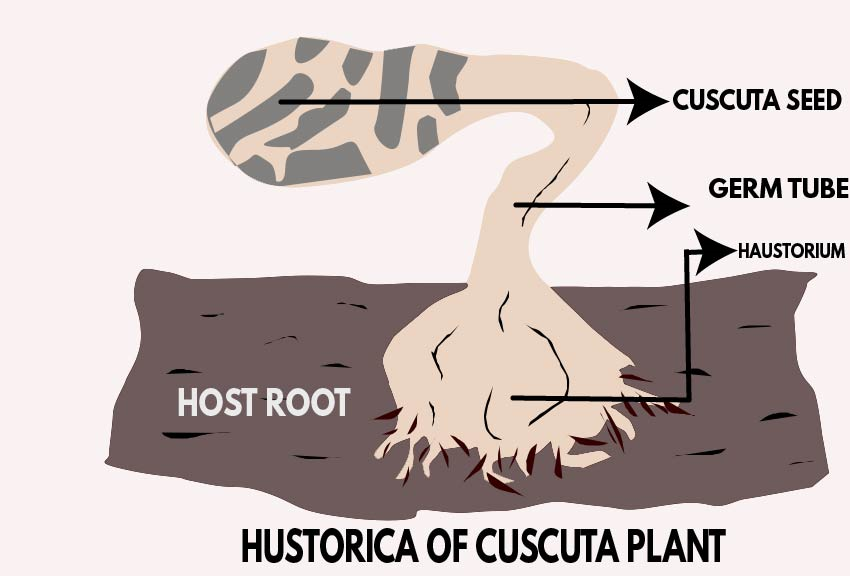
Haustoria is the structure developed by parasitic plants to draw food from their hosts by penetrating the tissues of its host and absorbing nutrients (and sap) from it. They may develop from roots or stems and it displays a wide range of morphologies. Mostly the parasite is located externally to the host and gets nutrients from the haustorium embedded inside the host. In mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the haustorium penetrates the host's tissue to draw nutrients. Cuscuta (Dodder) plant is a total stem parasite. It has no connection with the soil after the seedling stage and lacks chlorophyll and is dependent on the host for organic food materials, water, and minerals salts.
Parasites tend to have additional mechanisms to detect their specific host plants. For instance, the family Orobanchaceae (Orobanche, Phelipanche, and Striga) has seeds that are extremely small and may sit in the soil for years. The seed of the parasite detects a chemical signal generally a strigolactone (a type of plant hormone) from the host root, and then the parasite radicle (embryonic root) grows a short distance (less than 2 mm) to contact the host root and produce a haustorium.
Some species vegetative grow within the host and the haustorium proliferates in such a manner that the parasite emerges only to the flower. For instance, it includes the members of the genus Rafflesia, which grow inside the tropical Tetrastigma, and stemsuckers which grow within members of the pea family.
So, the correct answer is option ‘Haustoria’.
Note: An organism that lives in or on another organism and takes some or all of its nourishment from that other organism (or host) is known as a parasite. Parasitic plants don’t contribute to the benefit of the host and sometimes may cause extreme damage to the host.
Complete answer:
Haustoria is the structure developed by parasitic plants to draw food from their hosts by penetrating the tissues of its host and absorbing nutrients (and sap) from it. They may develop from roots or stems and it displays a wide range of morphologies. Mostly the parasite is located externally to the host and gets nutrients from the haustorium embedded inside the host. In mistletoe or members of the broomrape family, the haustorium penetrates the host's tissue to draw nutrients. Cuscuta (Dodder) plant is a total stem parasite. It has no connection with the soil after the seedling stage and lacks chlorophyll and is dependent on the host for organic food materials, water, and minerals salts.
Parasites tend to have additional mechanisms to detect their specific host plants. For instance, the family Orobanchaceae (Orobanche, Phelipanche, and Striga) has seeds that are extremely small and may sit in the soil for years. The seed of the parasite detects a chemical signal generally a strigolactone (a type of plant hormone) from the host root, and then the parasite radicle (embryonic root) grows a short distance (less than 2 mm) to contact the host root and produce a haustorium.
Some species vegetative grow within the host and the haustorium proliferates in such a manner that the parasite emerges only to the flower. For instance, it includes the members of the genus Rafflesia, which grow inside the tropical Tetrastigma, and stemsuckers which grow within members of the pea family.
So, the correct answer is option ‘Haustoria’.
Note: An organism that lives in or on another organism and takes some or all of its nourishment from that other organism (or host) is known as a parasite. Parasitic plants don’t contribute to the benefit of the host and sometimes may cause extreme damage to the host.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




