
Which part of the velocity time-graph signifies the distance covered by a body?
Answer
521.1k+ views
Hint:Learn the concept of velocity of a body, the acceleration and other different aspects of motion of a body. The velocity of a body is defined by the displacement covered by the body per unit time.
Formula used:
The instantaneous velocity of a body is given by the
\[v = \dfrac{{ds}}{{dt}}\]
where \[v\] is the velocity of the body, \[ds\] is the infinitesimal displacement of the body covered in infinitesimal time \[dt\].
The instantaneous acceleration of the body is given by,
\[a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}\]
where \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, \[dv\] is the infinitesimal velocity of the body in infinitesimal time \[dt\].
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the velocity of a body is the rate of change of displacement of the body per unit time. Now, when we draw a velocity time graph we plot the velocity along Y-axis and the time along X-axis. So, the slope of the curve is acceleration of the body at a given time. Now, that we can write as, instantaneous acceleration of the body,
\[a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}\]
Now, we know that, instantaneous velocity of a body is given by the
\[v = \dfrac{{ds}}{{dt}}\]
Now, if we integrate the equation simply we can have, \[s = \int {vdt} \] which is the distance covered by the body.
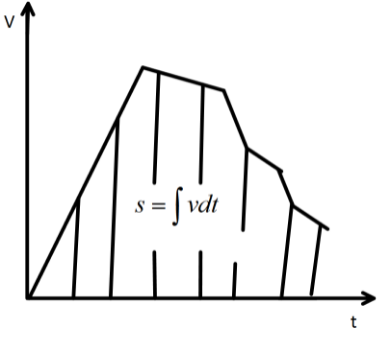
Now this integration is nothing but the area under the curve since if we simply multiply the length and breadth of a rectangle we get the area of the rectangle. Here the length is the velocity and the breadth is the time.
So, in a velocity time graph the area under the curve represents the distance covered by the body.
Note: In thermodynamics the area under the curve of the P-V curve signifies work done, which is a scalar quantity or in force displacement curve the area under the curve is also work done. In the velocity time graph the area under the curve represents a vector quantity.
Formula used:
The instantaneous velocity of a body is given by the
\[v = \dfrac{{ds}}{{dt}}\]
where \[v\] is the velocity of the body, \[ds\] is the infinitesimal displacement of the body covered in infinitesimal time \[dt\].
The instantaneous acceleration of the body is given by,
\[a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}\]
where \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, \[dv\] is the infinitesimal velocity of the body in infinitesimal time \[dt\].
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the velocity of a body is the rate of change of displacement of the body per unit time. Now, when we draw a velocity time graph we plot the velocity along Y-axis and the time along X-axis. So, the slope of the curve is acceleration of the body at a given time. Now, that we can write as, instantaneous acceleration of the body,
\[a = \dfrac{{dv}}{{dt}}\]
Now, we know that, instantaneous velocity of a body is given by the
\[v = \dfrac{{ds}}{{dt}}\]
Now, if we integrate the equation simply we can have, \[s = \int {vdt} \] which is the distance covered by the body.

Now this integration is nothing but the area under the curve since if we simply multiply the length and breadth of a rectangle we get the area of the rectangle. Here the length is the velocity and the breadth is the time.
So, in a velocity time graph the area under the curve represents the distance covered by the body.
Note: In thermodynamics the area under the curve of the P-V curve signifies work done, which is a scalar quantity or in force displacement curve the area under the curve is also work done. In the velocity time graph the area under the curve represents a vector quantity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




