
Which part of the brain regulates body temperature, hunger, and water balance.
A. Hypothalamus
B. Infundibulum
C. Medulla oblongata
D. Pons varoli
Answer
575.7k+ views
Hint: Brain forms the central organ of the human body. Regulation of body temperature, water balance, and hunger are all under the control of the organ present in the brain which connects the link between the nervous system and endocrine system.
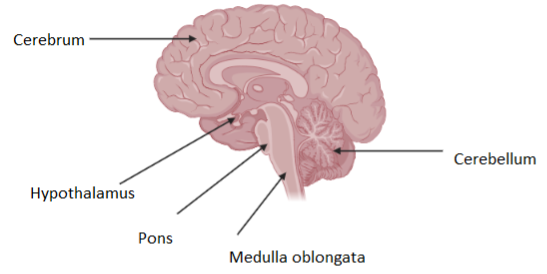
Complete answer: The human brain is divided into three parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem which includes medulla oblongata and pons varolii. A long stem like structure called the medulla oblongata forms the upper part of the brain stem. It is a cone shaped organ which regulates the involuntary functions of the body. The higher levels of the brain are connected to the spinal cord by the medulla oblongata. It plays an important role in cardiovascular center, vasomotor center, and reflex actions which involves swallowing, coughing and sneezing. A deep structure of the brain which contains a large number of nuclei is called hypothalamus. The nervous system is connected to the endocrine system by the hypothalamus via pituitary gland. Certain metabolic processes and activities of the autonomic nervous system are carried out by hypothalamus. Hypothalamus is responsible for the various activities of the body. hunger, sleep, thirst, and sexual response is under the control of the hypothalamus. The body temperature is under the control of the anterior hypothalamus.
So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Motivated behaviors are controlled by the medial zone of the hypothalamus. Damage to the hypothalamus can cause disruption in growth, body weight, sodium, water balance, and sleep cycles. Damage to the hypothalamus will also impact the endocrine system as well as the pituitary gland.
Complete answer: The human brain is divided into three parts: cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem which includes medulla oblongata and pons varolii. A long stem like structure called the medulla oblongata forms the upper part of the brain stem. It is a cone shaped organ which regulates the involuntary functions of the body. The higher levels of the brain are connected to the spinal cord by the medulla oblongata. It plays an important role in cardiovascular center, vasomotor center, and reflex actions which involves swallowing, coughing and sneezing. A deep structure of the brain which contains a large number of nuclei is called hypothalamus. The nervous system is connected to the endocrine system by the hypothalamus via pituitary gland. Certain metabolic processes and activities of the autonomic nervous system are carried out by hypothalamus. Hypothalamus is responsible for the various activities of the body. hunger, sleep, thirst, and sexual response is under the control of the hypothalamus. The body temperature is under the control of the anterior hypothalamus.

So, option A is the correct option.
Note: Motivated behaviors are controlled by the medial zone of the hypothalamus. Damage to the hypothalamus can cause disruption in growth, body weight, sodium, water balance, and sleep cycles. Damage to the hypothalamus will also impact the endocrine system as well as the pituitary gland.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




