
Which out of \[N{H_3}\] and $N{F_3}$ has a higher dipole moment and why?
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: Dipole moment is a vector quantity and hence the resultant dipole moment in a molecule depends upon the direction of dipole moments of individual bonds. In \[N{H_3}\], Nitrogen has a lone pair and is more electronegative than hydrogen. In \[N{H_3}\], fluorine is more electronegative than nitrogen.
Complete answer:
In both molecules i.e., \[N{H_3}\] and $N{F_3}$, the central atom (N) has a lone pair electron and there are three bond pairs. Hence, both molecules have a pyramidal molecular geometry. The dipole moment of ammonia (1.47D) is higher than the dipole moment of $N{F_3}$ (0.24D). In each molecule, N atom has one lone pair.
In \[N{H_3}\], Nitrogen is more electronegative than H, so it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself. As a result, the dipole due to Nitrogen is in the same direction as the resultant dipole moment due to N-H bond & hence the net dipole increases.
Since in the case of $N{F_3}$, fluorine is more electronegative than nitrogen, so it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself from nitrogen. As a result, the dipole due to all F is in the opposite direction to the resultant dipole due to N-F bonds, therefore the net dipole decreases.
F is more electronegative than H and N−F bond is more polar than N−H bond. Hence, $N{F_3}$Is expected to have much larger dipole moment than \[N{H_3}\] However reverse is true as in case of ammonia, the direction of the lone pair dipole moment and the bond pair dipole moment is same whereas in case of $N{F_3}$. It is the opposite. Thus, in ammonia molecules, individual dipole moment vectors add whereas in $N{F_3}$, they cancel each other.
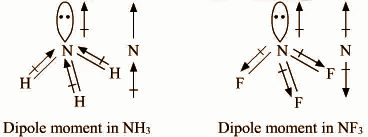
Dipole moment in \[N{H_3}\] Dipole moment in $N{F_3}$
Hence, the net dipole moment of $N{F_3}$ is less than that of \[N{H_3}\].
Note: Ammonia is an inorganic compound which is composed of a single nitrogen atom that is covalently bonded to three hydrogen atoms. It is manufactured as well as produced naturally from bacterial processes and the breakdown of organic matter. Ammonia is used in many industrial processes, and it is also used as a fertilizer and refrigerant. It is a colorless gas or compressed liquid which has a pungent odor and exposure occurs by inhalation, ingestion, or in contact.
Complete answer:
In both molecules i.e., \[N{H_3}\] and $N{F_3}$, the central atom (N) has a lone pair electron and there are three bond pairs. Hence, both molecules have a pyramidal molecular geometry. The dipole moment of ammonia (1.47D) is higher than the dipole moment of $N{F_3}$ (0.24D). In each molecule, N atom has one lone pair.
In \[N{H_3}\], Nitrogen is more electronegative than H, so it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself. As a result, the dipole due to Nitrogen is in the same direction as the resultant dipole moment due to N-H bond & hence the net dipole increases.
Since in the case of $N{F_3}$, fluorine is more electronegative than nitrogen, so it will attract the shared pair of electrons towards itself from nitrogen. As a result, the dipole due to all F is in the opposite direction to the resultant dipole due to N-F bonds, therefore the net dipole decreases.
F is more electronegative than H and N−F bond is more polar than N−H bond. Hence, $N{F_3}$Is expected to have much larger dipole moment than \[N{H_3}\] However reverse is true as in case of ammonia, the direction of the lone pair dipole moment and the bond pair dipole moment is same whereas in case of $N{F_3}$. It is the opposite. Thus, in ammonia molecules, individual dipole moment vectors add whereas in $N{F_3}$, they cancel each other.

Dipole moment in \[N{H_3}\] Dipole moment in $N{F_3}$
Hence, the net dipole moment of $N{F_3}$ is less than that of \[N{H_3}\].
Note: Ammonia is an inorganic compound which is composed of a single nitrogen atom that is covalently bonded to three hydrogen atoms. It is manufactured as well as produced naturally from bacterial processes and the breakdown of organic matter. Ammonia is used in many industrial processes, and it is also used as a fertilizer and refrigerant. It is a colorless gas or compressed liquid which has a pungent odor and exposure occurs by inhalation, ingestion, or in contact.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




