
Which organs perform the same function but structurally different?
(a) Homologous organs
(b) Analogous organs
(c) Vestigial organs
(d) Structurally homologous organs
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: These organs are proof that organisms may have evolved from a common ancestor. The human arm, the wings of a bat, the leg of a panther, and the flipper of a whale are the example for these kinds of organs.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Homologous organs perform the same function but are structurally different. The structure of the vertebrae is a common homologous structure in all mammals. Human beings are related to dinosaurs by an auditory bone that exists inside the human ears is homologous to a dinosaurs’ jawbone.
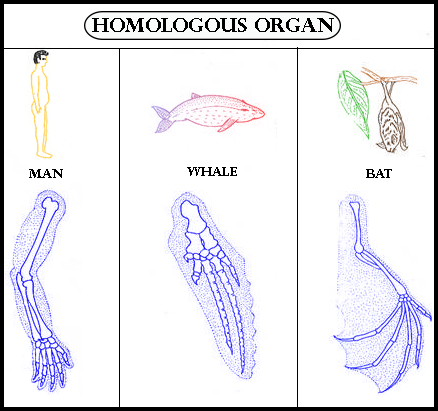
So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Homologous organ’.
Additional information:
- Homologous organs are formed as a result of divergent evolution, where the same species develops two distinct abilities as they are separated by any geographical barriers.
Analogous organs: Organs that have similar or equivalent functions but not evolved from the same ancestor or evolutionary origin.
- This formed due to convergent evolution, for example, both bees and birds have wings which they use for flight; their wings came from different evolutionary origins or ancestors.
Vestigial organs: Organs which lost their ancestral function in the process of evolution are known as vestigial organs.
- The appendix of humans and wings of flightless birds are the example for vestigial organs where the structures are retained but the functions are lost.
Structurally homologous organs: A system of organs that are structurally different but function for the same plan or process is known as the structurally homologous organs.
Note:
- Organisms when exposed to a new environment try to adapt and evolve to survive better, forming the basic principle divergent evolution.
- Humans and giraffes have the same number of cervical vertebrae but due to the variation in the size of the bone, giraffes look taller than humans.
- Genetic similarity provides a better understanding of the connection between related species and about their common ancestor.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Homologous organs perform the same function but are structurally different. The structure of the vertebrae is a common homologous structure in all mammals. Human beings are related to dinosaurs by an auditory bone that exists inside the human ears is homologous to a dinosaurs’ jawbone.

So, the correct answer is ‘(a) Homologous organ’.
Additional information:
- Homologous organs are formed as a result of divergent evolution, where the same species develops two distinct abilities as they are separated by any geographical barriers.
Analogous organs: Organs that have similar or equivalent functions but not evolved from the same ancestor or evolutionary origin.
- This formed due to convergent evolution, for example, both bees and birds have wings which they use for flight; their wings came from different evolutionary origins or ancestors.
Vestigial organs: Organs which lost their ancestral function in the process of evolution are known as vestigial organs.
- The appendix of humans and wings of flightless birds are the example for vestigial organs where the structures are retained but the functions are lost.
Structurally homologous organs: A system of organs that are structurally different but function for the same plan or process is known as the structurally homologous organs.
Note:
- Organisms when exposed to a new environment try to adapt and evolve to survive better, forming the basic principle divergent evolution.
- Humans and giraffes have the same number of cervical vertebrae but due to the variation in the size of the bone, giraffes look taller than humans.
- Genetic similarity provides a better understanding of the connection between related species and about their common ancestor.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




