
Which organelle of the cell is called the powerhouse of the cell?
A. Cell-wall
B. Nucleus
C. Mitochondria
D. Complete cell
Answer
588.6k+ views
Hint: Cell organelles are located at the cell cytoplasm. An organelle is called the powerhouse of the cell, because it can extract energy from some other substances. Released energy is known as energy currency of the cell.
Complete step by step answer:
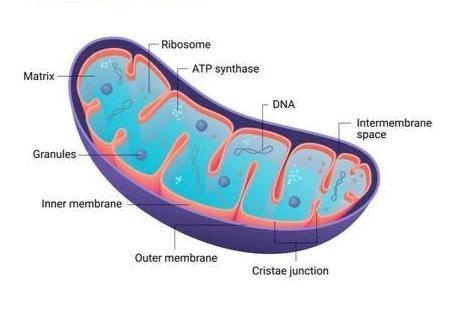
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. It can extract energy from food particles. It releases energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Mitochondria is the self-duplicating spherical, granular cell organelles. They are found in all eukaryotic cells except mature mammalian RBC. They serve as the centers of aerobic respiration, energy transduction, oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis.
Mitochondria are mobile organelles, uniformly distributed within the cell. They are often crowded or clustered around sites of maximum energy demand. Thus, the distribution of mitochondria appears to be related to their function as energy suppliers. In some cases, they perform active and passive movements. This ensures the supply of ATP wherever it is required. But, in some other instances, many of them are permanently stationed in regions where more energy is needed. For example, in muscle cells, they occur in large numbers in the I-band; in sperm tail, they remain wrapped around the axoneme (axial filament); in protein synthetically active cells, they mostly remain attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
The form and size of mitochondria vary with cell types, but are characteristics for each cell type. The number of mitochondria per cell varies greatly with species. It may range from zero to many thousand. In prokaryotes, mature mammalian RBCs and in some colorless algae mitochondria are absent.
Mitochondria are double walled and fluid filled bags. A Mitochondrion consists of a gelatinous, enzyme rich and proteinaceous matrix, enveloped by two concentric membranes. The membranes are almost fluid films, with a compact molecular arrangement. They are lamellar in organization, formed of lipid bilayer and extrinsic and intrinsic proteins. In between the two membranes is the intermembrane space. It is filled with a fluid, rich with enzymes and coenzymes. The outer membrane protects the mitochondrion from the enzymatic disintegration and also provides channels for passage of solutes.
Here, the correct answer is C) Mitochondria.
Additional information:
1. Mitochondrial outer membranes contain unique intrinsic protein porin, which is resistant to enzyme action.
2. Porin serves as a transport protein and also forms aqueous channel across the lipid bilayer.
3. Mitochondrial inner membrane is the center of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis.
Note:
The number of mitochondria per cell is variable depending on the physiological activity of the cells. Mitochondria is sausage or cylindrical in shape. They divide by fission.
Complete step by step answer:
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. It can extract energy from food particles. It releases energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Mitochondria is the self-duplicating spherical, granular cell organelles. They are found in all eukaryotic cells except mature mammalian RBC. They serve as the centers of aerobic respiration, energy transduction, oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis.
Mitochondria are mobile organelles, uniformly distributed within the cell. They are often crowded or clustered around sites of maximum energy demand. Thus, the distribution of mitochondria appears to be related to their function as energy suppliers. In some cases, they perform active and passive movements. This ensures the supply of ATP wherever it is required. But, in some other instances, many of them are permanently stationed in regions where more energy is needed. For example, in muscle cells, they occur in large numbers in the I-band; in sperm tail, they remain wrapped around the axoneme (axial filament); in protein synthetically active cells, they mostly remain attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
The form and size of mitochondria vary with cell types, but are characteristics for each cell type. The number of mitochondria per cell varies greatly with species. It may range from zero to many thousand. In prokaryotes, mature mammalian RBCs and in some colorless algae mitochondria are absent.
Mitochondria are double walled and fluid filled bags. A Mitochondrion consists of a gelatinous, enzyme rich and proteinaceous matrix, enveloped by two concentric membranes. The membranes are almost fluid films, with a compact molecular arrangement. They are lamellar in organization, formed of lipid bilayer and extrinsic and intrinsic proteins. In between the two membranes is the intermembrane space. It is filled with a fluid, rich with enzymes and coenzymes. The outer membrane protects the mitochondrion from the enzymatic disintegration and also provides channels for passage of solutes.

Here, the correct answer is C) Mitochondria.
Additional information:
1. Mitochondrial outer membranes contain unique intrinsic protein porin, which is resistant to enzyme action.
2. Porin serves as a transport protein and also forms aqueous channel across the lipid bilayer.
3. Mitochondrial inner membrane is the center of oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis.
Note:
The number of mitochondria per cell is variable depending on the physiological activity of the cells. Mitochondria is sausage or cylindrical in shape. They divide by fission.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




