
Which one of the following life cycle stages of Wuchereria bancrofti is infective to man?
A. Microfilaria
B. 1ststage larva
C. 2ndstage larva
D. 3rdstage larva
Answer
588k+ views
Hint:
The microfilaria of W. Bancrofti develop into first-stage larvae and then into third-stage infective larvae in the human body. The third-stage infective larvae can infect another human when the mosquito takes a blood meal.
Complete answer:
In this question, we have asked about the infective stage of W. Bancrofti. For this we'll first learn about the life cycle of W. Bancrofti.
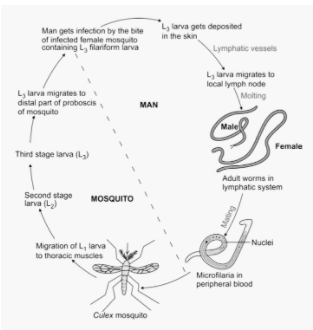
The infective larvae of B. Bancroft enters into the blood through the mosquito bite. They then reach the nearest lymph node where they grow into the thin thread like an adult worm. The maturation takes 3 months to 1 year. The mature adult worm damages or blocks the lymphatic vessels during this period.
The male and female nematodes reproduce and give birth to microfilarias. This is first stage larvae which we call L1. This L1 stage moves in the vessels and gathers in arterioles of the lung during the day and emerges at night. When a mosquito bites, the microfilariae enter into the mosquito. The L1 stage then enters the insect's gut wall by penetrating it, then moving to the thoracic muscles of the mosquito. They mature into thoracic muscles and complete two life stages: L2 and L3. When this mosquito bites a healthy human, the L3 stage enters into the human body and infests the person. So, the infective stage of W. Bancrofti is L3 or 3rd stage of larva. So, the correct option is D. 3rd stage larva
Note: W. Bancrofti causes elephantiasis. It occurs due to obstruction of the lymphatic system, which results in the accumulation of a fluid, which results in gross enlargement of an area of the body, especially the limbs.
The microfilaria of W. Bancrofti develop into first-stage larvae and then into third-stage infective larvae in the human body. The third-stage infective larvae can infect another human when the mosquito takes a blood meal.
Complete answer:
In this question, we have asked about the infective stage of W. Bancrofti. For this we'll first learn about the life cycle of W. Bancrofti.
The infective larvae of B. Bancroft enters into the blood through the mosquito bite. They then reach the nearest lymph node where they grow into the thin thread like an adult worm. The maturation takes 3 months to 1 year. The mature adult worm damages or blocks the lymphatic vessels during this period.
The male and female nematodes reproduce and give birth to microfilarias. This is first stage larvae which we call L1. This L1 stage moves in the vessels and gathers in arterioles of the lung during the day and emerges at night. When a mosquito bites, the microfilariae enter into the mosquito. The L1 stage then enters the insect's gut wall by penetrating it, then moving to the thoracic muscles of the mosquito. They mature into thoracic muscles and complete two life stages: L2 and L3. When this mosquito bites a healthy human, the L3 stage enters into the human body and infests the person. So, the infective stage of W. Bancrofti is L3 or 3rd stage of larva. So, the correct option is D. 3rd stage larva

Note: W. Bancrofti causes elephantiasis. It occurs due to obstruction of the lymphatic system, which results in the accumulation of a fluid, which results in gross enlargement of an area of the body, especially the limbs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




