
Which one of the following does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation?
A) (+) Sucrose
B) (+) Lactose
C) (+) Maltose
D) (-) Fructose
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: It is important to know that only reducing sugars have a free aldehyde (-CHO) or ketone (>C=0) group capable of mutarotation. As a result, only reducing sugars can undergo mutarotation, while non-reducing sugars cannot.
Complete answer:
First, we have to understand that mutarotation is the process in which the optical rotation of the compound changes in the aqueous solution. This is due to difference in the equipoise
between two anomers.
Now we shall discuss the structure of the given options in detail.
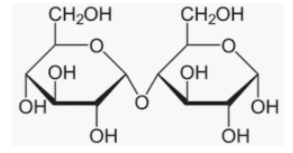
(+) Sucrose: Sucrose does not mutarotate. All sugars, however, do not have this mutarotation property. Sucrose lacks the ketone (>C-0) or free aldehyde (-CHO) groups. As a result, sucrose is incapable of mutarotation. This is the right option.
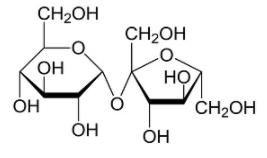
(+) Lactose: We know that the disaccharide sugar is lactose. It also contains a β (1→4)-glycosidic linkage that connects one glucose molecule to a galactose molecule. As a result, it is a reducing sugar that exhibits mutarotation. Therefore, this is not the right answer.
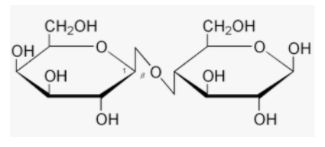
(+) Maltose: It's important to note that maltose is a reducing sugar with a hydroxyl group on the ring. It can mutarotate in aqueous solution because the α- and β-isomers formed by different conformations of the anomeric carbon have different specific rotations, and these two forms are in equilibrium in aqueous solutions. Therefore, this is not the right answer.
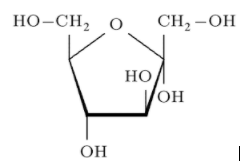
(-) Fructose: Fructose is classified as a monosaccharide and a reducing sugar which exhibits mutarotation. Therefore, this is not the right answer.
Therefore, we can conclude that sucrose is not a reducing sugar as it lacks a hydroxyl group in the ring. Hence, A) is the correct option. (+) Sucrose does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation.
Note:
We also know that cellulose does not undergo mutarotation like sucrose. At the anomeric location of cellulose, they do not have hydroxyl group (OH) availability. As a result, cellulose does not undergo mutarotation.
Complete answer:
First, we have to understand that mutarotation is the process in which the optical rotation of the compound changes in the aqueous solution. This is due to difference in the equipoise
between two anomers.
Now we shall discuss the structure of the given options in detail.
(+) Sucrose: Sucrose does not mutarotate. All sugars, however, do not have this mutarotation property. Sucrose lacks the ketone (>C-0) or free aldehyde (-CHO) groups. As a result, sucrose is incapable of mutarotation. This is the right option.

(+) Lactose: We know that the disaccharide sugar is lactose. It also contains a β (1→4)-glycosidic linkage that connects one glucose molecule to a galactose molecule. As a result, it is a reducing sugar that exhibits mutarotation. Therefore, this is not the right answer.

(+) Maltose: It's important to note that maltose is a reducing sugar with a hydroxyl group on the ring. It can mutarotate in aqueous solution because the α- and β-isomers formed by different conformations of the anomeric carbon have different specific rotations, and these two forms are in equilibrium in aqueous solutions. Therefore, this is not the right answer.

(-) Fructose: Fructose is classified as a monosaccharide and a reducing sugar which exhibits mutarotation. Therefore, this is not the right answer.

Therefore, we can conclude that sucrose is not a reducing sugar as it lacks a hydroxyl group in the ring. Hence, A) is the correct option. (+) Sucrose does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation.
Note:
We also know that cellulose does not undergo mutarotation like sucrose. At the anomeric location of cellulose, they do not have hydroxyl group (OH) availability. As a result, cellulose does not undergo mutarotation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




