
Which one is more acidic?
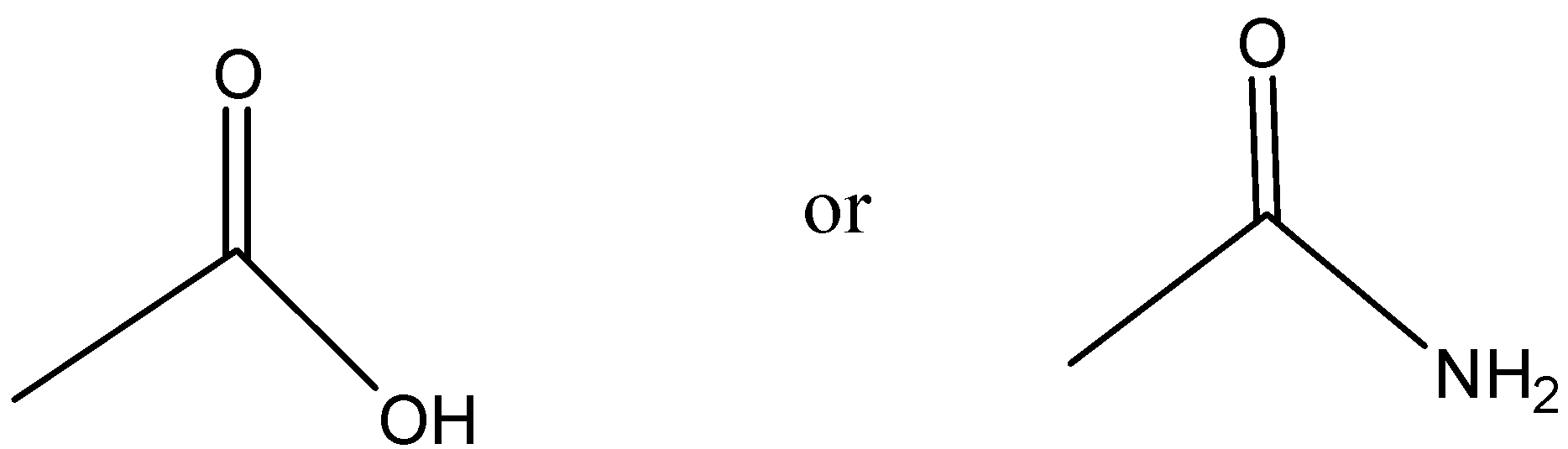
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: A compound which is capable of donating \[{H^ + }\] ions is termed as an acid. The compound which readily donates \[{H^ + }\] ions is termed as a good acid while the compound which does not easily donate \[{H^ + }\] ions is known as a bad acid. A good acid and a bad acid is a relative term.
Complete answer:
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of donating a proton (according to the Bronsted – Lowry theory) or alternatively, capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair (according to Lewis acid – base theory). The molecule which donates its \[{H^ + }\] ions more readily is known as a better acid than the one which does not easily donate it \[{H^ + }\] ions.
An aqueous solution of an acid has a pH of less than 7. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, and can turn blue litmus red.
In the given question, the acidity of both compounds can be compared by forming their conjugate bases and comparing their stability. More stable the conjugate base of a molecule, the better acid it is.
The conjugate bases of both compounds are:
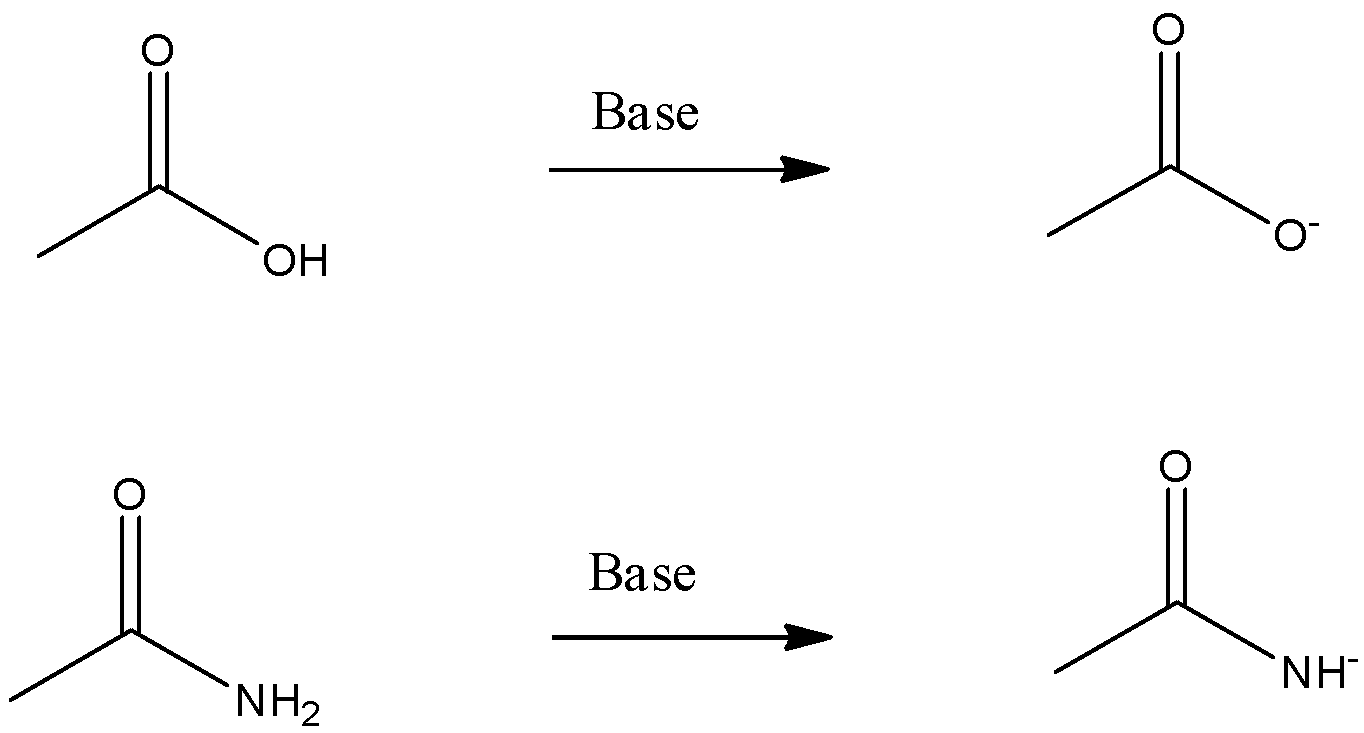
Oxygen and nitrogen are the elements of the same period. If we move along a period, the more electronegative element is more capable of holding a negative charge on it. Since, oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, thus negative charge on oxygen is more stable than negative charge on nitrogen. Thus, acetate ion is a more stable conjugate base.
Hence, acetic acid (\[C{H_3}COOH\]) is more acidic than \[C{H_3}CON{H_2}\].
Note:
Remember that when we move along a group, the stability of negative charge on an atom is determined by the size of the atom. Bigger the size, the more stable the negative charge.
Complete answer:
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of donating a proton (according to the Bronsted – Lowry theory) or alternatively, capable of forming a covalent bond with an electron pair (according to Lewis acid – base theory). The molecule which donates its \[{H^ + }\] ions more readily is known as a better acid than the one which does not easily donate it \[{H^ + }\] ions.
An aqueous solution of an acid has a pH of less than 7. A lower pH means a higher acidity, and thus a higher concentration of positive hydrogen ions in the solution. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, and can turn blue litmus red.
In the given question, the acidity of both compounds can be compared by forming their conjugate bases and comparing their stability. More stable the conjugate base of a molecule, the better acid it is.
The conjugate bases of both compounds are:

Oxygen and nitrogen are the elements of the same period. If we move along a period, the more electronegative element is more capable of holding a negative charge on it. Since, oxygen is more electronegative than nitrogen, thus negative charge on oxygen is more stable than negative charge on nitrogen. Thus, acetate ion is a more stable conjugate base.
Hence, acetic acid (\[C{H_3}COOH\]) is more acidic than \[C{H_3}CON{H_2}\].
Note:
Remember that when we move along a group, the stability of negative charge on an atom is determined by the size of the atom. Bigger the size, the more stable the negative charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




