
Which one is glucose?
(A) ${ C }_{ 3 }{ H }_{ 8 }{ O }_{ 3 }$
(B) ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
(C) ${ C }_{ 55 }{ H }_{ 70 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
(D) ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 10 }{ O }_{ 6 }$
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Glucose is a carbohydrate, which further in carbohydrates, comes under the class monosaccharide which means simple sugars and comes under the aldose group. Carbohydrate has the general formula as ${ C }_{ n }{ H }_{ 2n }{ O }_{ }$.
Complete step by step answer:
Monosaccharides are also known as simple sugars, and the most common of which is glucose whose formula is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from 3 to 7. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix –ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group, it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group, it is known as a ketose. The ratio of the number of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrate molecules. is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon and also the water.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$ ’.
Additional Information: Carbohydrates are classified into three categories, which are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides: Monosaccharides are simple sugars and cannot be broken down into a simpler form. Examples include glucose, fructose, etc.
- Disaccharides: Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction. During this process, the hydroxyl of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule is called a glycosidic bond. Common examples are lactose, maltose, and sucrose.
- Polysaccharides: A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is called a polysaccharide. The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it either contains the same type of monosaccharides or may contain different types of monosaccharides. Common examples are Amylose, Starch, etc.
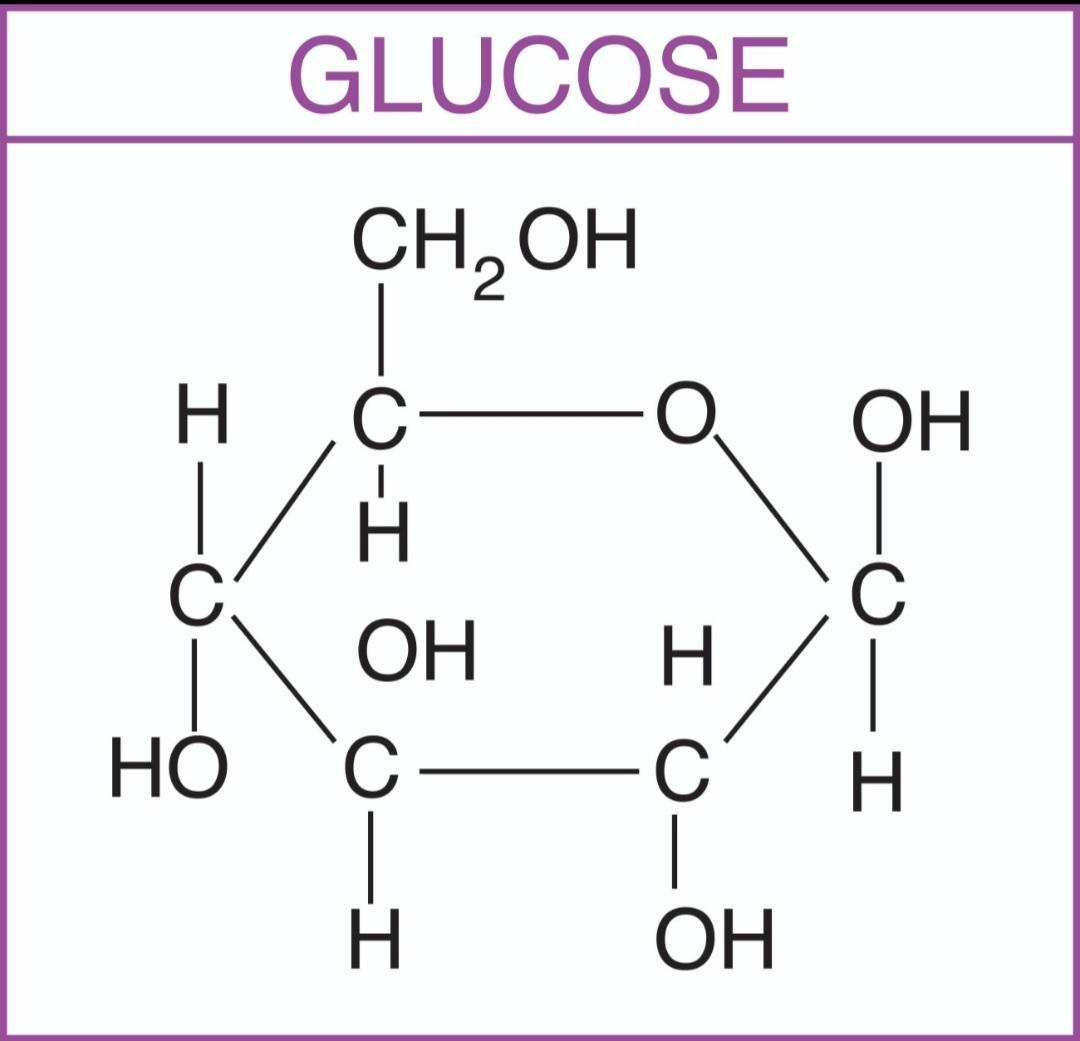
Note: Glucose in its ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (- OH) around the anomeric carbon. If the - OH is below carbon number one in the sugar, it's said to be in the alpha ($\alpha$) position, and if it's above the plane, it's said to be in the beta ($\beta$) position.
Complete step by step answer:
Monosaccharides are also known as simple sugars, and the most common of which is glucose whose formula is ${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from 3 to 7. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix –ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group, it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group, it is known as a ketose. The ratio of the number of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrate molecules. is 1:2:1. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon and also the water.
So, the correct answer is ‘${ C }_{ 6 }{ H }_{ 12 }{ O }_{ 6 }$ ’.
Additional Information: Carbohydrates are classified into three categories, which are monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
- Monosaccharides: Monosaccharides are simple sugars and cannot be broken down into a simpler form. Examples include glucose, fructose, etc.

- Disaccharides: Disaccharides form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction. During this process, the hydroxyl of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule is called a glycosidic bond. Common examples are lactose, maltose, and sucrose.
- Polysaccharides: A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is called a polysaccharide. The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it either contains the same type of monosaccharides or may contain different types of monosaccharides. Common examples are Amylose, Starch, etc.
Note: Glucose in its ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (- OH) around the anomeric carbon. If the - OH is below carbon number one in the sugar, it's said to be in the alpha ($\alpha$) position, and if it's above the plane, it's said to be in the beta ($\beta$) position.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




