
Which one is a component of the ornithine cycle?
(a)Arginine and ornithine
(b)Glycine and methionine
(c)Aspartic and glutamic acids
(d)Valine and cysteine
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: The liver contains a system of carrier molecules and enzymes, which quickly converts the ammonia (and carbon dioxide) into urea. This is called the urea cycle or ornithine cycle. Urea is the chief nitrogenous waste of mammals and comes from the breakdown of proteins (amino acids).
Complete answer:
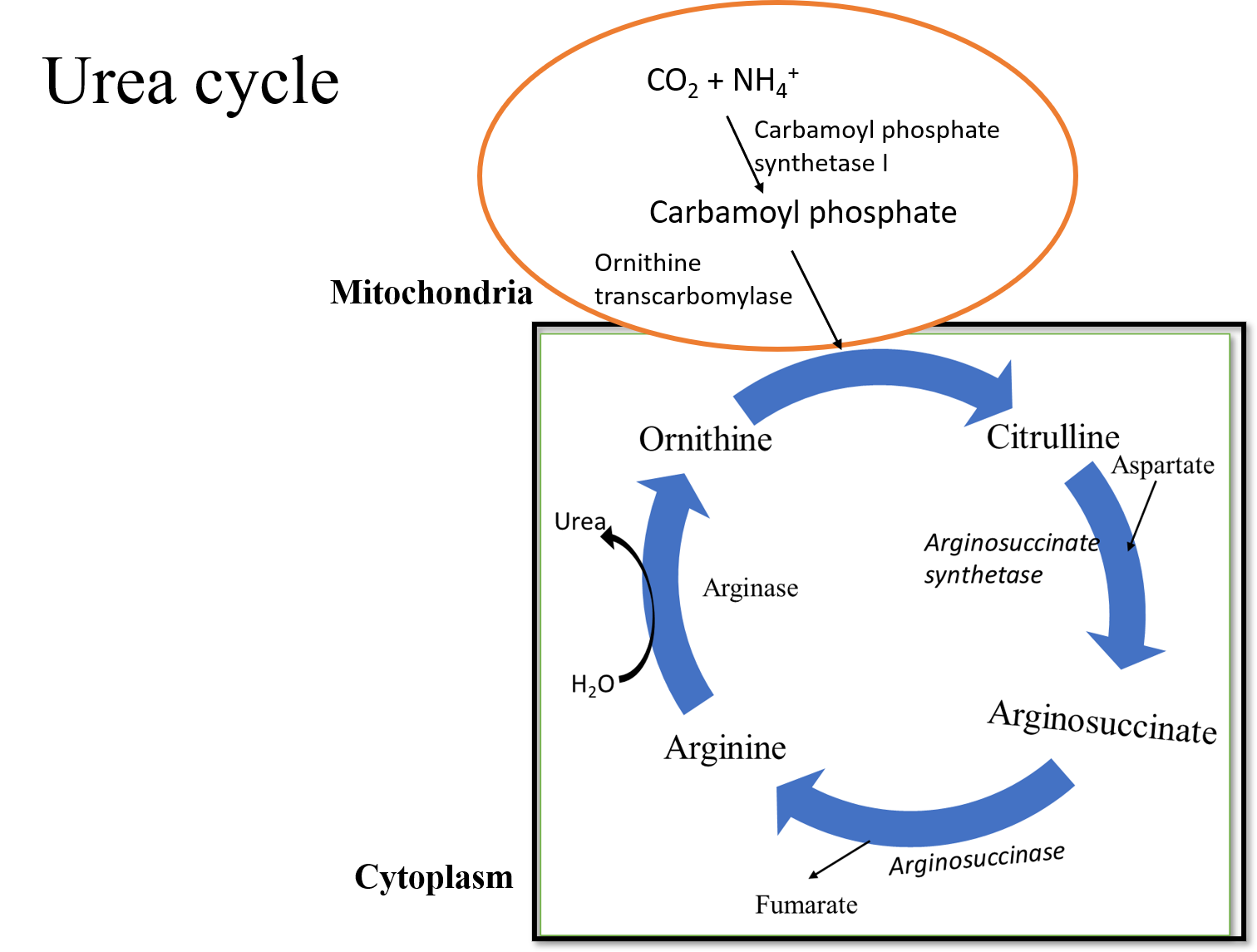
Ornithine is the end product of the urea cycle. It again combines with carbamoyl phosphate to form citrulline. Arginine is formed at the fourth step of the urea cycle with the help of enzyme argininosuccinase, which acts reversibly to cleave argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate.
One complete urea cycle:
-Consumes 2 molecules of ammonia.
-Consumes 1 molecule of carbon dioxide.
-Produces 1 molecule of urea.
-Regenerates one molecule of ornithine for another cycle.
The carbamoyl phosphate used in this cycle is synthesized in the mitochondria from bicarbonate and ammonia. This synthesis, in turn, is dependent on the presence of N-acetylglutamate, which activates the carbamoyl synthetase I enzyme. The formation of N-acetylglutamate is stimulated by high levels of arginine. The synthesis of urea is an energy-dependent process. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 requires 2 ATP molecules, which are hydrolyzed to ADP, while the argininosuccinate synthetase only requires a single ATP molecule.
Increased levels of free amino acids, indicated by elevated arginine levels, stimulate the synthesis of urea. Two enzymes are involved in the hydrolysis of arginine to yield ornithine and urea. Cytosolic ARG1 is the urea cycle enzyme and mitochondrial ARG2 catalyzes urea production from arginine.
So, The correct answer is Option ‘A’.
Note:
-The urea cycle is extremely important because the ammonia is neurotoxic and must be removed from the body. Hepatocytes are the liver cells where the urea cycle occurs.
-The first and second step of the urea cycle occurs within the mitochondrion and the subsequent steps in the cytosol.
Complete answer:
Ornithine is the end product of the urea cycle. It again combines with carbamoyl phosphate to form citrulline. Arginine is formed at the fourth step of the urea cycle with the help of enzyme argininosuccinase, which acts reversibly to cleave argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate.
One complete urea cycle:
-Consumes 2 molecules of ammonia.
-Consumes 1 molecule of carbon dioxide.
-Produces 1 molecule of urea.
-Regenerates one molecule of ornithine for another cycle.
The carbamoyl phosphate used in this cycle is synthesized in the mitochondria from bicarbonate and ammonia. This synthesis, in turn, is dependent on the presence of N-acetylglutamate, which activates the carbamoyl synthetase I enzyme. The formation of N-acetylglutamate is stimulated by high levels of arginine. The synthesis of urea is an energy-dependent process. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 requires 2 ATP molecules, which are hydrolyzed to ADP, while the argininosuccinate synthetase only requires a single ATP molecule.
Increased levels of free amino acids, indicated by elevated arginine levels, stimulate the synthesis of urea. Two enzymes are involved in the hydrolysis of arginine to yield ornithine and urea. Cytosolic ARG1 is the urea cycle enzyme and mitochondrial ARG2 catalyzes urea production from arginine.
So, The correct answer is Option ‘A’.
Note:
-The urea cycle is extremely important because the ammonia is neurotoxic and must be removed from the body. Hepatocytes are the liver cells where the urea cycle occurs.
-The first and second step of the urea cycle occurs within the mitochondrion and the subsequent steps in the cytosol.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




