
Which one in the following is not the resonating structure of $C{{O}_{2}}$?
(a) $O=C=O$
(b) $^{-}O-C\equiv {{O}^{+}}$
(c) $^{+}O\equiv C-{{O}^{-}}$
(d) $O\equiv C=O$
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: In the carbon dioxide molecule there are 3 resonating structures. In all the resonating structures of carbon dioxide, the total numbers of bonds are 4.
Complete step by step answer:
We usually explain the structure of the molecule with the help of Lewis structure but in certain molecules, the single Lewis structure cannot explain all the properties of the molecule. Then the molecule is supposed to have many structures, each of the molecule structures can explain most of the properties but none can explain all the properties of the molecule. Resonance hybrid is the actual structure in-between all these contributing structures and the different individual structures are called resonating structures or canonical forms and the phenomenon is called resonance.
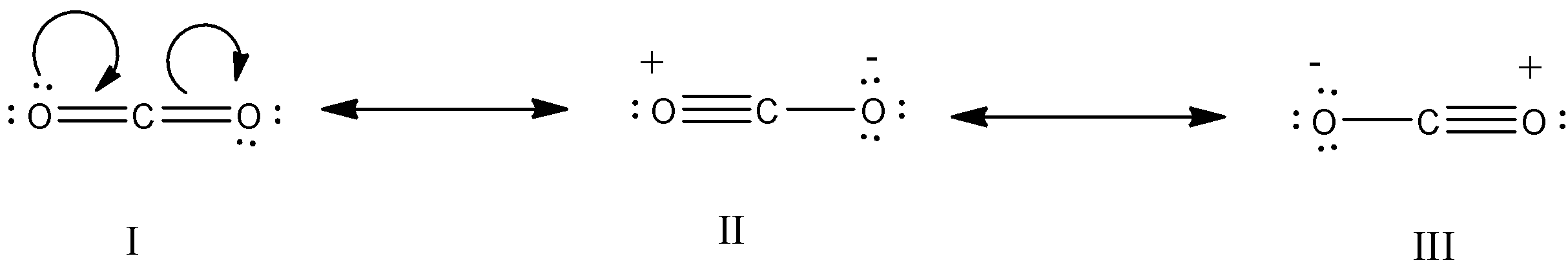
The resonating structure of $C{{O}_{2}}$ is explained below:
The Lewis structure of carbon dioxide is I. That means to have two oxygen atoms on either side of the carbon atom and are joined with double bonds. The normal $C=O$ double bond has a bond length of 121 pm. However, experimentally each carbon to oxygen bond length in $C{{O}_{2}}$ is found to be 115 pm which is in-between the bond length of $C=O$ double bond (121 pm) and $C\equiv O$ triple bond (110 pm). Hence, $C{{O}_{2}}$ is considered to be a resonance hybrid of the following three Lewis structures:
Hence, the option (d)- $O\equiv C=O$ is not a resonating structure of carbon dioxide.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We can explain the resonance energy of the molecule as the difference in the energy of the resonance hybrid and the most stable contributing structure which has the least energy.
Complete step by step answer:
We usually explain the structure of the molecule with the help of Lewis structure but in certain molecules, the single Lewis structure cannot explain all the properties of the molecule. Then the molecule is supposed to have many structures, each of the molecule structures can explain most of the properties but none can explain all the properties of the molecule. Resonance hybrid is the actual structure in-between all these contributing structures and the different individual structures are called resonating structures or canonical forms and the phenomenon is called resonance.
The resonating structure of $C{{O}_{2}}$ is explained below:
The Lewis structure of carbon dioxide is I. That means to have two oxygen atoms on either side of the carbon atom and are joined with double bonds. The normal $C=O$ double bond has a bond length of 121 pm. However, experimentally each carbon to oxygen bond length in $C{{O}_{2}}$ is found to be 115 pm which is in-between the bond length of $C=O$ double bond (121 pm) and $C\equiv O$ triple bond (110 pm). Hence, $C{{O}_{2}}$ is considered to be a resonance hybrid of the following three Lewis structures:

Hence, the option (d)- $O\equiv C=O$ is not a resonating structure of carbon dioxide.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We can explain the resonance energy of the molecule as the difference in the energy of the resonance hybrid and the most stable contributing structure which has the least energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




