
Which of the functions defined below are one-one function(s)?
A) $f\left( x \right) = x + 1$, $\left( {x \geqslant - 1} \right)$
B) $g\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$, $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$
C) $h\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4x - 5$, $\left( {x > 0} \right)$
D) $f\left( x \right) = {e^{ - x}}$, $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:
We know that a function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to be one-one if $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$ is true only when ${x_1} = {x_2}$. Then we can check these conditions in each of the given functions. The functions which satisfy this condition are one-one and others are not one-one.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to be one-one if $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$ is true only when ${x_1} = {x_2}$.
Now consider option A, $f\left( x \right) = x + 1$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant - 1} \right)$.
Now let us take $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} + 1 = {x_2} + 1$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option A is one-one.
Now consider option B, $g\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $g\left( {{x_1}} \right) = g\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} + \dfrac{1}{{{x_1}}} = {x_2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x_2}}}$
On taking the LCM, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x_1}^2 + 1}}{{{x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{x_2}^2 + 1}}{{{x_2}}}$
As the fractions are equal when denominators and numerators are equal, we can say that
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option B is one-one.
Now consider option c, $h\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4x - 5$. It is defined for $\left( {x > 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $h\left( {{x_1}} \right) = h\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1}^2 + 4{x_1} - 5 = {x_2}^2 + 4{x_2} - 5$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x_1} + 4} \right){x_1} = \left( {{x_2} + 4} \right){x_2}$
As the function is defined for positive numbers, we can say that
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option C is also one-one.
Now consider option D, $f\left( x \right) = {e^{ - x}}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {e^{ - {x_1}}} = {e^{ - {x_2}}}$
On taking log on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow - {x_1}\log e = - {x_2}\log e$
On cancelling the common terms, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option D is one-one.
From the 4 results, we can say that all the given functions are one-one.
So, the correct answers are option A, B, C and D.
Note:
Note: Alternate solution to solve this problem is given by plotting the graph of the function and checking whether the function has the same value for different values of x.
Now consider option A, $f\left( x \right) = x + 1$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant - 1} \right)$.
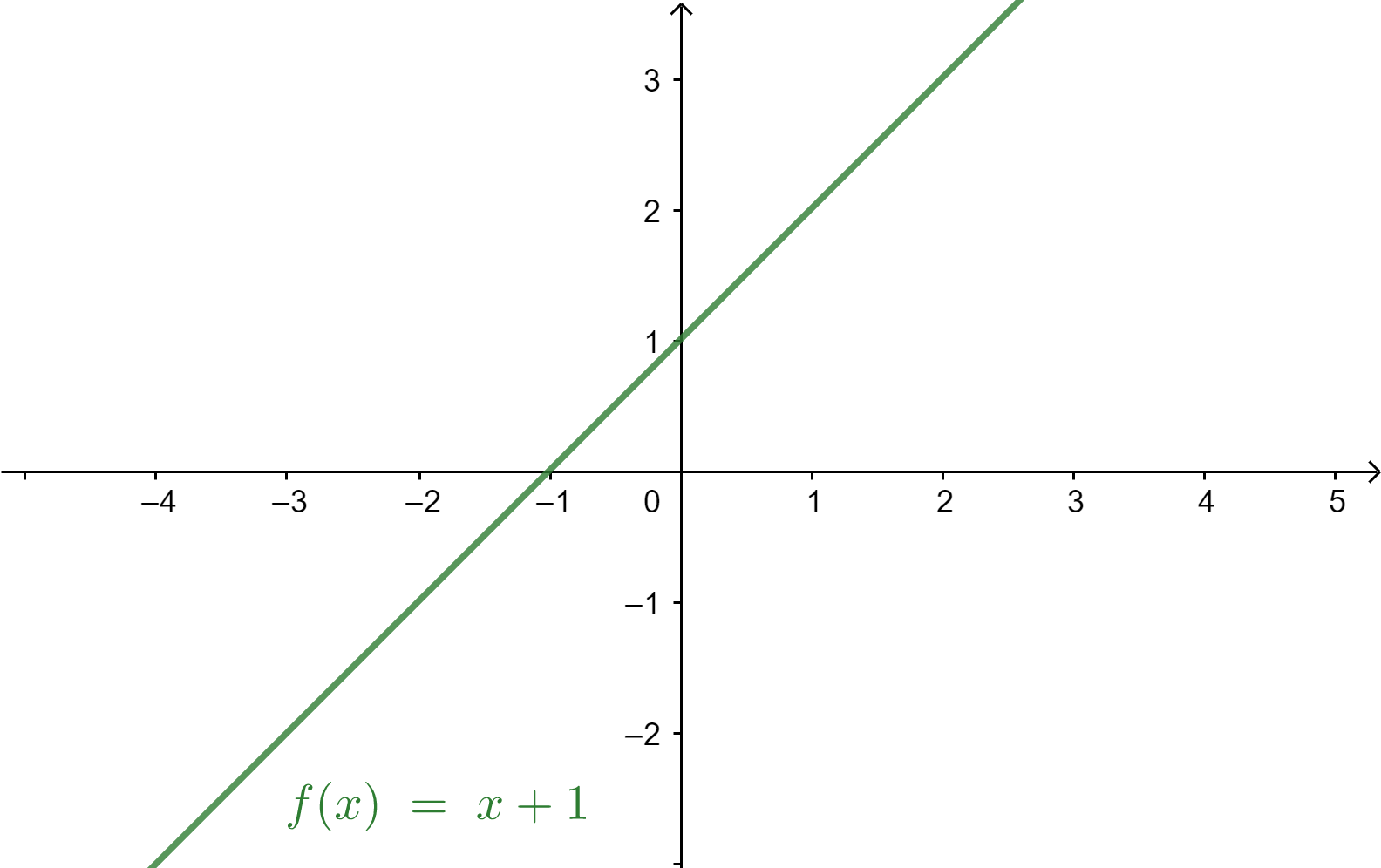
As the graph is linear, there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So it is a one-one function.
Now consider option B, $g\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
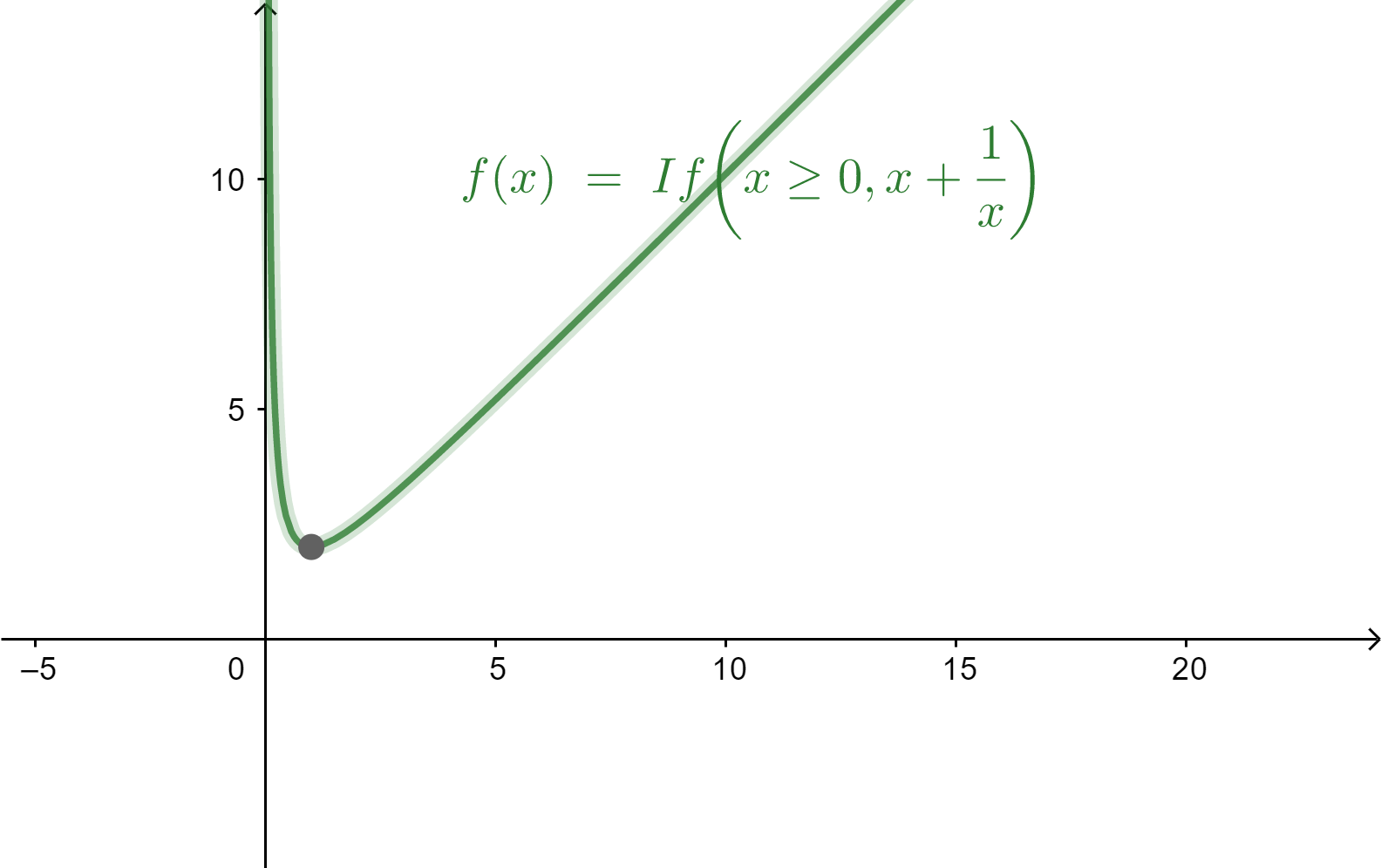
From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
Now consider option c, $h\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4x - 5$. It is defined for $\left( {x > 0} \right)$.
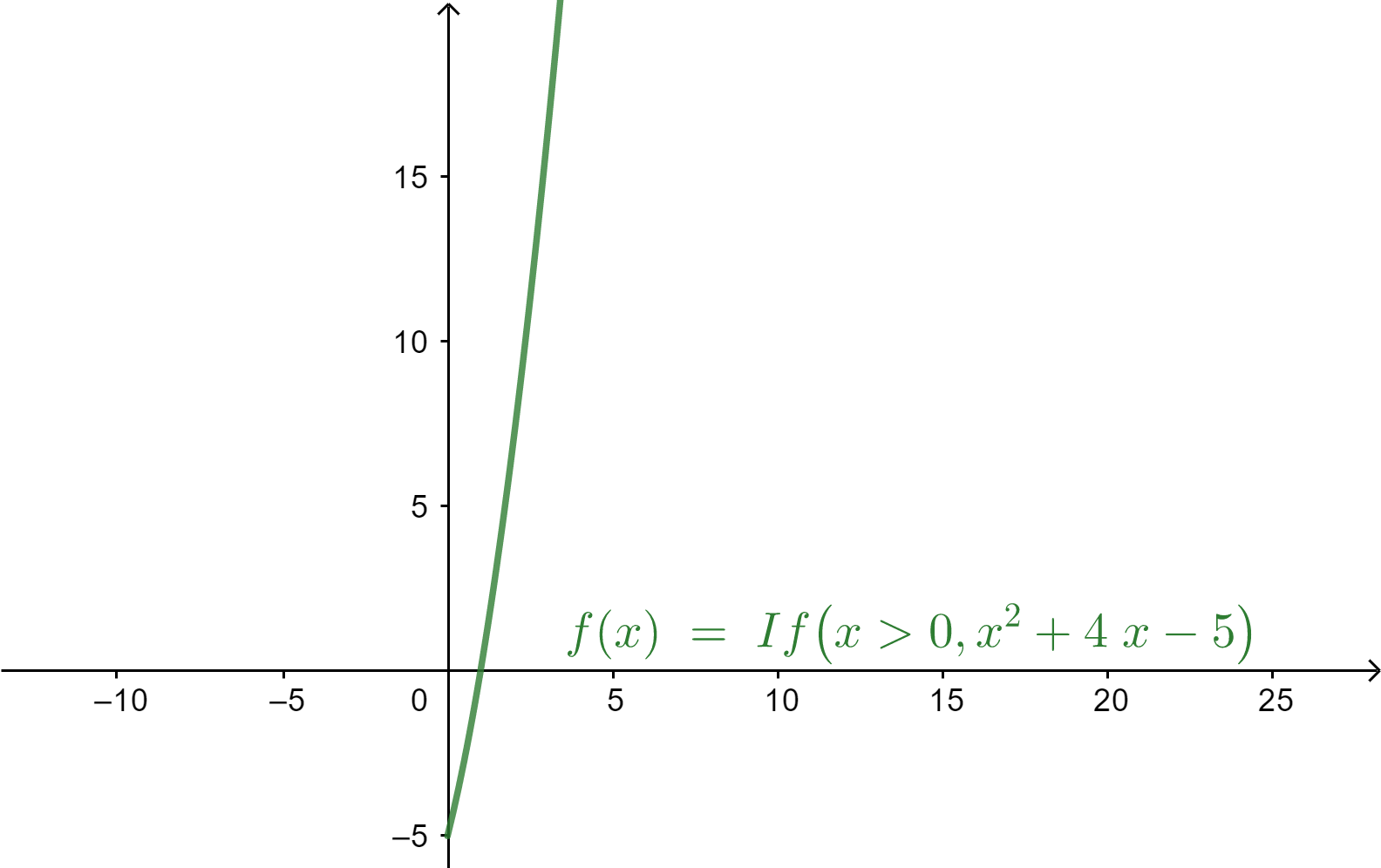
From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
Now consider option D, $f\left( x \right) = {e^{ - x}}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
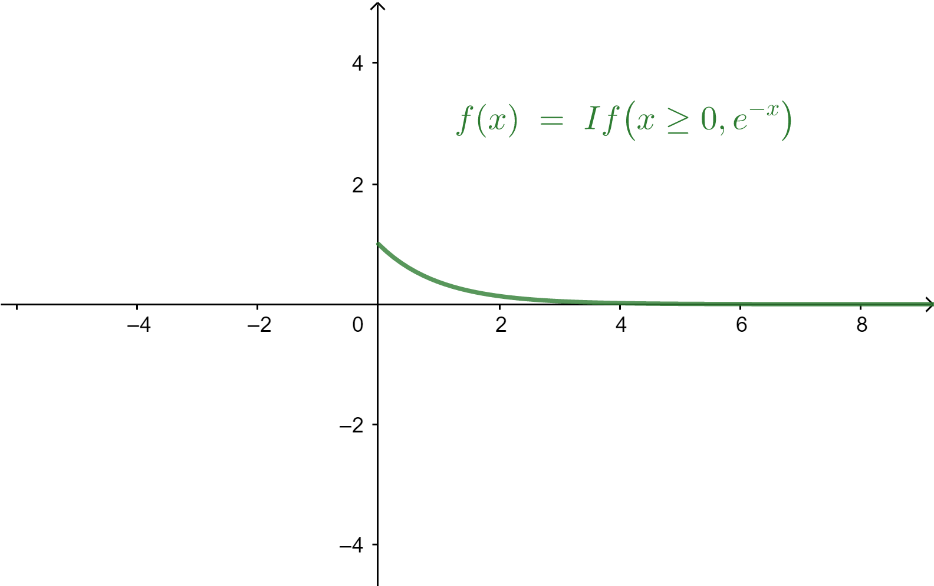
From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
From the 4 results, we can say that all the given functions are one-one.
We know that a function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to be one-one if $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$ is true only when ${x_1} = {x_2}$. Then we can check these conditions in each of the given functions. The functions which satisfy this condition are one-one and others are not one-one.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a function $f\left( x \right)$ is said to be one-one if $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$ is true only when ${x_1} = {x_2}$.
Now consider option A, $f\left( x \right) = x + 1$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant - 1} \right)$.
Now let us take $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} + 1 = {x_2} + 1$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option A is one-one.
Now consider option B, $g\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $g\left( {{x_1}} \right) = g\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} + \dfrac{1}{{{x_1}}} = {x_2} + \dfrac{1}{{{x_2}}}$
On taking the LCM, we get
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x_1}^2 + 1}}{{{x_1}}} = \dfrac{{{x_2}^2 + 1}}{{{x_2}}}$
As the fractions are equal when denominators and numerators are equal, we can say that
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option B is one-one.
Now consider option c, $h\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4x - 5$. It is defined for $\left( {x > 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $h\left( {{x_1}} \right) = h\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {x_1}^2 + 4{x_1} - 5 = {x_2}^2 + 4{x_2} - 5$
On simplification, we get
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x_1} + 4} \right){x_1} = \left( {{x_2} + 4} \right){x_2}$
As the function is defined for positive numbers, we can say that
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option C is also one-one.
Now consider option D, $f\left( x \right) = {e^{ - x}}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.
Now let us take $f\left( {{x_1}} \right) = f\left( {{x_2}} \right)$.
$ \Rightarrow {e^{ - {x_1}}} = {e^{ - {x_2}}}$
On taking log on both sides, we get
$ \Rightarrow - {x_1}\log e = - {x_2}\log e$
On cancelling the common terms, we get
$ \Rightarrow {x_1} = {x_2}$
Therefore, the function in option D is one-one.
From the 4 results, we can say that all the given functions are one-one.
So, the correct answers are option A, B, C and D.
Note:
Note: Alternate solution to solve this problem is given by plotting the graph of the function and checking whether the function has the same value for different values of x.
Now consider option A, $f\left( x \right) = x + 1$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant - 1} \right)$.

As the graph is linear, there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So it is a one-one function.
Now consider option B, $g\left( x \right) = x + \dfrac{1}{x}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.

From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
Now consider option c, $h\left( x \right) = {x^2} + 4x - 5$. It is defined for $\left( {x > 0} \right)$.

From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
Now consider option D, $f\left( x \right) = {e^{ - x}}$. It is defined for $\left( {x \geqslant 0} \right)$.

From the graph, we can say that there is only one value of x for which the function has the same value. So, it is a one-one function.
From the 4 results, we can say that all the given functions are one-one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




