
Which of the following statement (s) is/ are true?
a. Two chords of a circle equidistant from the centre are equal.
b. Equal chords in a circle subtend equal angles at the centre.
c. Angle in a semicircle is a right angle
d. All of the above
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint: To solve this sum you must know the logics and concepts of circle semicircles and stuff when you know them, you will easily be able to solve this. Now to find the right answers in this question you must go from option a to option d and check each and every one of those options to check if the answer is right or wrong. And if all of the options are factually correct that means that the answer will be option d.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now here in this let us start by the first option. Two chords of a circle equidistant from the centre are equal.
Now we know that any chord from the centre of a circle to its end is called radius. And radius is uniform throughout it doesn’t change this can be proved from Pythagoras theorem. Therefore we can say that option a is correct.
Coming to option b, it says that equal chords in a circle subtend equal angles at the centre.
Now since the chords are equal hence their distance from centre will be equal which we showed in option a therefore congruent triangles will be formed and we can say that chords always subtend equal angles at the centre
Now option c says that the angle in a semicircle is a right angle. This statement is also always true and is a standard result.
Now therefore since all options are true the answer for this question is d. All of the above
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: To prove all angles in a semi-circle subtend to right angle
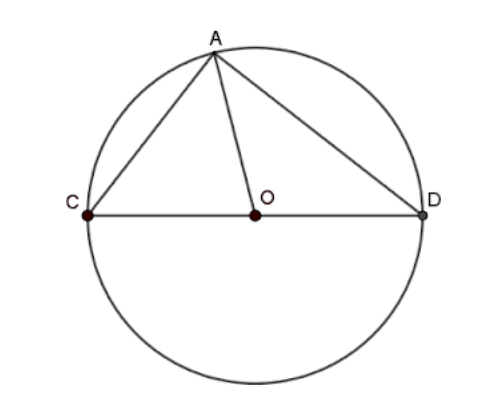
Now here taking a point let us say \[C\] on a circle. Now we draw a line from \[C\] to the centre. Now we know that
\[AO=CO=DO\]
Since these are radius of the circle
Therefore in triangle \[AOC\] it is now a isosceles triangle therefore we can say
\[\angle OCA=\angle OAC=x\]
Similarly for the second triangle
\[\angle ODA=\angle OAD=y\]
Now since \[ACD\] makes a complete triangle sum of all angles should be \[180{}^\circ \] therefore
\[\angle DCA+\angle ACD+\angle CAD=180{}^\circ \]
\[x+y+x+y=180{}^\circ \]
Therefore we can prove that
\[x+y=90{}^\circ =\angle CAD\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now here in this let us start by the first option. Two chords of a circle equidistant from the centre are equal.
Now we know that any chord from the centre of a circle to its end is called radius. And radius is uniform throughout it doesn’t change this can be proved from Pythagoras theorem. Therefore we can say that option a is correct.
Coming to option b, it says that equal chords in a circle subtend equal angles at the centre.
Now since the chords are equal hence their distance from centre will be equal which we showed in option a therefore congruent triangles will be formed and we can say that chords always subtend equal angles at the centre
Now option c says that the angle in a semicircle is a right angle. This statement is also always true and is a standard result.
Now therefore since all options are true the answer for this question is d. All of the above
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: To prove all angles in a semi-circle subtend to right angle

Now here taking a point let us say \[C\] on a circle. Now we draw a line from \[C\] to the centre. Now we know that
\[AO=CO=DO\]
Since these are radius of the circle
Therefore in triangle \[AOC\] it is now a isosceles triangle therefore we can say
\[\angle OCA=\angle OAC=x\]
Similarly for the second triangle
\[\angle ODA=\angle OAD=y\]
Now since \[ACD\] makes a complete triangle sum of all angles should be \[180{}^\circ \] therefore
\[\angle DCA+\angle ACD+\angle CAD=180{}^\circ \]
\[x+y+x+y=180{}^\circ \]
Therefore we can prove that
\[x+y=90{}^\circ =\angle CAD\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




