
Which of the following quantities is always negative in SHM?
A. $\overrightarrow F .\overrightarrow r $
B. $\overrightarrow F .\overrightarrow r $
C. $\overrightarrow v .\overrightarrow r $
D. $\overrightarrow a .\overrightarrow r $
Answer
480.3k+ views
Hint:This question utilizes the concept of Simple harmonic motion. We know that dot products of two vectors are negative when their directions are opposite to each other. So, we need to find the quantities whose directions are always opposite to each other.
Complete step by step answer:
Let there be a ball $Q$ which is hanging from a pendulum.Let its mean position be $A$. Let it oscillate in SHM and there be a point $B$ along its path. There, the forces acting on the ball will be as shown in the figure.
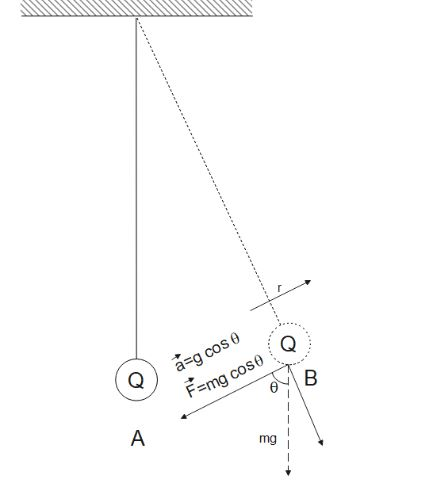
Here, we can see that the displacement $\overrightarrow r $ is always opposite to the force $\overrightarrow F $. Also, the acceleration $\overrightarrow a $ is always opposite to the direction of displacement $\overrightarrow r $. Here, for calculating displacement $\overrightarrow r $ , $A$ is taken as the origin point. But, for certain points, velocity $\overrightarrow v $ is opposite to displacement $\overrightarrow r $ and for the other points, they are in the same direction. Force $\overrightarrow F $ and acceleration $\overrightarrow a $ are always in the same direction.
Therefore, option A and option D are correct.
Additional Information: When the ball $Q$ is released from the right top point of the motion, the velocity vector becomes negative whereas the displacement vector is positive. Then, when it moves from the mean position to the left side, the velocity vector is still negative and the displacement is also negative. Here, Right side of the $x$ axis is considered positive for displacement and travelling towards the right is considered positive velocity.
Note:Students usually get confused when resolving a vector into two parts. Just remember that the vertical component of the vector is the vector multiplied by $\sin \theta $ and the horizontal component is the vector multiplied by $\cos \theta $ . Here, $\theta $ is the angle between the vector and the assumed horizontal axis.
Complete step by step answer:
Let there be a ball $Q$ which is hanging from a pendulum.Let its mean position be $A$. Let it oscillate in SHM and there be a point $B$ along its path. There, the forces acting on the ball will be as shown in the figure.

Here, we can see that the displacement $\overrightarrow r $ is always opposite to the force $\overrightarrow F $. Also, the acceleration $\overrightarrow a $ is always opposite to the direction of displacement $\overrightarrow r $. Here, for calculating displacement $\overrightarrow r $ , $A$ is taken as the origin point. But, for certain points, velocity $\overrightarrow v $ is opposite to displacement $\overrightarrow r $ and for the other points, they are in the same direction. Force $\overrightarrow F $ and acceleration $\overrightarrow a $ are always in the same direction.
Therefore, option A and option D are correct.
Additional Information: When the ball $Q$ is released from the right top point of the motion, the velocity vector becomes negative whereas the displacement vector is positive. Then, when it moves from the mean position to the left side, the velocity vector is still negative and the displacement is also negative. Here, Right side of the $x$ axis is considered positive for displacement and travelling towards the right is considered positive velocity.
Note:Students usually get confused when resolving a vector into two parts. Just remember that the vertical component of the vector is the vector multiplied by $\sin \theta $ and the horizontal component is the vector multiplied by $\cos \theta $ . Here, $\theta $ is the angle between the vector and the assumed horizontal axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




