
Which of the following pairs are isostructural ?
(A) $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $
(B) $N{H_3}$ and $NH_4^ + $
(C) $CO_3^{2 - }$ and $C{O_2}$
(D) $C{H_4}$ and $B{F_3}$
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: Isostructural species are those which have the same shape and hybridization.
Number of election pair $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {N + V - C + A} \right]$
Where
$V = $ Number of valence electron present in central atom
$N = $ Number of non-monovalent atoms bonded to covalent atom
$C = $ Charge of cation
$A = $ Charge of anion
Hybridisation can be calculated by using this formula then we will be able to find the structure from hybridisation.
Complete step by step answer:
The given molecules are –
(A) $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $
Number of electron pair in $SO_4^{2 - } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {6 + 0 + 2} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry of the molecule will be tetrahedral.
Number of electron pair in $BF_4^ - = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {3 + 4 + 1} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pair are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry of molecule will be tetrahedral
Structures
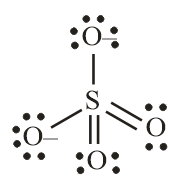
$SO_4^{2 - }$ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure)
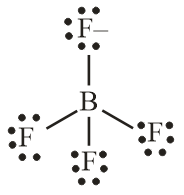
$BF_4^ - $ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure)
(B) $N{H_3}$ and $NH_4^ + $
Number of electron pair in $N{H_3} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {5 + 3 + 0} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and geometry will be tetrahedral. But, In $N{H_3}$ Nitrogen is surrounded by 3 atoms and the fourth position will be occupied by lone pairs of electrons.
Hence, the structure of $N{H_3}$ will be pyramidal.
Number of electron pair in $NH_4^ + = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {5 + 4 - 1} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry will be tetrahedral.
Structures

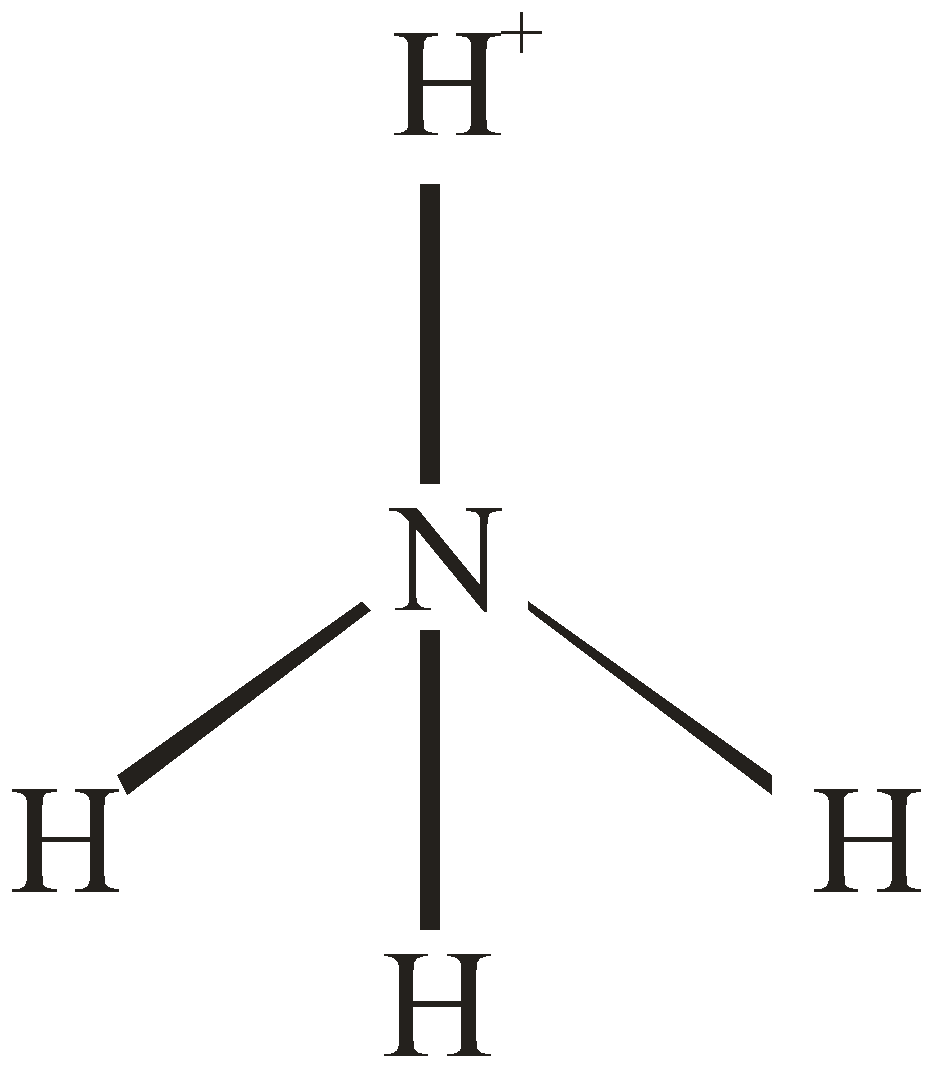
$N{H_3}$ molecule $NH_4^ + $ molecule
[Pyramidal structure] [Tetrahedral molecule]
(C) $CO_3^{2 - }$ and $C{O_2}$
Number of electron pair in $CO_3^{2 - } = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 + 2} \right] = 3$
The number of electron pairs are 3 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^2}$ and the geometry will be trigonal planar.
Number of electron pair in $C{O_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 + 0} \right] = 2$
Number of electron pairs are 2 that means the hybridisation will be sp and the geometry will be linear.
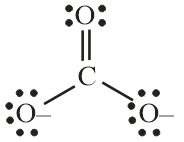
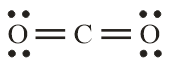
$CO_3^{2 - }$ molecule $C{O_2}$ molecule
(Trigonal planar structure) (Linear structure)
(D) $C{H_4}$ and $B{F_3}$
Number of electron pair in $C{H_4} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 4 + 0} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pair are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry will be tetrahedral
Number of electron pair in $B{F_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3 + 3 + 0} \right] = 3$
Number of electron pairs are 3 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and geometry will be trigonal planar.
Structures
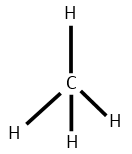
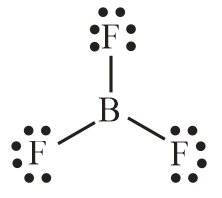
$C{H_4}$ molecule $B{F_3}$ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure) (Trigonal planar)
From this, we conclude that $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $ have the same structure.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $
Note: Geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of lone pair and bond pair while shape is the molecular structure excluding lone pairs of central atoms.
Number of election pair $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {N + V - C + A} \right]$
Where
$V = $ Number of valence electron present in central atom
$N = $ Number of non-monovalent atoms bonded to covalent atom
$C = $ Charge of cation
$A = $ Charge of anion
Hybridisation can be calculated by using this formula then we will be able to find the structure from hybridisation.
Complete step by step answer:
The given molecules are –
(A) $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $
Number of electron pair in $SO_4^{2 - } = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {6 + 0 + 2} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry of the molecule will be tetrahedral.
Number of electron pair in $BF_4^ - = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {3 + 4 + 1} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pair are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry of molecule will be tetrahedral
Structures

$SO_4^{2 - }$ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure)

$BF_4^ - $ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure)
(B) $N{H_3}$ and $NH_4^ + $
Number of electron pair in $N{H_3} = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \left[ {5 + 3 + 0} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and geometry will be tetrahedral. But, In $N{H_3}$ Nitrogen is surrounded by 3 atoms and the fourth position will be occupied by lone pairs of electrons.
Hence, the structure of $N{H_3}$ will be pyramidal.
Number of electron pair in $NH_4^ + = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {5 + 4 - 1} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pairs are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry will be tetrahedral.
Structures


$N{H_3}$ molecule $NH_4^ + $ molecule
[Pyramidal structure] [Tetrahedral molecule]
(C) $CO_3^{2 - }$ and $C{O_2}$
Number of electron pair in $CO_3^{2 - } = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 + 2} \right] = 3$
The number of electron pairs are 3 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^2}$ and the geometry will be trigonal planar.
Number of electron pair in $C{O_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 0 + 0} \right] = 2$
Number of electron pairs are 2 that means the hybridisation will be sp and the geometry will be linear.

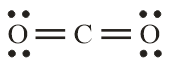
$CO_3^{2 - }$ molecule $C{O_2}$ molecule
(Trigonal planar structure) (Linear structure)
(D) $C{H_4}$ and $B{F_3}$
Number of electron pair in $C{H_4} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {4 + 4 + 0} \right] = 4$
Number of electron pair are 4 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and the geometry will be tetrahedral
Number of electron pair in $B{F_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3 + 3 + 0} \right] = 3$
Number of electron pairs are 3 that means the hybridisation will be $s{p^3}$ and geometry will be trigonal planar.
Structures


$C{H_4}$ molecule $B{F_3}$ molecule
(Tetrahedral structure) (Trigonal planar)
From this, we conclude that $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $ have the same structure.
Hence, the correct answer is (A) $SO_4^{2 - }$ and $BF_4^ - $
Note: Geometry of a molecule is the arrangement of lone pair and bond pair while shape is the molecular structure excluding lone pairs of central atoms.
| S.No. | Molecules | Hybridization | Geometry | Molecular Structure |
| 1 | $C{H_4}$ | $s{p^3}$ | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral |
| 2 | $N{H_3}$ | $s{p^3}$ | Tetrahedral | Pyramidal |
| 3 | ${H_2}O$ | $s{p^3}$ | Tetrahedral | V-shape or Angular |
| 4 | $B{F_3}$ | $s{p^2}$ | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planar |
| 5 | $Be{H_2}$ | sp | Linear | Linear |
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




