
Which of the following nitrogen bases is not found in DNA?
(A)Thymine
(B)Cytosine
(C)Guanine
(D)Uracil
Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: Nitrogenous bases structure hydrogen connections between restricting DNA strands to shape the rungs of the "bent stepping stool" or twofold helix of DNA or a natural impetus found in nucleotides. Adenine consistently joins with thymine and guanine consistently consolidates with cytosine. These are called base sets.
Complete answer:
A nitrogenous base, or nitrogen-containing base, is a natural particle with a nitrogen molecule that has the substance properties of a base. The important biological role of a nitrogenous base is to bind nucleic acids. A nitrogenous base helps its basic properties to the single pair of electrons in a nitrogen atom. Nitrogenous bases are normally classified as derivatives of two-parent compounds, pyrimidine, and purine. They are nonpolar and because of their aromaticity, flat. Pyrimidines and purines are similar to pyridine and therefore are weak bases that are relatively unresponsive to electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Additional information:
In DNA Adenine structures have two hydrogen bonds with thymine while in RNA the two hydrogen bonds with uracil, while three hydrogen bonds structure among guanine and cytosine. There is an assortment of other non-accepted base matches that happen in nature because of the flexibility of these subatomic structures. Uracil is just present in RNA, supplanting thymine. Pyrimidines incorporate thymine, cytosine, and uracil. Presence of the exceptional ring structure. Purines incorporate adenine and guanine.
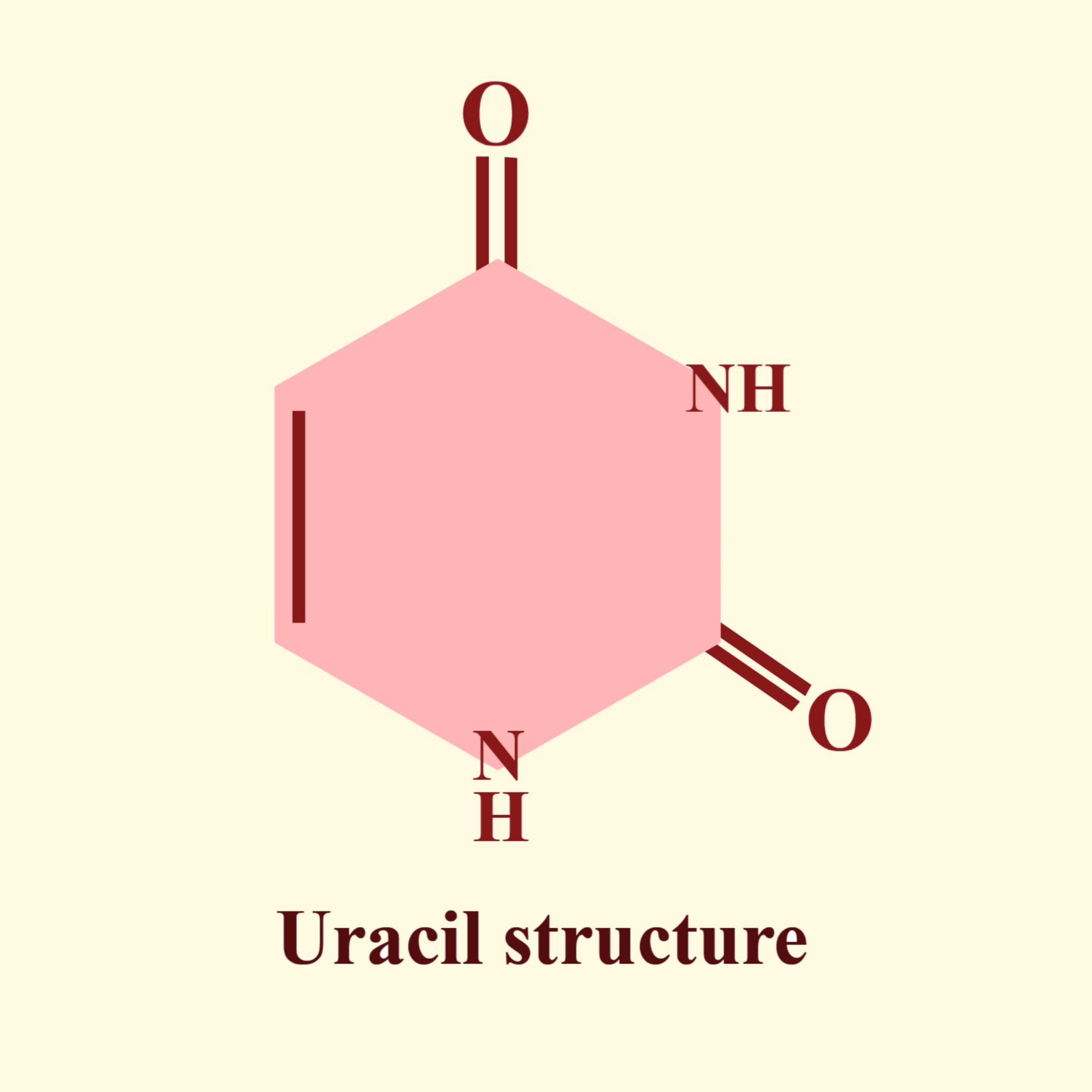
So the correct answer is ‘Uracil’.
Note: On account of the organic sciences, nitrogenous bases are progressively called nucleic bases because of their capacity in nucleic acids; their level shape is fundamentally urgent while thinking about their capacities as building squares of DNA and RNA. A set of five nitrogenous bases are used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn form nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. These nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). Thymine and uracil are distinguished simply by the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these six-membered heterocyclic ring
Complete answer:
A nitrogenous base, or nitrogen-containing base, is a natural particle with a nitrogen molecule that has the substance properties of a base. The important biological role of a nitrogenous base is to bind nucleic acids. A nitrogenous base helps its basic properties to the single pair of electrons in a nitrogen atom. Nitrogenous bases are normally classified as derivatives of two-parent compounds, pyrimidine, and purine. They are nonpolar and because of their aromaticity, flat. Pyrimidines and purines are similar to pyridine and therefore are weak bases that are relatively unresponsive to electrophilic aromatic substitution.
Additional information:
In DNA Adenine structures have two hydrogen bonds with thymine while in RNA the two hydrogen bonds with uracil, while three hydrogen bonds structure among guanine and cytosine. There is an assortment of other non-accepted base matches that happen in nature because of the flexibility of these subatomic structures. Uracil is just present in RNA, supplanting thymine. Pyrimidines incorporate thymine, cytosine, and uracil. Presence of the exceptional ring structure. Purines incorporate adenine and guanine.

So the correct answer is ‘Uracil’.
Note: On account of the organic sciences, nitrogenous bases are progressively called nucleic bases because of their capacity in nucleic acids; their level shape is fundamentally urgent while thinking about their capacities as building squares of DNA and RNA. A set of five nitrogenous bases are used in the construction of nucleotides, which in turn form nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. These nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), uracil (U), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). Thymine and uracil are distinguished simply by the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these six-membered heterocyclic ring
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




