
Which of the following metal oxide is anti-ferromagnetic in nature?
(A) $Mn{O_2}$
(B) $Ti{O_2}$
(C) $V{O_2}$
(D) $Cr{O_2}$
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: Magnetic substances possess magnetic properties and they produce different responses when placed under the effect of magnetic field. On applying a magnetic field and at a temperature less than that of critical temperature, on an antiferromagnetic material, the magnetic moments of that material are aligned in an antiparallel manner. The antiferromagnetic material will retain the antiparallel alignment of its magnetic moments even when an external magnetic field is removed. This antiferromagnetic nature of the substance will remain constant even when temperature drops below that of critical temperature.
Complete step by step solution:
The options of compounds given above are oxides of different metals. To find out which of the given oxide is antiferromagnetic in nature, we need to know more about antiferromagnetism.
Let us first see how magnetic moments are aligned in antiferromagnetic substances which is shown in the given diagram. The ordering of magnetic moments in an antiferromagnetic material is shown below.
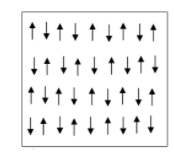
When a material is antiferromagnetic in nature, it has zero net magnetic moment that means no magnetic field will be produced by them.
Now, let us understand the structure of $Mn{O_2}$.
The compound $Mn{O_2}$ is also known as manganese IV oxide because in this compound Mn is in +4 oxidation state. In $Mn{O_2}$, there are 2 oxygen atoms with -2 charge. The overall charge on anion is -4.
The structure of $Mn{O_2}$ is shown below.
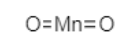
When a material is antiferromagnetic in nature, it is a result of superexchange of spin energy in that material. The superexchange is the term used for interaction between two cations over an intermediate anion. It is a combination of direct exchange and electron transfer. So, in $Mn{O_2}$, two $M{n^{ + 4}}$ ions interact with each other despite there being ${O^{2 - }}$ ion in-between.
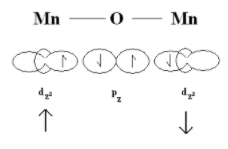
Due to superexchange, the spins of $M{n^{ + 4}}$ ions are flipped and these ions are aligned with opposing spins in its structure. Hence, $Mn{O_2}$ is antiferromagnetic in nature.
The compound $Mn{O_2}$ will behave as an antiferromagnetic up to a critical temperature known as Neel Temperature. Below Neel Temperature, the compound will behave as a paramagnet.
We know that the oxides of transition metals are commonly known antiferromagnetic substances.
The compound titanium dioxide, $Ti{O_2}$ is diamagnetic in nature as there are no unpaired electrons in it. The compound $V{O_2}$ is paramagnetic in nature as the compound contains ${V^{ + 4}}$ ion and this ion has unpaired electrons. The compound $Cr{O_2}$ is ferromagnetic in nature.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
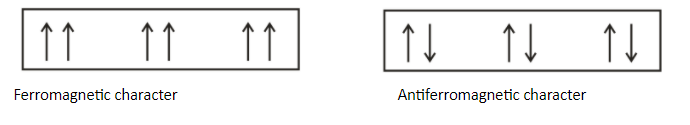
Note: Students should keep in mind that there is just a difference of alignment in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic is the alignment of magnetic moments. In ferromagnetic substances, the alignment of magnetic moments occurs in the same direction and in anti-ferromagnetic substances, the alignment of magnetic moments occurs in a compensatory manner to give resultant zero.
Complete step by step solution:
The options of compounds given above are oxides of different metals. To find out which of the given oxide is antiferromagnetic in nature, we need to know more about antiferromagnetism.
Let us first see how magnetic moments are aligned in antiferromagnetic substances which is shown in the given diagram. The ordering of magnetic moments in an antiferromagnetic material is shown below.

When a material is antiferromagnetic in nature, it has zero net magnetic moment that means no magnetic field will be produced by them.
Now, let us understand the structure of $Mn{O_2}$.
The compound $Mn{O_2}$ is also known as manganese IV oxide because in this compound Mn is in +4 oxidation state. In $Mn{O_2}$, there are 2 oxygen atoms with -2 charge. The overall charge on anion is -4.
The structure of $Mn{O_2}$ is shown below.
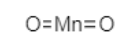
When a material is antiferromagnetic in nature, it is a result of superexchange of spin energy in that material. The superexchange is the term used for interaction between two cations over an intermediate anion. It is a combination of direct exchange and electron transfer. So, in $Mn{O_2}$, two $M{n^{ + 4}}$ ions interact with each other despite there being ${O^{2 - }}$ ion in-between.

Due to superexchange, the spins of $M{n^{ + 4}}$ ions are flipped and these ions are aligned with opposing spins in its structure. Hence, $Mn{O_2}$ is antiferromagnetic in nature.
The compound $Mn{O_2}$ will behave as an antiferromagnetic up to a critical temperature known as Neel Temperature. Below Neel Temperature, the compound will behave as a paramagnet.
We know that the oxides of transition metals are commonly known antiferromagnetic substances.
The compound titanium dioxide, $Ti{O_2}$ is diamagnetic in nature as there are no unpaired electrons in it. The compound $V{O_2}$ is paramagnetic in nature as the compound contains ${V^{ + 4}}$ ion and this ion has unpaired electrons. The compound $Cr{O_2}$ is ferromagnetic in nature.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: Students should keep in mind that there is just a difference of alignment in ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic is the alignment of magnetic moments. In ferromagnetic substances, the alignment of magnetic moments occurs in the same direction and in anti-ferromagnetic substances, the alignment of magnetic moments occurs in a compensatory manner to give resultant zero.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




