
Which of the following is/are true about the ellipse ${x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0$?
(A) The latus rectum of the ellipse is $1$.
(B) Distance between foci of the ellipse is $4\sqrt 3 $.
(C) Sum of the focal distance of a point P (x, y) on the ellipse is $4$.
(D) $y = 3$ meets the tangents drawn at the vertices of the ellipse at point P and Q, then PQ subtends a right angle at any of its foci.
Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: First we will convert the above equation in the standard form of ellipse so that we can find the value of a and b from the equation. Next, we need to find the eccentricity of this ellipse which is required in finding the latus rectum using the formula $e = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $.
Complete answer:
In the above question, first we will convert the equation ${x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0$ in the standard equation of an ellipse, which is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 0$.
Therefore,
${x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0$
We can also write the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 2x + 1 + 4{y^2} - 16y + 16 - 4 = 0$
Now, taking $4$ as common
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) + 4\left( {{y^2} - 4y + 4} \right) - 4 = 0$
On transposing, we get
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) + 4\left( {{y^2} - 4y + 4} \right) = 4$
Now we will use the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$in the above equation
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = 4$
Now, we will divide the whole equation by $4$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 1} \right)}^2}}}{4} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - 2} \right)}^2}}}{1} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - 2} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}} = 1$
On comparing with $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 0$, we get $a = 2\,\,and\,\,b = 1$
Now,
(A) The length of latus rectum $ = \dfrac{{2{b^2}}}{a}$
On substituting the values of a and b
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2 \times {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow 1$
(B) $e = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
$e = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{1}{4}} $
$ \Rightarrow e = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{4}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
Distance between foci of the ellipse $ = 2ae = 2 \times 2 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 2\sqrt 3 $
(C) Sum of the focal distance $ = 2a = 2 \times 2 = 4$
(D) In this part we have to prove that if$y = 3$ meets the tangents drawn at the vertices of the ellipse at point P and Q, then PQ subtends a right angle at any of its foci. Here O denotes the focus of given ellipse.
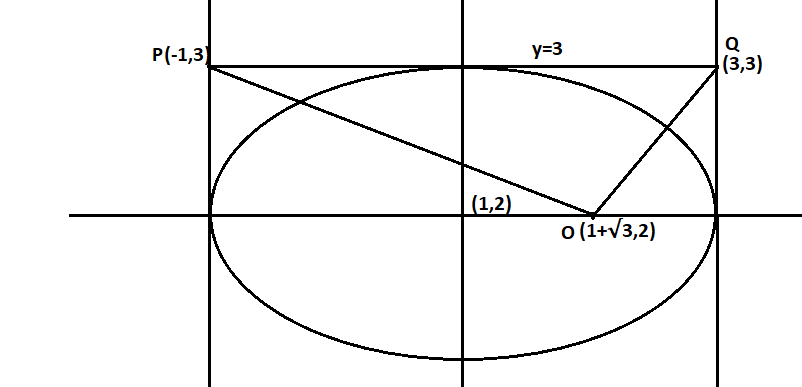
Now we use the relation ${m_1}{m_2} = - 1$to prove that line OP and OQ subtend right angle at its focus. Here ${m_1}$is the slope of OP and ${m_2}$ is the slope of OQ.
Here, in this figure ${x_1} = 1 + \sqrt 3 \,,\,{y_1} = 2\,\,,\,{x_2} = - 1,\,\,{y_2} = 3\,,\,{x_3} = 3\,,\,{y_3} = 3\,\,$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{{3 - 2}}{{ - 1 - \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{{3 - 2}}{{3 - \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 2 - \sqrt 3 }}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{1}{{ - \left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$and ${m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }}$
Now, we will multiply both the terms
${m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} - {{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{4 - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = - 1\]
Therefore, OP and OQ subtend the right angle at the focus.
Hence, option A, C and D are correct.
Therefore, the correct option is A, C and D
Note: All ellipses have two focal points, or foci. The sum of the distances from every point on the ellipse to the two foci is a constant. All ellipses have a centre and a major and minor axis. All ellipses have eccentricity values greater than or equal to zero, and less than one.
Complete answer:
In the above question, first we will convert the equation ${x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0$ in the standard equation of an ellipse, which is $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 0$.
Therefore,
${x^2} + 4{y^2} - 2x - 16y + 13 = 0$
We can also write the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 2x + 1 + 4{y^2} - 16y + 16 - 4 = 0$
Now, taking $4$ as common
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) + 4\left( {{y^2} - 4y + 4} \right) - 4 = 0$
On transposing, we get
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{x^2} - 2x + 1} \right) + 4\left( {{y^2} - 4y + 4} \right) = 4$
Now we will use the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$in the above equation
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + 4{\left( {y - 2} \right)^2} = 4$
Now, we will divide the whole equation by $4$.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 1} \right)}^2}}}{4} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - 2} \right)}^2}}}{1} = 1$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - 1} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - 2} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}} = 1$
On comparing with $\dfrac{{{{\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 0$, we get $a = 2\,\,and\,\,b = 1$
Now,
(A) The length of latus rectum $ = \dfrac{{2{b^2}}}{a}$
On substituting the values of a and b
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{2 \times {{\left( 1 \right)}^2}}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow 1$
(B) $e = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
$e = \sqrt {1 - \dfrac{1}{4}} $
$ \Rightarrow e = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{4}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
Distance between foci of the ellipse $ = 2ae = 2 \times 2 \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} = 2\sqrt 3 $
(C) Sum of the focal distance $ = 2a = 2 \times 2 = 4$
(D) In this part we have to prove that if$y = 3$ meets the tangents drawn at the vertices of the ellipse at point P and Q, then PQ subtends a right angle at any of its foci. Here O denotes the focus of given ellipse.

Now we use the relation ${m_1}{m_2} = - 1$to prove that line OP and OQ subtend right angle at its focus. Here ${m_1}$is the slope of OP and ${m_2}$ is the slope of OQ.
Here, in this figure ${x_1} = 1 + \sqrt 3 \,,\,{y_1} = 2\,\,,\,{x_2} = - 1,\,\,{y_2} = 3\,,\,{x_3} = 3\,,\,{y_3} = 3\,\,$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{{3 - 2}}{{ - 1 - \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{{3 - 2}}{{3 - \left( {1 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{1}{{ - 2 - \sqrt 3 }}$ and ${m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }}$
$ \Rightarrow $${m_1} = \dfrac{1}{{ - \left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$and ${m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }}$
Now, we will multiply both the terms
${m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{1}{{2 - \sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{\left( {2 + \sqrt 3 } \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} - {{\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right)}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{{4 - 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{1}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {m_1}{m_2} = - 1\]
Therefore, OP and OQ subtend the right angle at the focus.
Hence, option A, C and D are correct.
Therefore, the correct option is A, C and D
Note: All ellipses have two focal points, or foci. The sum of the distances from every point on the ellipse to the two foci is a constant. All ellipses have a centre and a major and minor axis. All ellipses have eccentricity values greater than or equal to zero, and less than one.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




