
Which of the following is/are non-reducing sugars?
A) \[{\text{Methyl }}\alpha - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glycopyranose}}\]
B) \[{\text{Methyl }}\beta - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glycopyranose}}\]
C) Glucose pentacetate
D) \[\alpha - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glycopyranose}}\]
Answer
548.4k+ views
Hint:
To check whether a sugar is reducing or non-reducing we must check whether the aldehyde group is in free form or not. If the aldehyde is in free form then it is reducing in nature and if the aldehyde is in acetal form then the sugar is non reducing sugar.
Complete step by step solution:
Sugar is basically a carbohydrate. carbohydrates are those molecules which are made up of carbon and hydrogen. They are aldehyde or ketones or which upon hydrolysis gives aldehyde or ketone are known as carbohydrates.
Sugars can also be classified as reducing and non reducing sugar. A reducing sugar always has a free aldehyde or ketone or they are in hemiacetal or hemiketal form. A non reducing sugar is that sugar which does not have free aldehyde or ketone group. They are either in acetal or ketal form.
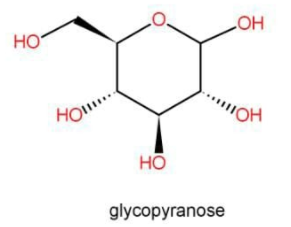
The above molecule possesses a hemiacetal structure and hence can form open chains which will give free aldehyde and hence is reducing sugar.
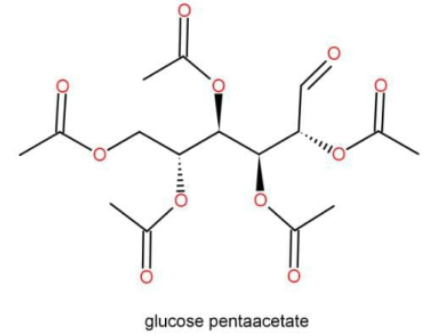
There are clearly so many free aldehyde groups present in the above molecule and hence is a reducing sugar.
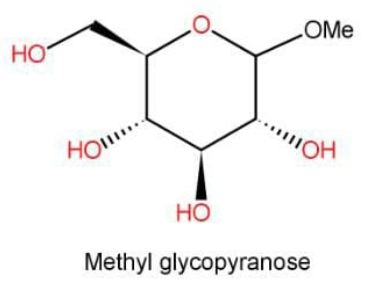
The above molecule has neither hemiacetal or hemiketal form nor free aldehyde or ketone and hence is non reducing in nature. \[{\text{Methyl }}\alpha - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glucopyranose}}\] and \[{\text{Methyl }}\beta - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glucopyranose}}\] are just the stereoisomers of the molecule methyl glucopyranoside. The structure for both remains same, just the arrangement of molecules in space will differ.
Hence, the correct option is A and B.
Note:
Sugars are further classified as monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest sugar they do not hydrolyze to give more simple carbohydrates. Examples of monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Disaccharides give units of monosaccharide upon hydrolysis examples of disaccharides sucrose and fructose.
To check whether a sugar is reducing or non-reducing we must check whether the aldehyde group is in free form or not. If the aldehyde is in free form then it is reducing in nature and if the aldehyde is in acetal form then the sugar is non reducing sugar.
Complete step by step solution:
Sugar is basically a carbohydrate. carbohydrates are those molecules which are made up of carbon and hydrogen. They are aldehyde or ketones or which upon hydrolysis gives aldehyde or ketone are known as carbohydrates.
Sugars can also be classified as reducing and non reducing sugar. A reducing sugar always has a free aldehyde or ketone or they are in hemiacetal or hemiketal form. A non reducing sugar is that sugar which does not have free aldehyde or ketone group. They are either in acetal or ketal form.

The above molecule possesses a hemiacetal structure and hence can form open chains which will give free aldehyde and hence is reducing sugar.

There are clearly so many free aldehyde groups present in the above molecule and hence is a reducing sugar.

The above molecule has neither hemiacetal or hemiketal form nor free aldehyde or ketone and hence is non reducing in nature. \[{\text{Methyl }}\alpha - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glucopyranose}}\] and \[{\text{Methyl }}\beta - {\text{D}}( + ) - {\text{glucopyranose}}\] are just the stereoisomers of the molecule methyl glucopyranoside. The structure for both remains same, just the arrangement of molecules in space will differ.
Hence, the correct option is A and B.
Note:
Sugars are further classified as monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the simplest sugar they do not hydrolyze to give more simple carbohydrates. Examples of monosaccharides are glucose and fructose. Disaccharides give units of monosaccharide upon hydrolysis examples of disaccharides sucrose and fructose.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




