
Which of the following is the most stable carbocation?
a)
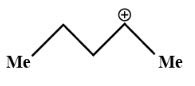
b)

c)

d)
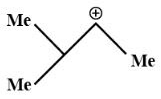




Answer
602.1k+ views
Hint: The stability of carbocations increases as we go from primary to secondary to tertiary carbons. In other words, we can say that the neighboring carbon pays the carbocation with electrons it steals from the hydrogens.
Complete step by step solution:
The three main features that affect the stability of the carbocation are:
Neighboring carbon atoms.
Neighboring carbon multiple bonds.
Neighboring atoms with lone pairs.
As there are no adjacent pi bonds in any of the given figures above, that means we will see the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbocation.
In the given question, carbocation in figure (c) is connected to only one methyl group, So, its stability will be less.
Now the rest three figures are secondary carbocation, in organic chemistry, hyperconjugation is the interaction of the electrons in a sigma orbital with an adjacent empty non-bonding or antibonding sigma or pi orbital to give an extended molecular orbital. Increased electron delocalization associated with hyperconjugation increases the stability of the system called hyperconjugation.
According to this concept, structure two will show hyperconjugation as its electrons can move more freely here. Thus, structure two is the most stable carbocation.
Therefore, from the above statements we can conclude that the correct answer is (b).
Note: The other factor that affect the stability of a carbocation are:
Inductive effect
Electronegativity
Resonance
Rearrangements like hydride shift, methyl shift, phenyl shift.
Complete step by step solution:
The three main features that affect the stability of the carbocation are:
Neighboring carbon atoms.
Neighboring carbon multiple bonds.
Neighboring atoms with lone pairs.
As there are no adjacent pi bonds in any of the given figures above, that means we will see the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbocation.
In the given question, carbocation in figure (c) is connected to only one methyl group, So, its stability will be less.
Now the rest three figures are secondary carbocation, in organic chemistry, hyperconjugation is the interaction of the electrons in a sigma orbital with an adjacent empty non-bonding or antibonding sigma or pi orbital to give an extended molecular orbital. Increased electron delocalization associated with hyperconjugation increases the stability of the system called hyperconjugation.
According to this concept, structure two will show hyperconjugation as its electrons can move more freely here. Thus, structure two is the most stable carbocation.
Therefore, from the above statements we can conclude that the correct answer is (b).
Note: The other factor that affect the stability of a carbocation are:
Inductive effect
Electronegativity
Resonance
Rearrangements like hydride shift, methyl shift, phenyl shift.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




