
Which of the following is the main difference between AC generator and DC generator?
$\text{A}\text{. Carbon Brushes}$
$\text{B}\text{. Magnets}$
$\text{C}\text{. Coil}$
$\text{D}\text{. Commutator}$
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: AC generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy in the form of alternating emf or current. A DC generator is a device used to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. Both are based on the law of electromagnetic induction.
Complete step by step answer:
An AC generator consists of a coil mounted on a rotor shaft. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field generated by magnets. The coil is rotated mechanically by external forces. The rotation in the coil causes change in magnetic flux through it and as a consequence emf is induced. The ends of the coil are connected to an external circuit through slip rings and brushes.
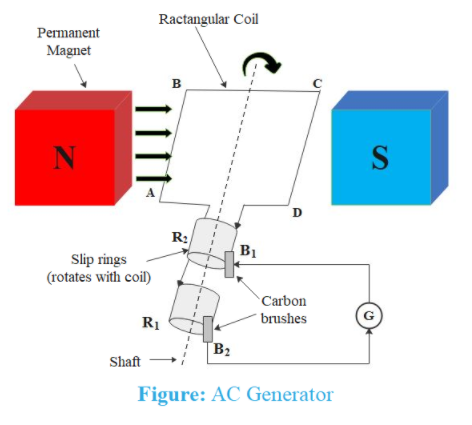
When the coil is rotated with a constant angular speed ($\omega$), the instantaneous emf induced according to Faraday’s is $\epsilon ={{\epsilon }_{0}}\sin \omega t$ where ${{\epsilon }_{0}}$ is maximum value of emf that occurs at $\omega t={{90}^{{}^\circ }}$
As $\sin \omega t$varies between +1 and -1, polarity of emf changes with time and the induced current is called as alternating current.
In DC generators, the same procedure is used to produce current except the commutator. A commutator is a kind of electrical switch which reverses the direction between coil and external circuit. It’s thus used to convert ac signals to dc.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Additional information:
If a conductor is placed in a time varying magnetic field, emf is induced in it. This process of induction is known as electromagnetic induction.
Faraday introduced a law to mathematically represent induced emf. This law is known as Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. This law states that, “the magnitude of the induced emf in a circuit is equal to the time rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.”
$\epsilon =-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}$ where $\phi_B$ represents magnetic flux and $\epsilon$represents induced emf.
The negative sign indicates that the direction of induced emf is such that it produces a current such that it opposes change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is known as Lenz’s law.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The negative sign in Faraday’s law indicates that the direction of induced emf is such that it produces a current such that it opposes change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is known as Lenz’s law. It is very useful in determining the direction of induced emf.
Complete step by step answer:
An AC generator consists of a coil mounted on a rotor shaft. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field generated by magnets. The coil is rotated mechanically by external forces. The rotation in the coil causes change in magnetic flux through it and as a consequence emf is induced. The ends of the coil are connected to an external circuit through slip rings and brushes.

When the coil is rotated with a constant angular speed ($\omega$), the instantaneous emf induced according to Faraday’s is $\epsilon ={{\epsilon }_{0}}\sin \omega t$ where ${{\epsilon }_{0}}$ is maximum value of emf that occurs at $\omega t={{90}^{{}^\circ }}$
As $\sin \omega t$varies between +1 and -1, polarity of emf changes with time and the induced current is called as alternating current.
In DC generators, the same procedure is used to produce current except the commutator. A commutator is a kind of electrical switch which reverses the direction between coil and external circuit. It’s thus used to convert ac signals to dc.
Therefore, option D is correct.
Additional information:
If a conductor is placed in a time varying magnetic field, emf is induced in it. This process of induction is known as electromagnetic induction.
Faraday introduced a law to mathematically represent induced emf. This law is known as Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. This law states that, “the magnitude of the induced emf in a circuit is equal to the time rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit.”
$\epsilon =-\dfrac{d{{\phi }_{B}}}{dt}$ where $\phi_B$ represents magnetic flux and $\epsilon$represents induced emf.
The negative sign indicates that the direction of induced emf is such that it produces a current such that it opposes change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is known as Lenz’s law.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The negative sign in Faraday’s law indicates that the direction of induced emf is such that it produces a current such that it opposes change in magnetic flux that produced it. This is known as Lenz’s law. It is very useful in determining the direction of induced emf.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




