
Which of the following is not the correct observation based on Ellingham diagram?
A.A metal can reduce the oxide of other metal which lies above it in Ellingham diagram.
B.CO is more effective than C as a reducing agent below \[{170^o}C\] .
C. \[\Delta {G^o}\] metal oxide is higher than \[C{O_2}\] hence oxidation of metal sulphides to oxides is not favourable.
D.Need for conversion of metal sulphide to metal oxide before reduction can be explained thermodynamically.
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Ellingham diagram was basically a curve which related the Gibbs energy value with the temperature. Metal oxides which are reduced by a metal lie above in the diagram. Oxidation of metal sulphides to oxides takes place before reduction.
Complete step by step answer:
H.G.T Ellingham proposed the Ellingham diagram so as to predict the spontaneity of reduction of various metal oxides obtained from oxidation of metal sulphides. It was basically a curve which related the Gibbs energy value with the temperature. Gibbs energy is given as: \[\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta S\] ,
where \[\Delta H\] is the change in enthalpy and \[\Delta S\] is the change in entropy.
Certain observations can be drawn from the Ellingham diagram. These are:
Ellingham diagram is plotted between \[\Delta {G^o}\] and T for the formation of oxides of metals. Except for the processes in which phase change takes place, each plot is a straight line.
This temperature at which change of phase takes place is indicated by a positive increase in the slope.
A given metal can reduce the oxides of all other metals whose lines lie above theirs on the diagram. For example, magnesium can reduce titanium oxide to metallic titanium.
As the temperature increases, generally \[\Delta {G^o}\] value for the formation of the metal oxide becomes less negative and zero at a particular temperature. Below this temperature, \[\Delta {G^o}\] is negative and the oxide is stable and above this temperature it is positive. This trend suggests that metal oxides become less stable at higher temperature and their decomposition becomes easier.
Since the \[2C + {O_2} \to 2CO\] line is downward-sloping, it cuts across the lines for many of the other metals by making carbon useful as a reducing agent, because as soon as the carbon oxidation line goes below a metal oxidation line, the carbon can then easily reduce the metal oxide to metal. CO is more effective than C as a reducing agent below \[{170^o}C\] .
As we can see in the diagram, \[\Delta {G^o}\] of metal oxide is higher than that of \[C{O_2}\] thus the oxidation of metal sulphides to oxides is most favourable.
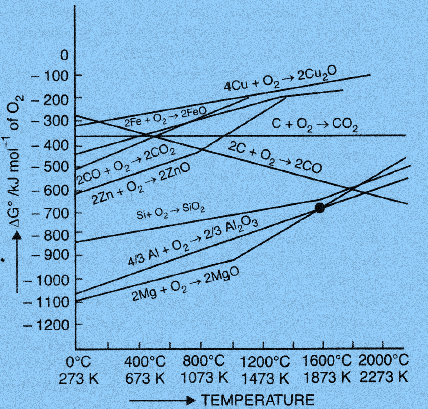
Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Ellingham diagram is based only on thermodynamic considerations as it gives information about the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction but does not tell anything about the rate of the reaction or the possibility of other reactions that might be taking place. The interpretation is not true that \[\Delta G\] is based on the assumption that the reactants are in equilibrium with the products.
Complete step by step answer:
H.G.T Ellingham proposed the Ellingham diagram so as to predict the spontaneity of reduction of various metal oxides obtained from oxidation of metal sulphides. It was basically a curve which related the Gibbs energy value with the temperature. Gibbs energy is given as: \[\Delta G = \Delta H - T\Delta S\] ,
where \[\Delta H\] is the change in enthalpy and \[\Delta S\] is the change in entropy.
Certain observations can be drawn from the Ellingham diagram. These are:
Ellingham diagram is plotted between \[\Delta {G^o}\] and T for the formation of oxides of metals. Except for the processes in which phase change takes place, each plot is a straight line.
This temperature at which change of phase takes place is indicated by a positive increase in the slope.
A given metal can reduce the oxides of all other metals whose lines lie above theirs on the diagram. For example, magnesium can reduce titanium oxide to metallic titanium.
As the temperature increases, generally \[\Delta {G^o}\] value for the formation of the metal oxide becomes less negative and zero at a particular temperature. Below this temperature, \[\Delta {G^o}\] is negative and the oxide is stable and above this temperature it is positive. This trend suggests that metal oxides become less stable at higher temperature and their decomposition becomes easier.
Since the \[2C + {O_2} \to 2CO\] line is downward-sloping, it cuts across the lines for many of the other metals by making carbon useful as a reducing agent, because as soon as the carbon oxidation line goes below a metal oxidation line, the carbon can then easily reduce the metal oxide to metal. CO is more effective than C as a reducing agent below \[{170^o}C\] .
As we can see in the diagram, \[\Delta {G^o}\] of metal oxide is higher than that of \[C{O_2}\] thus the oxidation of metal sulphides to oxides is most favourable.

Hence, the correct option is (C).
Note:
Ellingham diagram is based only on thermodynamic considerations as it gives information about the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction but does not tell anything about the rate of the reaction or the possibility of other reactions that might be taking place. The interpretation is not true that \[\Delta G\] is based on the assumption that the reactants are in equilibrium with the products.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




