
Which of the following is non classical carbocation?
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: A non classical carbocation is stabilized by the 3 centre 2 electron bonds. A classical carbocation has a carbon atom having 6 electrons on the carbon bearing positive charge.
Complete step by step solution:
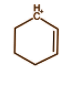
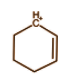
In the above molecule we have carbon having positive charge and six electrons. It is bonded with 3 bonds with 2 carbon atoms and 1 hydrogen atom. Each bond comprises 2 electrons and hence it will have 6 electrons from 3 bonds. So this is a classical carbocation.
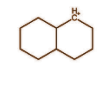
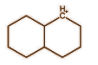
In the above molecule we again have carbon having positive charge and six electrons. It is bonded with 3 bonds with 2 carbon atoms and 1 hydrogen atom. Each bond comprises 2 electrons and hence it will have 6 electrons from 3 bonds. So this is also a classical carbocation.
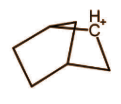
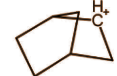
The above molecule seems like a classical carbocation but it is not, it actually exists in resonance via bond rotation as:
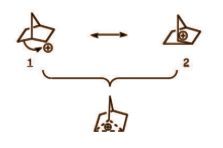
As we can see that this carbocation has 3 centre 2 electron bonds. That means there are 3 carbon forming rings but it has only 2 electrons because actually only 1 bond is here. Hence it is a non classical carbocation.
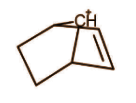
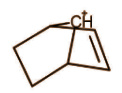
It is also a classical carbocation as no such delocalisation is present that will make 3 centre 2 electron bonds.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Classical carbocation are typically carbocation which we usually encounter in the reaction. The most stable carbocation is that carbocation which is stabilized by the resonance especially the mesomeric effect. In the above option, A is most stable due to resonance.
Complete step by step solution:

In the above molecule we have carbon having positive charge and six electrons. It is bonded with 3 bonds with 2 carbon atoms and 1 hydrogen atom. Each bond comprises 2 electrons and hence it will have 6 electrons from 3 bonds. So this is a classical carbocation.

In the above molecule we again have carbon having positive charge and six electrons. It is bonded with 3 bonds with 2 carbon atoms and 1 hydrogen atom. Each bond comprises 2 electrons and hence it will have 6 electrons from 3 bonds. So this is also a classical carbocation.

The above molecule seems like a classical carbocation but it is not, it actually exists in resonance via bond rotation as:

As we can see that this carbocation has 3 centre 2 electron bonds. That means there are 3 carbon forming rings but it has only 2 electrons because actually only 1 bond is here. Hence it is a non classical carbocation.

It is also a classical carbocation as no such delocalisation is present that will make 3 centre 2 electron bonds.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note: Classical carbocation are typically carbocation which we usually encounter in the reaction. The most stable carbocation is that carbocation which is stabilized by the resonance especially the mesomeric effect. In the above option, A is most stable due to resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




