
Which of the following is most acidic?
A. Benzyl alcohol
B. Cyclohexanol
C. Phenol
D. m-chlorophenol
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: Alcohols are generally weaker acids. Generally alcohols lose hydrogen ions to show acidic character. Phenoxide ion is very stable since it has four resonating structures.
Complete step by step answer:
Alcohols are the organic compounds which have hydroxyl group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ connected to a saturated carbon $\left( {{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}} \right)$. Phenols contain ${\text{OH}}$ group connected to a carbon of a benzene ring.
In ${\text{OH}}$ group, oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. So oxygen pulls shared electrons towards it. In aqueous solution, alcohol will donate its proton to water molecules to give an alkoxide ion. The acid-dissociation constant, ${{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$, of an alcohol is defined by the equilibrium.
${\text{ROH}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\overset {{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}} \leftrightarrows {\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }$
${{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }} \right]\left[ {{\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }} \right]}}{{\left[ {{\text{ROH}}} \right]}}$
${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} = - \log \left( { - {{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}} \right)$
The smaller the ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ value, the alcohol is more acidic.
Phenols are generally more acidic than alcohols by considering the resonance effect. A benzene ring is generally considered electron withdrawing (inductive effect) the benzene ring stabilizes the negative charge of phenoxide ion through resonance. Benzyl group stabilizes the negative charge on the oxygen atom.
The carbon-oxygen bond in benzyl alcohol is electron-deficient and is able to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen in alkoxide.
Electron withdrawing substituents make a phenol more acidic by stabilizing phenoxide ion through delocalization of negative charge and through inductive effects. Some electron withdrawing groups are ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_2}, - {\text{Cl}}, - {\text{CN}}$ etc.
Electron donating groups make a phenol less acidic by destabilizing the phenoxide ion (resonance effect).The location of the substituent relative to the phenol is important. Some electron donating groups are ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{H}}_2}, - {\text{NR}}, - {\text{OR}}, - {\text{R}}$ etc.
So the order of acidic character is given below:
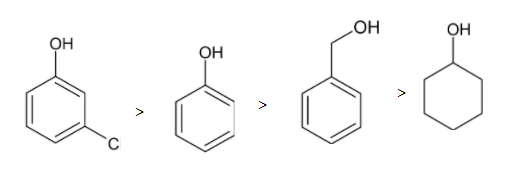
Thus meta-chlorophenol is more acidic
So, Option D is correct.
Note: Inductive effect and resonance effect are the major factors influencing the acidic character. The phenoxide ion is more stable because the negative charge is not confined to oxygen but delocalized into the benzene ring. The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized by the benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Alcohols are the organic compounds which have hydroxyl group $\left( { - {\text{OH}}} \right)$ connected to a saturated carbon $\left( {{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}} \right)$. Phenols contain ${\text{OH}}$ group connected to a carbon of a benzene ring.
In ${\text{OH}}$ group, oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen. So oxygen pulls shared electrons towards it. In aqueous solution, alcohol will donate its proton to water molecules to give an alkoxide ion. The acid-dissociation constant, ${{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$, of an alcohol is defined by the equilibrium.
${\text{ROH}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\overset {{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}} \leftrightarrows {\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }$
${{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} = \dfrac{{\left[ {{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }} \right]\left[ {{\text{R}}{{\text{O}}^ - }} \right]}}{{\left[ {{\text{ROH}}} \right]}}$
${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} = - \log \left( { - {{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}} \right)$
The smaller the ${\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}}$ value, the alcohol is more acidic.
Phenols are generally more acidic than alcohols by considering the resonance effect. A benzene ring is generally considered electron withdrawing (inductive effect) the benzene ring stabilizes the negative charge of phenoxide ion through resonance. Benzyl group stabilizes the negative charge on the oxygen atom.
The carbon-oxygen bond in benzyl alcohol is electron-deficient and is able to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen in alkoxide.
Electron withdrawing substituents make a phenol more acidic by stabilizing phenoxide ion through delocalization of negative charge and through inductive effects. Some electron withdrawing groups are ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{O}}_2}, - {\text{Cl}}, - {\text{CN}}$ etc.
Electron donating groups make a phenol less acidic by destabilizing the phenoxide ion (resonance effect).The location of the substituent relative to the phenol is important. Some electron donating groups are ${\text{ - N}}{{\text{H}}_2}, - {\text{NR}}, - {\text{OR}}, - {\text{R}}$ etc.
So the order of acidic character is given below:

Thus meta-chlorophenol is more acidic
So, Option D is correct.
Note: Inductive effect and resonance effect are the major factors influencing the acidic character. The phenoxide ion is more stable because the negative charge is not confined to oxygen but delocalized into the benzene ring. The phenoxide ion is resonance stabilized by the benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




