
Which of the following is inner orbital complex as well as diamagnetic in nature?
A.${{[Ir{{({{H}_{2}}O)}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$
B.${{[Ni{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$
C. ${{[Cr{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$
D. ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint: A chemical complex contains a central metal atom attached with different ligands. When the hybridization of the central metal consists of the filling of inner d – orbital, and the outer electron in the s and p orbital, then the complex is inner orbital complex. Diamagnetic compounds consist of no unpaired electrons.
Complete answer:
A chemical compound having a central metal atom attached with ligands is called a complex. The electronic configuration of the central metal atom defines the hybridization of the complex. A complex that has the valence electrons of the central metal atom in the outer d orbitals are called outer orbital complexes, while in the metal atom, when the valence electrons are present in the inner d orbital it is called inner orbital complex. This is because the vacant d – orbital of the metals take part in bonding with the ligands and making complexes.
Among the given complexes, the central atoms has the electronic configurations as, $Ir=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{7}}6{{s}^{2}}$, $Ni=[Ar]3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{2}}$ , $Cr=[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}4{{s}^{1}}$ and$Co=[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}4{{s}^{2}}$ . So, atoms with inner d orbital like Nickel, chromium, and cobalt can form inner orbital complexes. But we have to identify the complex which is diamagnetic as well as the inner orbital complex. As $N{{H}_{3}}$ is attached with these three atoms, which is a weak ligand, but with $C{{o}^{3+}}$ cobalt ion it acts as a strong ligand that pairs the electrons, so, ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ is the inner orbital complex with hybridization ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ that is diamagnetic in nature.
The diagram shows the diamagnetic nature of ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ that has all the electrons paired as:
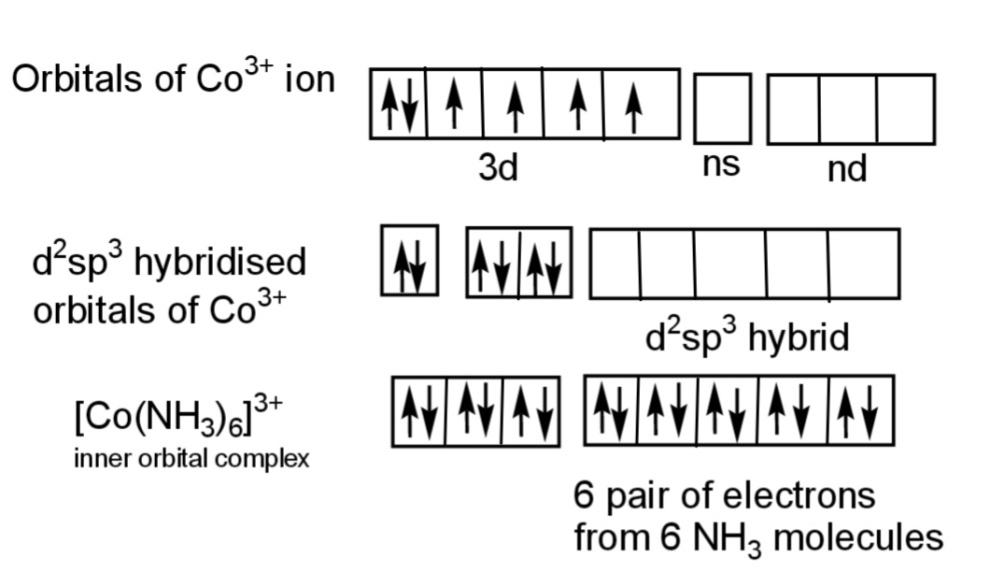
Hence, the complex that is inner orbital and is diamagnetic is ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$.
So option D is correct.
Note:
A strong ligand is that ligand which is able to pair up the electrons of the central metal atom, while a weak ligand is not able to pair up the electrons. A complex which has few or no unpaired electrons is of low spin, which are mostly the inner orbital complexes, while the outer orbital complexes have high spin as they have weak field and more unpaired electrons.
Complete answer:
A chemical compound having a central metal atom attached with ligands is called a complex. The electronic configuration of the central metal atom defines the hybridization of the complex. A complex that has the valence electrons of the central metal atom in the outer d orbitals are called outer orbital complexes, while in the metal atom, when the valence electrons are present in the inner d orbital it is called inner orbital complex. This is because the vacant d – orbital of the metals take part in bonding with the ligands and making complexes.
Among the given complexes, the central atoms has the electronic configurations as, $Ir=[Xe]4{{f}^{14}}5{{d}^{7}}6{{s}^{2}}$, $Ni=[Ar]3{{d}^{8}}4{{s}^{2}}$ , $Cr=[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}4{{s}^{1}}$ and$Co=[Ar]3{{d}^{7}}4{{s}^{2}}$ . So, atoms with inner d orbital like Nickel, chromium, and cobalt can form inner orbital complexes. But we have to identify the complex which is diamagnetic as well as the inner orbital complex. As $N{{H}_{3}}$ is attached with these three atoms, which is a weak ligand, but with $C{{o}^{3+}}$ cobalt ion it acts as a strong ligand that pairs the electrons, so, ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{2+}}$ is the inner orbital complex with hybridization ${{d}^{2}}s{{p}^{3}}$ that is diamagnetic in nature.
The diagram shows the diamagnetic nature of ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$ that has all the electrons paired as:

Hence, the complex that is inner orbital and is diamagnetic is ${{[Co{{(N{{H}_{3}})}_{6}}]}^{3+}}$.
So option D is correct.
Note:
A strong ligand is that ligand which is able to pair up the electrons of the central metal atom, while a weak ligand is not able to pair up the electrons. A complex which has few or no unpaired electrons is of low spin, which are mostly the inner orbital complexes, while the outer orbital complexes have high spin as they have weak field and more unpaired electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




