
Which of the following is heterocyclic aromatic species?
A.
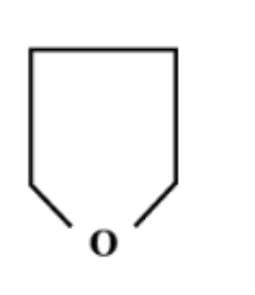
B.
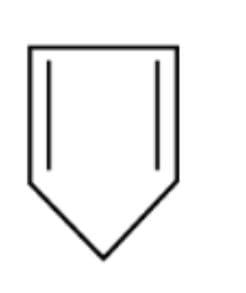
C.
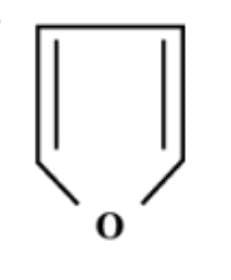
D.
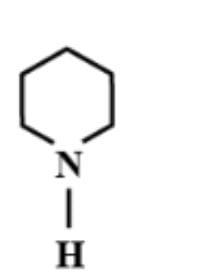




Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: Basically, a heterocyclic compound is an organic compound where an atom other than carbon atom has substituted one or more of the carbon atoms in the molecule’s backbone. Some of the normal hereto atoms are nitrogen, Sulphur and oxygen.
Complete step by step answer:
Aromatic compounds are the chemical compounds that consist of conjugated planar ring systems accomplished by delocalized pi- electron clouds in place of individual alternating double and single bonds. These are also known as aromatics or arenes. Now, aromatic compounds are divided into two categories, the first one is benzenoid, one containing the benzene ring whereas the other one is non- benzenoid, that does not contain a benzene ring like furan.
Further, any hydrocarbon can be classified as an aromatic compound provided, they follow the Huckel rule. Now, according to this rule, for a ring to be aromatic, it should follow the following properties:
a)Planarity
b)Complete delocalization of pi electrons in the ring
c)Presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring where n is an integer.
Now, the heterocyclic aromatic compound is an organic compound where an atom other than carbon atom has substituted one or more of the carbon atoms in the molecule’s backbone. Nitrogen, oxygen, Sulphur are normal hetero atoms. So, option C i.e. furan is heterocyclic aromatic species as it is planar, cyclic, conjugated
$(4n + 2)\pi $ electron system.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Don’t get confused with aliphatic and aromatic compounds. In case of aliphatic compounds, there is a straight chain representation whereas in case of aromatic compounds, the carbon compounds are associated with conjugated pi electrons in the form of a ring structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Aromatic compounds are the chemical compounds that consist of conjugated planar ring systems accomplished by delocalized pi- electron clouds in place of individual alternating double and single bonds. These are also known as aromatics or arenes. Now, aromatic compounds are divided into two categories, the first one is benzenoid, one containing the benzene ring whereas the other one is non- benzenoid, that does not contain a benzene ring like furan.
Further, any hydrocarbon can be classified as an aromatic compound provided, they follow the Huckel rule. Now, according to this rule, for a ring to be aromatic, it should follow the following properties:
a)Planarity
b)Complete delocalization of pi electrons in the ring
c)Presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring where n is an integer.
Now, the heterocyclic aromatic compound is an organic compound where an atom other than carbon atom has substituted one or more of the carbon atoms in the molecule’s backbone. Nitrogen, oxygen, Sulphur are normal hetero atoms. So, option C i.e. furan is heterocyclic aromatic species as it is planar, cyclic, conjugated
$(4n + 2)\pi $ electron system.
Hence, option C is correct.
Note: Don’t get confused with aliphatic and aromatic compounds. In case of aliphatic compounds, there is a straight chain representation whereas in case of aromatic compounds, the carbon compounds are associated with conjugated pi electrons in the form of a ring structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




