
Which of the following is called the limit up to which the stress is directly proportional to strain?
${\text{A}}{\text{.}}$ Elastic limit
${\text{B}}{\text{.}}$ Elastic fatigue
${\text{C}}{\text{.}}$ Elastic relaxation
${\text{D}}{\text{.}}$ Breaking limit
Answer
604.2k+ views
Hint: Here, we will proceed by drawing the stress strain curve and will show various points on it. Then, we will proceed by each of the terms which are there in the options of the given problem.
Step By Step Answer:
The stress strain curve is shown in the figure and various important points are mentioned on it.
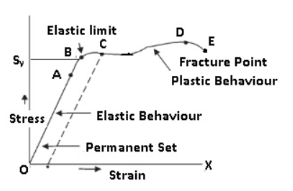
The maximum stress that a material can withstand before the permanent deformation is known as the elastic limit. It is the material 's highest limit before the material can develop plastic deformation. Upon removal of the stress or force from the material, the material returns to its original form. Elastomers such as rubber have overall elastic length. It is Hooke 's law that can explain this behaviour.
According to Hooke’s law, the stress applied to a body is directly proportional to the strain generated in the body within the elastic limit.
Mathematically, we can express Hooke’s law as
Stress $ \propto $ Strain
If an elastic body continuously undergoes alternating force of deformation, then the body's elastic property slowly decreases. Body's property by reason of which it loses its elastic property is known as elastic fatigue under the action of repeated alternating deforming force.
Creep refers to plastic strain increase under constant stress. Elastic relaxation is a reduction in stress under constant strain. In electrical applications Creep is rarely important. Contact design, although this can be a problem in the plastic housing where most connectors are moulded.
Breaking stress or breaking limits is a point where material strength breaks. The stress corresponding with this point is known as the breaking stress (or strength) or the rupture strength.
Therefore, elastic limit is called the limit up to which the stress is directly proportional to strain.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: The curve is called the engineering stress strain curve if it is based on the initial cross-section and gauge length, while the curve is called the true stress strain curve if it is based on the instantaneous cross-section area and length. Engineering stress-strain is commonly used, unless otherwise specified.
Step By Step Answer:
The stress strain curve is shown in the figure and various important points are mentioned on it.

The maximum stress that a material can withstand before the permanent deformation is known as the elastic limit. It is the material 's highest limit before the material can develop plastic deformation. Upon removal of the stress or force from the material, the material returns to its original form. Elastomers such as rubber have overall elastic length. It is Hooke 's law that can explain this behaviour.
According to Hooke’s law, the stress applied to a body is directly proportional to the strain generated in the body within the elastic limit.
Mathematically, we can express Hooke’s law as
Stress $ \propto $ Strain
If an elastic body continuously undergoes alternating force of deformation, then the body's elastic property slowly decreases. Body's property by reason of which it loses its elastic property is known as elastic fatigue under the action of repeated alternating deforming force.
Creep refers to plastic strain increase under constant stress. Elastic relaxation is a reduction in stress under constant strain. In electrical applications Creep is rarely important. Contact design, although this can be a problem in the plastic housing where most connectors are moulded.
Breaking stress or breaking limits is a point where material strength breaks. The stress corresponding with this point is known as the breaking stress (or strength) or the rupture strength.
Therefore, elastic limit is called the limit up to which the stress is directly proportional to strain.
Hence, option A is correct.
Note: The curve is called the engineering stress strain curve if it is based on the initial cross-section and gauge length, while the curve is called the true stress strain curve if it is based on the instantaneous cross-section area and length. Engineering stress-strain is commonly used, unless otherwise specified.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




