
Which of the following is called a sugar sink?
A. Roots
B. Developing seeds
C. Both A and B
D. Leaves
Answer
594.3k+ views
Hint: Leaves are the sugar sources of the plant and roots are the sugar sinks of the plant. Sinks are those parts which store the sugar.
Complete Answer: Plant has xylem and phloem as conducting tissues which transport sugar molecules in the form of sucrose. The sugar molecules are transported from source end to sink end. Plant is divided into source and sink. Sinks are the sites where it is stored or used. Plants include both source and sink parts. Sources are the parts where net fixation of carbon dioxide occurs.
The correct answer is C. Both A and B.
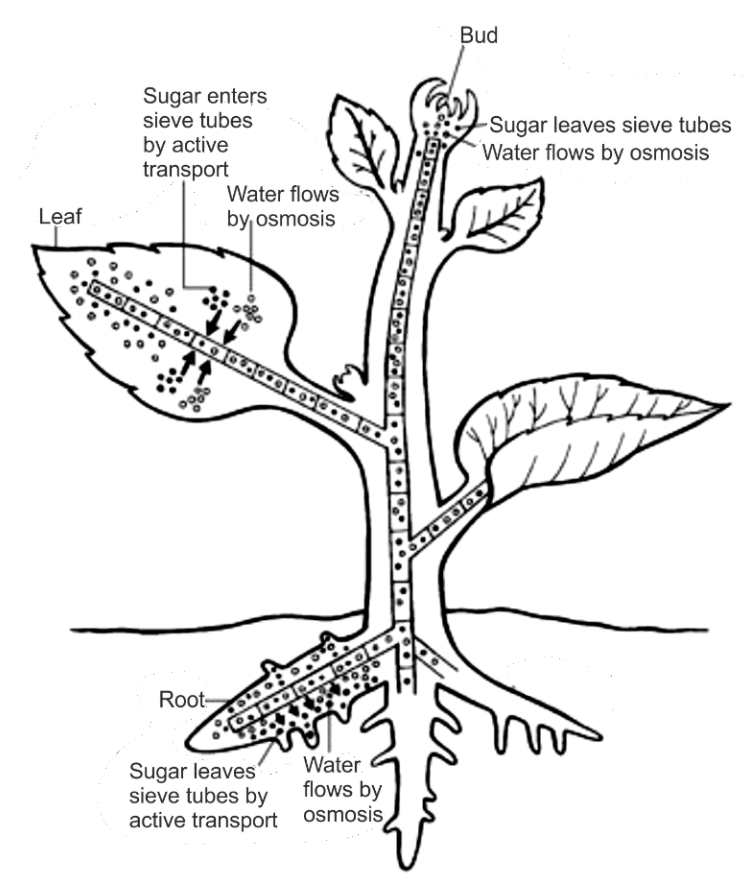
Additional Information: It is a longer distance movement of organic substances from the source or supply end to the region of utilization or sink. But the source and sink may be reversed depending on the season or need of the plant. Sugar stored in roots may be metabolized to become a source of food in the early spring when the buds of trees act as a sink and require energy for their growth and development. Since the source-sink relationship is variable, the direction of movement of organic solutes in phloem can be bidirectional that is upwards or downwards and in case of xylem, it is unidirectional. Translocation is directional movement of materials which occurs inside vascular tissues (Xylem and Phloem).
Note: Roots and developing seeds both act as sugar sink. The sugar is stored in the form of energy in roots which are acting as sinks.
Complete Answer: Plant has xylem and phloem as conducting tissues which transport sugar molecules in the form of sucrose. The sugar molecules are transported from source end to sink end. Plant is divided into source and sink. Sinks are the sites where it is stored or used. Plants include both source and sink parts. Sources are the parts where net fixation of carbon dioxide occurs.
The correct answer is C. Both A and B.

Additional Information: It is a longer distance movement of organic substances from the source or supply end to the region of utilization or sink. But the source and sink may be reversed depending on the season or need of the plant. Sugar stored in roots may be metabolized to become a source of food in the early spring when the buds of trees act as a sink and require energy for their growth and development. Since the source-sink relationship is variable, the direction of movement of organic solutes in phloem can be bidirectional that is upwards or downwards and in case of xylem, it is unidirectional. Translocation is directional movement of materials which occurs inside vascular tissues (Xylem and Phloem).
Note: Roots and developing seeds both act as sugar sink. The sugar is stored in the form of energy in roots which are acting as sinks.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




