
Which of the following is an example(s) of contact force?
A. Muscular force
B. Magnetic force
C. Gravitational force
D. Frictional force
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: As the name suggests, contact forces require a physical contact between the participating objects. Determine which of the above forces may fall under this category. For this, remember that contact forces are most often surface forces that act on an internal or external surface element of the object, and non-contact forces act throughout the volume of the body.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what contact forces are.
A contact force is a force that is exerted by objects that are in contact with each other. This force requires some sort of contact to occur between the force applicant and the object subjected to this force. Most macroscopic interactions occur via contact forces. This force can either be continuously applied or delivered in a short impulse. Contact forces can usually be decomposed into orthogonal components, one that is parallel to the surfaces in contact (shear forces) and one perpendicular to the surfaces in contact (normal forces). This is why contact forces are also known as surface forces and act across the surface element of the body.
From the options given to us, we see that the muscular force and the frictional force satisfy the criteria we’ve set for contact forces.
Muscular force is a force that is exerted as a result of the action of muscles. For example, lifting an object, or walking, or crushing an object, all require contact with the muscles of our body to execute motion or alter the state of the body. Thus, muscular force is a contact force.
Frictional force is a force that is exerted when two bodies are in contact and slide against each other. It is an impeding force that acts against the state of rest or motion of a body. Again, we see that walking on a cement path is much easier than walking on ice because cement offers more friction to the surface of our shoes than ice. Friction is also the reason why we’re able to light a matchstick by rubbing its head over the rough surface which produces heat converting red phosphorus to white phosphorus which is highly flammable and ignites the matchstick.
Let us look at an example. Consider a man pulling a crate up an inclined plane. He uses his muscular force to pull the crate up by holding a rope attached to it. He thus establishes contact with the rope in order to pull it.
Now, as the crate rests on the inclined plane, the plane exerts a normal reaction force on the crate in response to the weight exerted by the crate on the inclined plane. This is also a contact force. Additionally, the crate is also subject to a frictional force in a direction opposite to motion due to the contact between the crate and the inclined plane. Thus, frictional force is also a contact force.
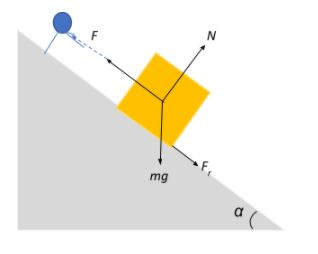
Magnetic and Gravitational forces are non-contact forces that are able to exert a force even when there is a finite separation between two objects. For example, a magnet is able to pull an iron nail close to it even if they are not in physical contact with each other. A ball when dropped from a height falls down towards the earth due to the gravitational force acting on it.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that forces due to gravity, and electric and magnetic fields fall under non-contact forces since they are able to initiate their action even when the bodies are not in physical contact with each other. This brings us to fictitious forces, such as the Centrifugal force, Euler force, and the Coriolis force, all of which fall under non-contact forces since they do not require any physical contact and are subjected throughout the volume of the body experiencing these forces.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us begin by understanding what contact forces are.
A contact force is a force that is exerted by objects that are in contact with each other. This force requires some sort of contact to occur between the force applicant and the object subjected to this force. Most macroscopic interactions occur via contact forces. This force can either be continuously applied or delivered in a short impulse. Contact forces can usually be decomposed into orthogonal components, one that is parallel to the surfaces in contact (shear forces) and one perpendicular to the surfaces in contact (normal forces). This is why contact forces are also known as surface forces and act across the surface element of the body.
From the options given to us, we see that the muscular force and the frictional force satisfy the criteria we’ve set for contact forces.
Muscular force is a force that is exerted as a result of the action of muscles. For example, lifting an object, or walking, or crushing an object, all require contact with the muscles of our body to execute motion or alter the state of the body. Thus, muscular force is a contact force.
Frictional force is a force that is exerted when two bodies are in contact and slide against each other. It is an impeding force that acts against the state of rest or motion of a body. Again, we see that walking on a cement path is much easier than walking on ice because cement offers more friction to the surface of our shoes than ice. Friction is also the reason why we’re able to light a matchstick by rubbing its head over the rough surface which produces heat converting red phosphorus to white phosphorus which is highly flammable and ignites the matchstick.
Let us look at an example. Consider a man pulling a crate up an inclined plane. He uses his muscular force to pull the crate up by holding a rope attached to it. He thus establishes contact with the rope in order to pull it.
Now, as the crate rests on the inclined plane, the plane exerts a normal reaction force on the crate in response to the weight exerted by the crate on the inclined plane. This is also a contact force. Additionally, the crate is also subject to a frictional force in a direction opposite to motion due to the contact between the crate and the inclined plane. Thus, frictional force is also a contact force.

Magnetic and Gravitational forces are non-contact forces that are able to exert a force even when there is a finite separation between two objects. For example, a magnet is able to pull an iron nail close to it even if they are not in physical contact with each other. A ball when dropped from a height falls down towards the earth due to the gravitational force acting on it.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Remember that forces due to gravity, and electric and magnetic fields fall under non-contact forces since they are able to initiate their action even when the bodies are not in physical contact with each other. This brings us to fictitious forces, such as the Centrifugal force, Euler force, and the Coriolis force, all of which fall under non-contact forces since they do not require any physical contact and are subjected throughout the volume of the body experiencing these forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




