
Which of the following is an example of aryl alkyl halide?
a.) P-chlorotoluene
b.) Chlorobenzene.
c.) Allyl chloride
d.) Benzyl chloride
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: Aryl group refers to the functional group attached to the aromatic ring of carbon, for example, toluene. An aryl alkyl halide is a compound that consists of an alkyl group (-R) and a halogen attached to an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step answer:
An aryl halide is formed when the hydrogen atom(s) bonded to the benzene ring are replaced by a halogen atom. This can happen by direct halogenation reaction. When a halogen reacts with benzene ring forming halogen benzene, as shown below:
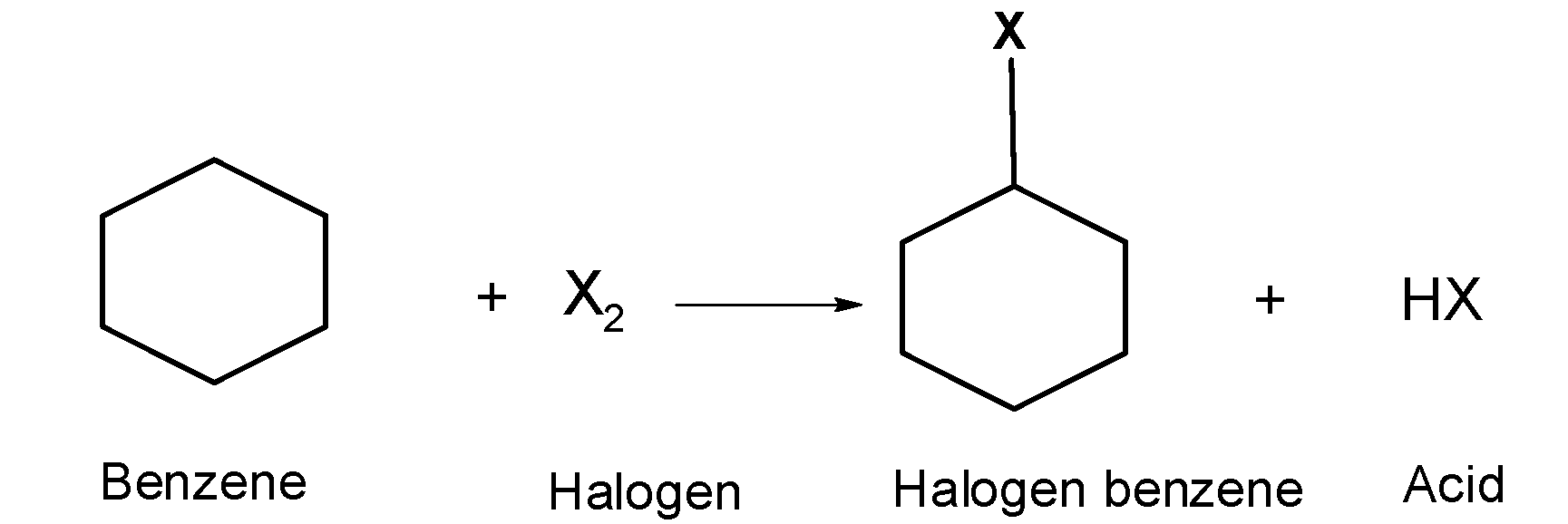
This reaction occurs in presence of sunlight or under high temperatures.
When an alkyl halide reacts with the aryl group, it forms an aryl alkyl halide.
Halogens are elements belonging to the halo family. These elements contain Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, and Iodine.
- If we look at the structure of P-chlorotoluene
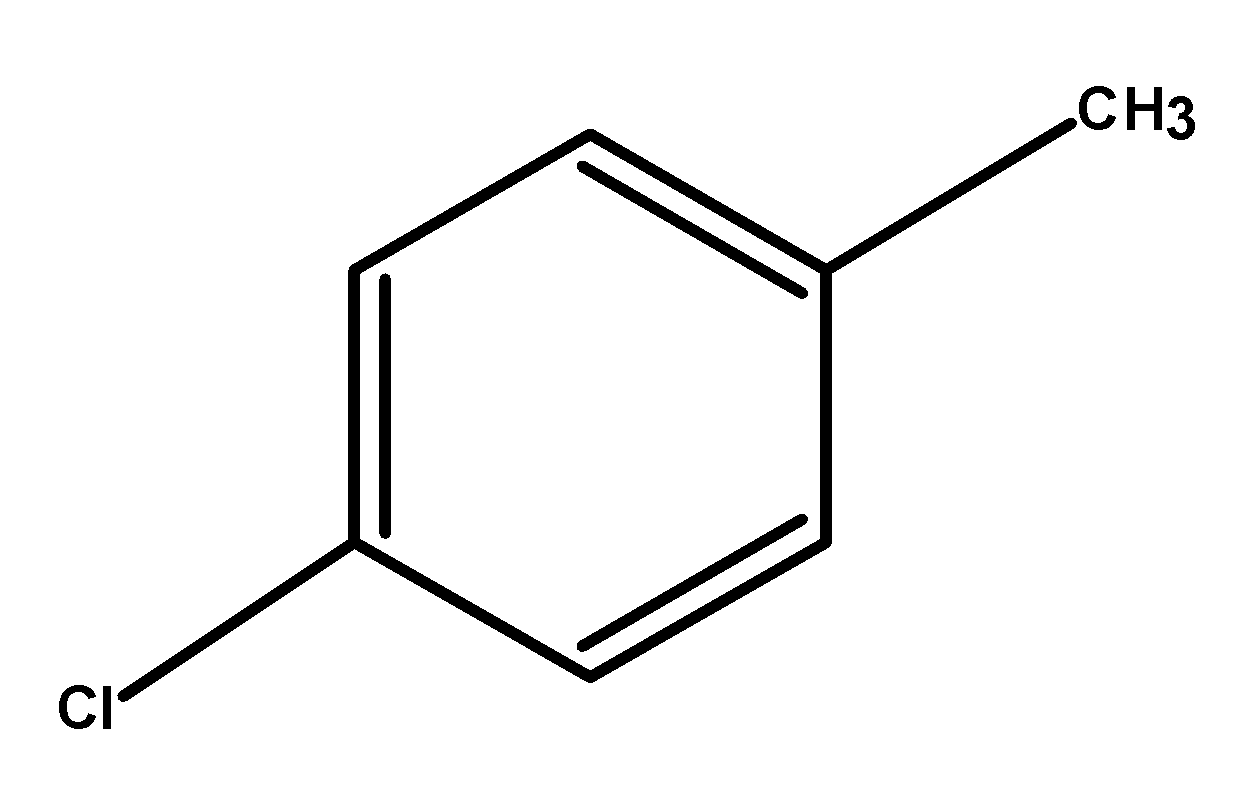
It does contain a halogen, an aryl group, and an alkyl group, but it cannot be called an aryl alkyl halide because no alkyl halide is present.
- Looking at the structure of chlorobenzene
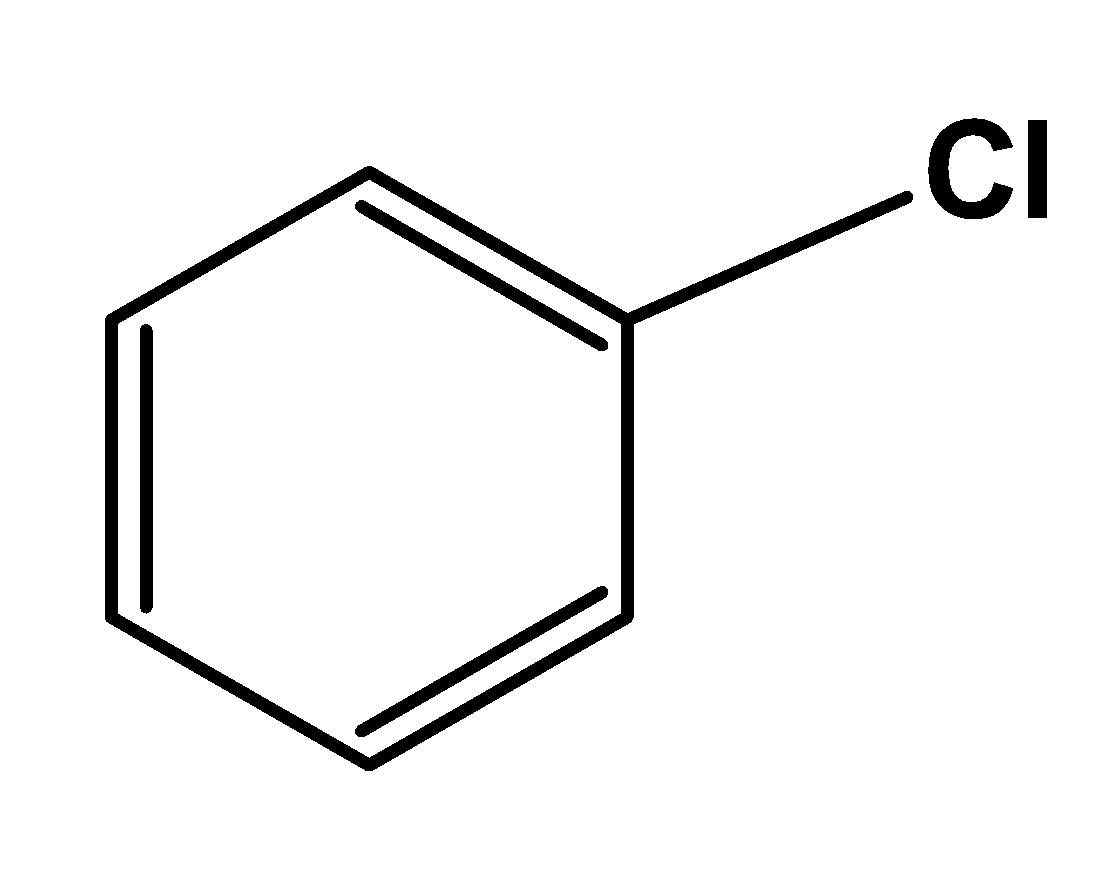
It does contain a halogen group and an aromatic ring, but it does not contain any alkyl group. Thus, it cannot be considered as an aryl alkyl halide.
- Now, if we look at the structure of allyl chloride
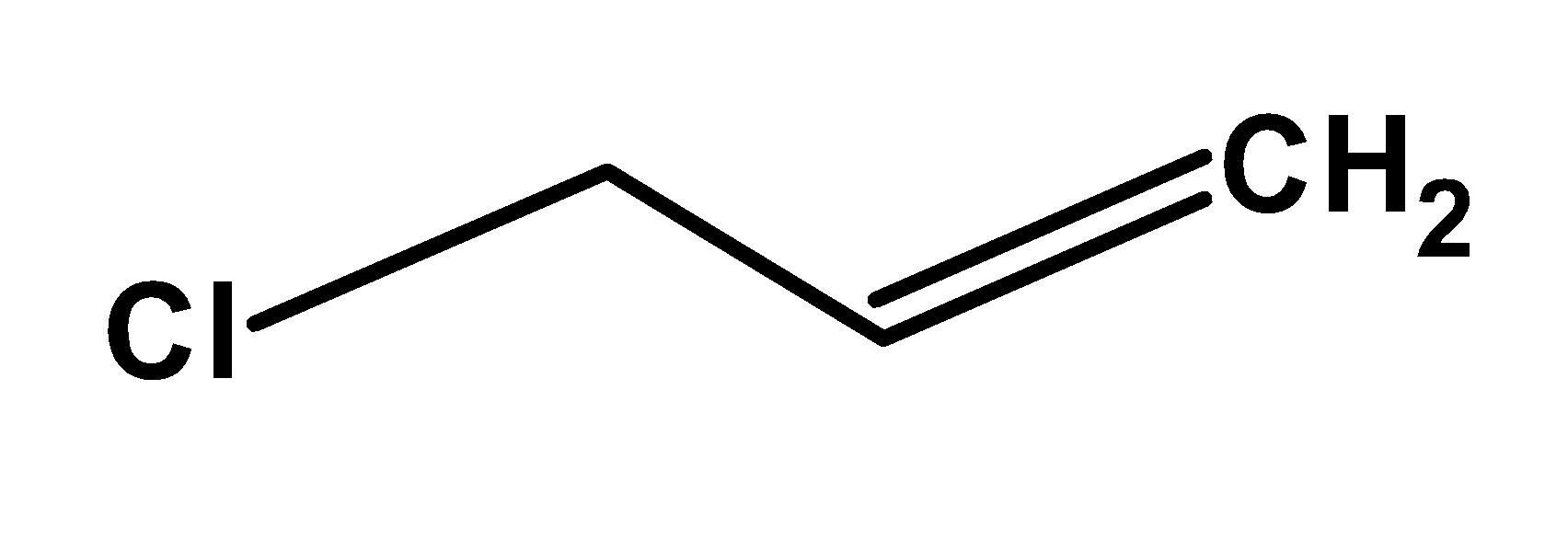
There are no alternate double bonds, which signifies that it is not an aromatic compound. Thus, it cannot be classified as an aryl alkyl halide.
In benzyl chloride,
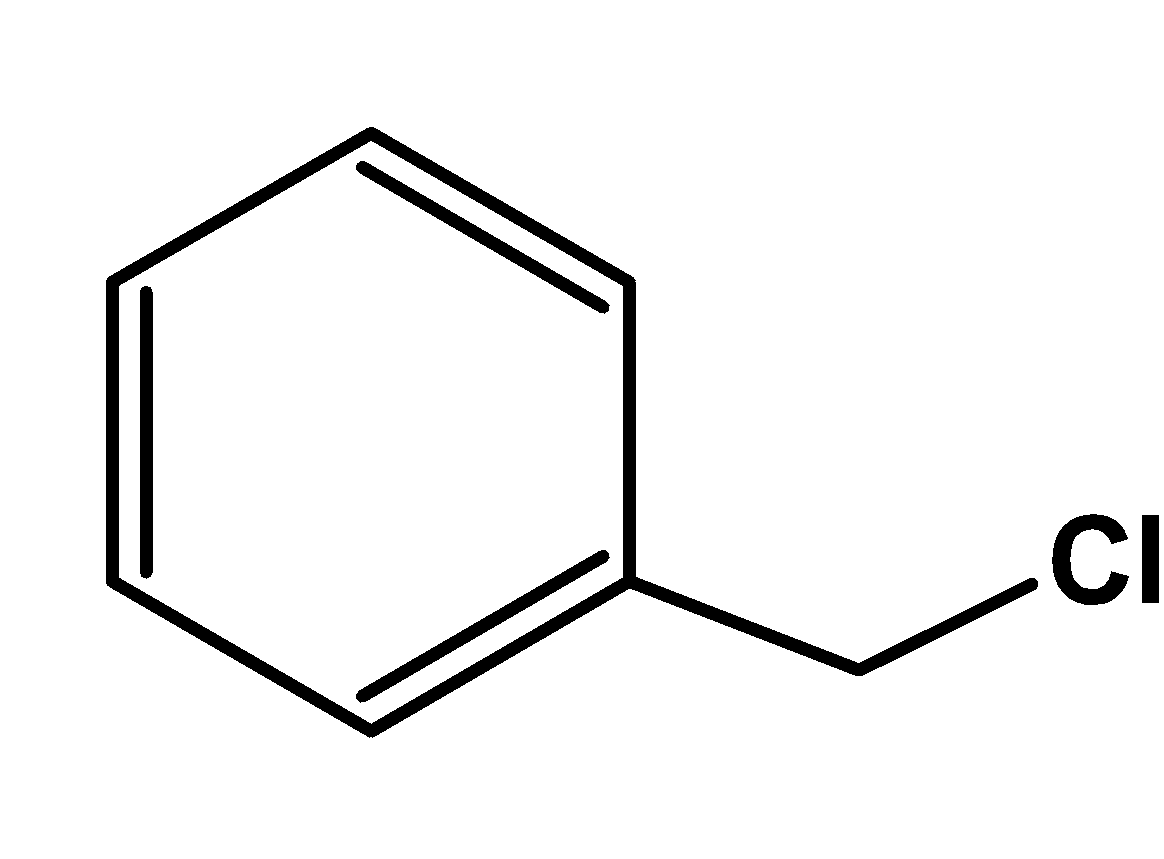
It consists of an aromatic ring and an alkyl halide group. Thus, it can be classified as an aryl alkyl halide.
Note: An alkyl halide means that the halogen group is attached to the Alkyl group. If the halogen group is attached directly to the aromatic ring then it will be called an aryl halide and not an aryl alkyl halide.
Complete step by step answer:
An aryl halide is formed when the hydrogen atom(s) bonded to the benzene ring are replaced by a halogen atom. This can happen by direct halogenation reaction. When a halogen reacts with benzene ring forming halogen benzene, as shown below:

This reaction occurs in presence of sunlight or under high temperatures.
When an alkyl halide reacts with the aryl group, it forms an aryl alkyl halide.
Halogens are elements belonging to the halo family. These elements contain Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, and Iodine.
- If we look at the structure of P-chlorotoluene

It does contain a halogen, an aryl group, and an alkyl group, but it cannot be called an aryl alkyl halide because no alkyl halide is present.
- Looking at the structure of chlorobenzene

It does contain a halogen group and an aromatic ring, but it does not contain any alkyl group. Thus, it cannot be considered as an aryl alkyl halide.
- Now, if we look at the structure of allyl chloride

There are no alternate double bonds, which signifies that it is not an aromatic compound. Thus, it cannot be classified as an aryl alkyl halide.
In benzyl chloride,

It consists of an aromatic ring and an alkyl halide group. Thus, it can be classified as an aryl alkyl halide.
Note: An alkyl halide means that the halogen group is attached to the Alkyl group. If the halogen group is attached directly to the aromatic ring then it will be called an aryl halide and not an aryl alkyl halide.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE

Find the foot of the perpendicular from point232to class 12 maths CBSE




