
Which of the following is a polar compound?
(A)- ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$
(B)- $CC{{l}_{4}}$
(C)- $HCl$
(D)- $C{{H}_{4}}$
Answer
567k+ views
Hint: The polar molecule can be determined from the molecular geometry and the resultant dipole moment of the bonds present in it, where the electronegativity difference governs its direction.
Complete Solution :
The nature of the molecule to be polar or nonpolar will be determined by the following two factors as follows:
- The shape of the molecule acquired from the VSEPR theory, will tell us about the symmetry of the molecule which includes the total sum of the dipole moments of all the bonds in the molecule.
Such that, all the dipoles in the molecule cancel out each other, making ${{\mu }_{net}}=0$ . Then the molecule is symmetric and non-polar in nature.
- The type of atoms attached to it also play a role in the symmetry of the molecule, as the electronegativity difference between the two atoms forming the bond will tell us about the direction of the dipole moment, which is toward the more electronegative atom or higher electron-density.
In the diatomic molecule, HCl in which the electronegativity difference is large, and the dipole is towards chlorine atom. Thus, the net dipole is not zero and the molecule is polar.
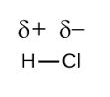
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
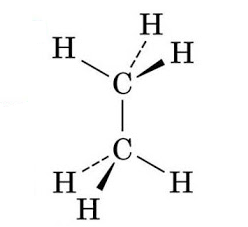
Note: So, now in the given molecule ethane, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ having both the carbon atoms in tetrahedral geometry, making it a symmetrical and a nonpolar molecule.
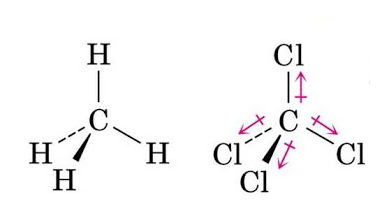
Similarly, in Methane, $C{{H}_{4}}$ having tetrahedral geometry, the dipole moments of the C-H bonds cancel out each other in the symmetric molecule, making it non-polar. And, in carbon-tetrachloride, $CC{{l}_{4}}$ having the chlorine atom being highly electronegative. The resultant dipole moment is again zero and the molecule is nonpolar.
Complete Solution :
The nature of the molecule to be polar or nonpolar will be determined by the following two factors as follows:
- The shape of the molecule acquired from the VSEPR theory, will tell us about the symmetry of the molecule which includes the total sum of the dipole moments of all the bonds in the molecule.
Such that, all the dipoles in the molecule cancel out each other, making ${{\mu }_{net}}=0$ . Then the molecule is symmetric and non-polar in nature.
- The type of atoms attached to it also play a role in the symmetry of the molecule, as the electronegativity difference between the two atoms forming the bond will tell us about the direction of the dipole moment, which is toward the more electronegative atom or higher electron-density.
In the diatomic molecule, HCl in which the electronegativity difference is large, and the dipole is towards chlorine atom. Thus, the net dipole is not zero and the molecule is polar.
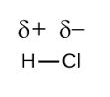
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: So, now in the given molecule ethane, ${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}$ having both the carbon atoms in tetrahedral geometry, making it a symmetrical and a nonpolar molecule.


Similarly, in Methane, $C{{H}_{4}}$ having tetrahedral geometry, the dipole moments of the C-H bonds cancel out each other in the symmetric molecule, making it non-polar. And, in carbon-tetrachloride, $CC{{l}_{4}}$ having the chlorine atom being highly electronegative. The resultant dipole moment is again zero and the molecule is nonpolar.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




