
Which of the following is a flowering plant with nodules containing filamentous nitrogen-fixing microorganism?
A. Cicer arietinum
B. Casuarina equisetifolia
C. Crotalaria juncea
D. Cycas revoluta
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: Nitrogen fixation is a mechanism that refers to the method in which the atmospheric nitrogen assimilates into the tissues of certain plants by some natural means such as a microorganism present in the soil.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen is a major component required by the plants for growth and metabolism, also a major source for the creation of chlorophyll. A major element of amino acid acts as a building block of proteins. Plants do not obtain nitrogen directly from the surrounding atmosphere. They get nitrogen from the soil where it already gets fixed by some microorganisms or bacteria present in the soil and these nitrogen-fixing bacteria such as rhizobium (symbiotic bacteria).
Nitrogen fixation is one of the methods through which these microorganisms fixed atmospheric nitrogen. Nitrogen fixation is a biochemical conversion in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into ammonia through an enzyme nitrogenase, a form utilized by the plants. As shown in the figure:
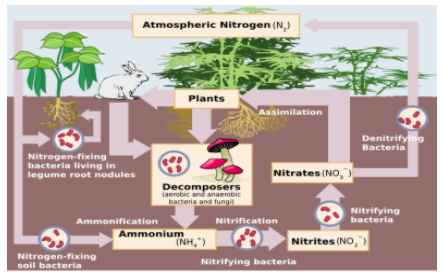
Casuarina equisetifolia is a pine tree that fixes its nitrogen through a root symbiotic association (i.e. function of nitrogen-fixing that lives in a symbiotic relationship with the host plants) with Frankia, a soil bacterium. Nodules are produced by the roots of Casuarina equisetifolia where bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen, which is a key element for the plant's growth and their metabolism.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Nitrogen fixation is done with the help of two types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria i.e. free-living bacteria (or non-symbiotic) and mutualistic (or symbiotic). Atmospheric Nitrogen is collected by microorganisms to form ammonia, nitrites, nitrates utilized by plants.
Complete answer:
Nitrogen is a major component required by the plants for growth and metabolism, also a major source for the creation of chlorophyll. A major element of amino acid acts as a building block of proteins. Plants do not obtain nitrogen directly from the surrounding atmosphere. They get nitrogen from the soil where it already gets fixed by some microorganisms or bacteria present in the soil and these nitrogen-fixing bacteria such as rhizobium (symbiotic bacteria).
Nitrogen fixation is one of the methods through which these microorganisms fixed atmospheric nitrogen. Nitrogen fixation is a biochemical conversion in which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into ammonia through an enzyme nitrogenase, a form utilized by the plants. As shown in the figure:

Casuarina equisetifolia is a pine tree that fixes its nitrogen through a root symbiotic association (i.e. function of nitrogen-fixing that lives in a symbiotic relationship with the host plants) with Frankia, a soil bacterium. Nodules are produced by the roots of Casuarina equisetifolia where bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen, which is a key element for the plant's growth and their metabolism.
Hence, the correct answer is option (B).
Note: Nitrogen fixation is done with the help of two types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria i.e. free-living bacteria (or non-symbiotic) and mutualistic (or symbiotic). Atmospheric Nitrogen is collected by microorganisms to form ammonia, nitrites, nitrates utilized by plants.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




