
Which of the following hydrogen will be the most acidic?

Answer
529.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we first need to know what is acidic hydrogen. The hydrogen atom of an atom that dissociates into a positive ion is known as acidic hydrogen.
\[R-H\rightleftharpoons {{R}^{-}}+{{H}^{+}}\]
Where R is an alkyl or an aryl group.
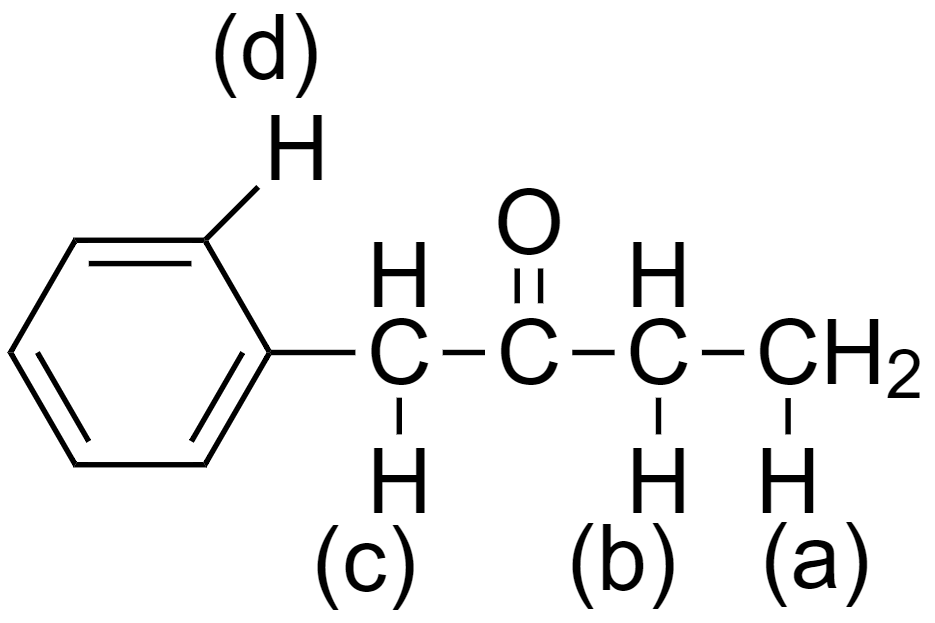
The molecule is 1-phenylbutan-2-one.
Complete answer:
The acidic nature depends on the ease of proton donation. And the ease of proton donation depends on the stability of the conjugate base.
So to determine which hydrogen is the most acidic, we have to compare the stability of the conjugate base or the carbanions formed when the acid dissociates into anion and cation (acidic hydrogen).
The carbanions formed when hydrogen is removed from (a), (b), (c), and (d) in 1-phenylbutan-2-one are as follows

Here we can see that there is no scope of delocalization in carbanion (a).
The carbanion (b) is in conjugation with the carbonyl (-C=O) functional group of the keto group.
The carbanion (c) is in resonance with both the benzene ring as well as the carbonyl (-C=O) functional group of the keto group.
The carbanion (d) is the least stable carbanion as removal of hydrogen from the benzene ring is extremely difficult.
So, we can say that the carbanion (c) is the most stable as it is the most conjugated among the four carbanions. Hence the conjugate base formed by this carbanion is the most stable, making the hydrogen (c) the most acidic.
So, hydrogen that will be the most acidic is option (c) hydrogen (c).
Note:
It should be noted that since stability is inversely proportional to reactivity, it means that the less reactive substance is more stable. We can also say that the strong acids have weak conjugate bases.
For example, since hydronium (${{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}$) is a strong acid, its corresponding conjugate base, that is water, is a stable yet weak base.
\[R-H\rightleftharpoons {{R}^{-}}+{{H}^{+}}\]
Where R is an alkyl or an aryl group.
The molecule is 1-phenylbutan-2-one.
Complete answer:
The acidic nature depends on the ease of proton donation. And the ease of proton donation depends on the stability of the conjugate base.
So to determine which hydrogen is the most acidic, we have to compare the stability of the conjugate base or the carbanions formed when the acid dissociates into anion and cation (acidic hydrogen).
The carbanions formed when hydrogen is removed from (a), (b), (c), and (d) in 1-phenylbutan-2-one are as follows

Here we can see that there is no scope of delocalization in carbanion (a).
The carbanion (b) is in conjugation with the carbonyl (-C=O) functional group of the keto group.
The carbanion (c) is in resonance with both the benzene ring as well as the carbonyl (-C=O) functional group of the keto group.
The carbanion (d) is the least stable carbanion as removal of hydrogen from the benzene ring is extremely difficult.
So, we can say that the carbanion (c) is the most stable as it is the most conjugated among the four carbanions. Hence the conjugate base formed by this carbanion is the most stable, making the hydrogen (c) the most acidic.
So, hydrogen that will be the most acidic is option (c) hydrogen (c).
Note:
It should be noted that since stability is inversely proportional to reactivity, it means that the less reactive substance is more stable. We can also say that the strong acids have weak conjugate bases.
For example, since hydronium (${{H}_{3}}{{O}^{+}}$) is a strong acid, its corresponding conjugate base, that is water, is a stable yet weak base.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




