
Which of the following hydrocarbons will give substitution reactions and why?
\[C{H_4},{C_3}{H_6},{C_3}{H_8},{C_4}{H_6},{C_5}{H_{12}},{C_5}{H_{10}}\]
Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: If the compound contains carbon and hydrogen atoms, such a type of compound is known as hydrocarbons. Fuels, natural gas etc are examples of hydrocarbons. And these are in two types which are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. And the substitution reaction is mainly in two types, that is, \[{S_N}1\] reaction and \[{S_N}2\] reaction.
Complete answer:
Among the given compounds, \[C{H_4},{C_3}{H_8}\] and \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\] undergo substitution reactions. Because, these three compounds are saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes and it contains only single bonds. The substitution reactions only take place in saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes.
For example, substitution reaction, here we take methane and it is reacted with chlorine gas. And the chlorine gas breaks and there is a formation of two radicals and they act as strong nucleophiles. This chlorine atom will break the carbon- hydrogen bond present in methane and the hydrogen is replaced by one chlorine atom and there is a formation of methyl chloride and HCl. Let’s see the reaction,
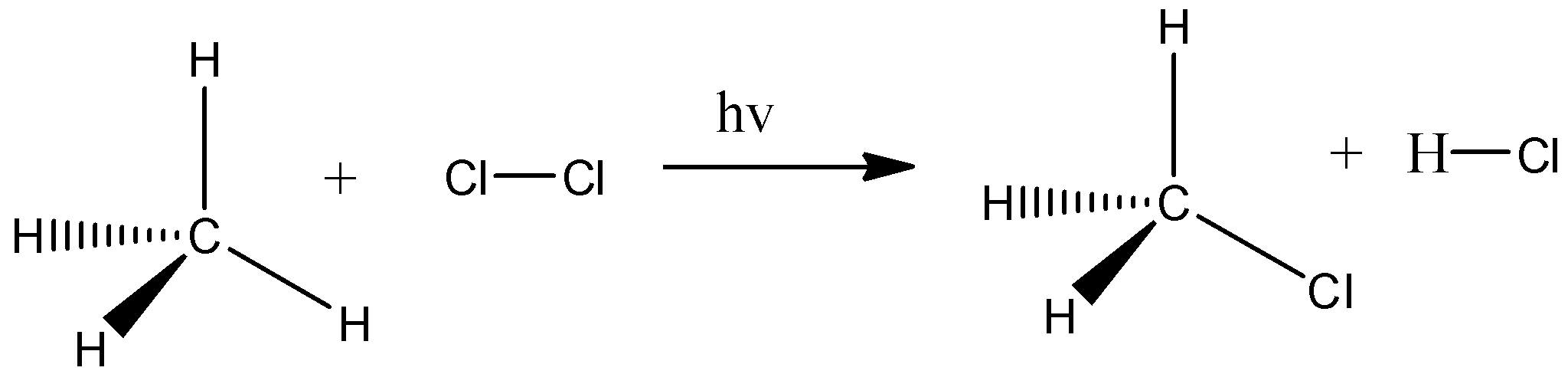
Similarly in\[{C_3}{H_8}\]and \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\] also takes place the substitution reaction.
Note:
We have to know that the substitution reaction is also called a single substitution reaction and here, the functional group which is present in the compound is replaced by another functional group. And these are in two types that is nucleophilic substitution reaction and electrophilic substitution reaction. In nucleophilic substitution reaction, the nucleophile is act as a leaving group and this reaction is mainly divided into two which is unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, \[({S_N}1)\] and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, \[({S_N}2)\].
Complete answer:
Among the given compounds, \[C{H_4},{C_3}{H_8}\] and \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\] undergo substitution reactions. Because, these three compounds are saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes and it contains only single bonds. The substitution reactions only take place in saturated hydrocarbons or alkanes.
For example, substitution reaction, here we take methane and it is reacted with chlorine gas. And the chlorine gas breaks and there is a formation of two radicals and they act as strong nucleophiles. This chlorine atom will break the carbon- hydrogen bond present in methane and the hydrogen is replaced by one chlorine atom and there is a formation of methyl chloride and HCl. Let’s see the reaction,

Similarly in\[{C_3}{H_8}\]and \[{C_5}{H_{12}}\] also takes place the substitution reaction.
Note:
We have to know that the substitution reaction is also called a single substitution reaction and here, the functional group which is present in the compound is replaced by another functional group. And these are in two types that is nucleophilic substitution reaction and electrophilic substitution reaction. In nucleophilic substitution reaction, the nucleophile is act as a leaving group and this reaction is mainly divided into two which is unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, \[({S_N}1)\] and bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, \[({S_N}2)\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




