
Which of the following ${\text{H}}$ can be easily removed for the process of bromination in presence of light?
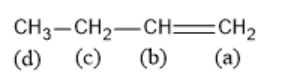
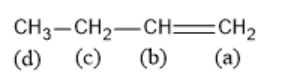
Answer
512.7k+ views
Hint :To solve this question, we have to find which radical will be more stable after removing the hydrogen atom. Note that free radicals are stabilized n=by resonance. The benzylic radical and allylic radical are stabilized by resonance.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question, we should know the factors that stabilize free radicals. Electron poor species are stabilized by their neighboring atoms which can donate electron density. This means that increasing the number of alkyl groups on the carbon atom bearing the free radical will increase its stability. So, a tertiary radical is more stable than a secondary radical which is more stable than a primary radical. Free radicals are also stabilized by delocalization. In the given compound, when the hydrogen is removed from carbon c, the resulting free radical will be stabilized by both resonance and $ + {\text{I}}$ effect.
Therefore, for the process of bromination in presence of light, hydrogen should be removed from position c.
Note :
Remember that any factor which makes the electron deficient site being delocalized over a large area will also stabilize electron poor species. For example, the positive charge of a carbocation is stabilized when it is adjacent to a pi bond. Because the carbocation is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and it bears an empty p orbital which allows overlap with adjacent p orbitals, thus leading the positive charge to be delocalized over multiple carbons, showing electron deficient sites can be stabilized by resonance.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To solve this question, we should know the factors that stabilize free radicals. Electron poor species are stabilized by their neighboring atoms which can donate electron density. This means that increasing the number of alkyl groups on the carbon atom bearing the free radical will increase its stability. So, a tertiary radical is more stable than a secondary radical which is more stable than a primary radical. Free radicals are also stabilized by delocalization. In the given compound, when the hydrogen is removed from carbon c, the resulting free radical will be stabilized by both resonance and $ + {\text{I}}$ effect.
Therefore, for the process of bromination in presence of light, hydrogen should be removed from position c.
Note :
Remember that any factor which makes the electron deficient site being delocalized over a large area will also stabilize electron poor species. For example, the positive charge of a carbocation is stabilized when it is adjacent to a pi bond. Because the carbocation is $s{p^2}$ hybridized and it bears an empty p orbital which allows overlap with adjacent p orbitals, thus leading the positive charge to be delocalized over multiple carbons, showing electron deficient sites can be stabilized by resonance.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




