
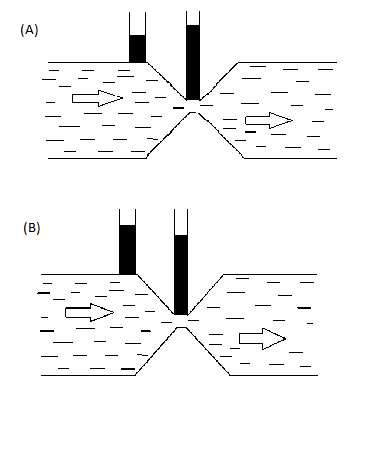
Which of the following figures shown below is correct regarding the steady flow of a non-viscous liquid?


Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint:We know that fluids that have no resistance to internal friction are referred to as nonviscous fluid. This fluid is incompressible i.e. the density remains constant. Apply the continuity equation to study the above figure for steady non viscous fluid.
Complete solution:
A steady flow is the type of the flow where the motion of the fluid remains constant with time.
We know that for a steady flow even if the fluid is incompressible, the density of the flow remains constant. This gives the continuity equation:
$Av = $Constant
Where $A$ is the area of cross section and $v$ is the velocity of flow.
This equation states that a fluid in motion must move in such a way that mass is conserved. Continuity equation is applicable in all types of fluid.
Now let's all the above figures to choose the correct figure of steady non viscous fluid.
As per continuity equation, $Av = $constant
Where $A$ is the area of cross section and $v$ is the velocity of flow.
When the area of the cross section is more, velocity of the flow will be less and vice versa is true. In the above figure, the flow of velocity is more in the constricted portion and the rise in the tube is more as compared to the tube rise in the wider section. By Bernoulli's theorem:
$P = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} = $Constant
Where, $P$ is the pressure
$\rho $ is the density of fluid
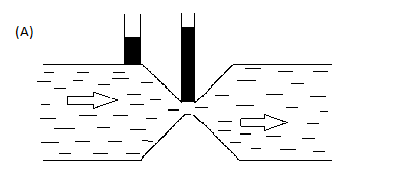
Therefore figure (A) is a correct figure of steady non viscous flow.
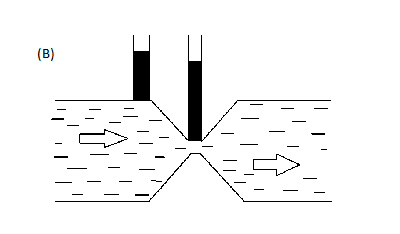 Figure (B) is not the correct figure as the capillary rise is more in a wider section than the narrow section hence continuity equation is not followed.
Figure (B) is not the correct figure as the capillary rise is more in a wider section than the narrow section hence continuity equation is not followed.
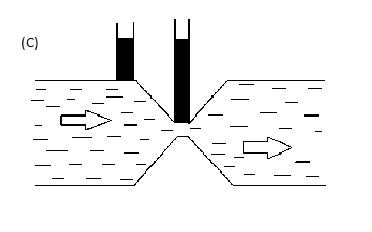
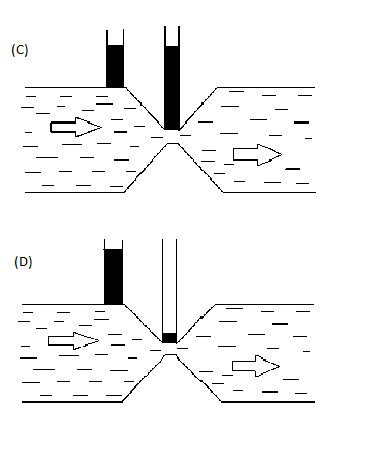
Similarly Figure (C) is incorrect as the rise is similar in both the tubes which defy continuity equation.
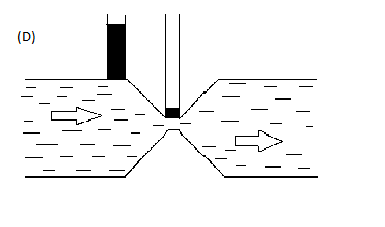 The above figure (D) is also not a correct steady non viscous flow, as the tube rise should be more in a constricted area rather than wider section as per the continuity equation.
The above figure (D) is also not a correct steady non viscous flow, as the tube rise should be more in a constricted area rather than wider section as per the continuity equation.
Note: Continuity equation is one of the conservation laws which is applied for fluid.
It works on the principle of conservation of mass and it reflects that mass is conserved in any non-nuclear continuum mechanics analysis.
Complete solution:
A steady flow is the type of the flow where the motion of the fluid remains constant with time.
We know that for a steady flow even if the fluid is incompressible, the density of the flow remains constant. This gives the continuity equation:
$Av = $Constant
Where $A$ is the area of cross section and $v$ is the velocity of flow.
This equation states that a fluid in motion must move in such a way that mass is conserved. Continuity equation is applicable in all types of fluid.
Now let's all the above figures to choose the correct figure of steady non viscous fluid.

As per continuity equation, $Av = $constant
Where $A$ is the area of cross section and $v$ is the velocity of flow.
When the area of the cross section is more, velocity of the flow will be less and vice versa is true. In the above figure, the flow of velocity is more in the constricted portion and the rise in the tube is more as compared to the tube rise in the wider section. By Bernoulli's theorem:
$P = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} = $Constant
Where, $P$ is the pressure
$\rho $ is the density of fluid
Therefore figure (A) is a correct figure of steady non viscous flow.


Similarly Figure (C) is incorrect as the rise is similar in both the tubes which defy continuity equation.

Note: Continuity equation is one of the conservation laws which is applied for fluid.
It works on the principle of conservation of mass and it reflects that mass is conserved in any non-nuclear continuum mechanics analysis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




