
Which of the following elements forms amphoteric oxides?
(A) Beryllium
(B) Aluminium
(C) Zinc
(D) All
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Amphoteric molecules are those which can act as both acids and bases. This means that molecules will be able to donate and accept \[{H^ + }\]. The common product of amphoteric molecules is salt and water.
Complete Solution :
What is Amphoteric? Any molecule or ion which can donate \[{H^ + }\] ions as well as accept \[{H^ + }\] ions are known as amphoteric. This means that the molecule or ion can act as both acid and base. Amphoteric can also be called as amphiprotic. Amphoterism means the molecule will act as acid in presence of basic solution and as base in presence of acidic solution. This was based on Bronsted- Lowry theory.
- Bronsted- Lowry theory is the fundamental of acid-base theory. In this theory they said that when acid and base combine with each other, acid will form conjugate base and base will form conjugate acids by exchange of \[{H^ + }\] ions. This is given by
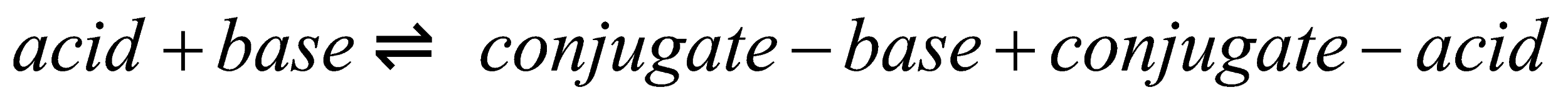
- Water is the best example for amphoteric substance. Water will act as proton donor and it forms hydronium ion \[({H_3}{O^ + })\] in the presence of hydrochloric acid. While in presence of ammonia, water will donate the proton to form hydroxide ion
\[{H_2}O + HCl{H_3}{O^ + } + C{l^ - }\]
\[{H_2}O + N{H_3}O{H^ - } + NH_4^ + \]
- Some metals oxides which react with acid and base to produce respective salt and water are called amphoteric oxides.
Metal oxides such as Zinc, aluminium, copper, beryllium, tin, lead form amphoteric oxides and hydroxides. This formation of amphoteric oxide is based on the oxidation state of the metal oxides. Amphoteric oxide i.e. ZnO reacts with HCl and NaOH to form water and salts.
\[ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) \to ZnC{l_2}(aq) + {H_2}O(l)\]
\[ZnO(s) + 2NaOH(aq) \to N{a_2}Zn{O_2}(aq) + {H_2}O(l)\]
Since all the three-element aluminium, zinc and beryllium forms amphoteric oxides.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
Bronsted-Lowry theory is the proton theory of acid and base. This theory was introduced in the year 1923 by two chemists namely Johannes Nicholas Bronsted and Thomas Martin Lowry. According to his theory any substance which can donate \[{H^ + }\] ions are called acids and any substance which can accept \[{H^ + }\] ions are called bases.
Note: Amino acid is also a good example of amphoteric substance. Amino acid group contains both acid as well as base group i.e. it has both \[ - N{H_3}\] and \[ - COOH\] groups. Here \[ - N{H_3}\] is the base group and \[ - COOH\] group is the acid group.
Complete Solution :
What is Amphoteric? Any molecule or ion which can donate \[{H^ + }\] ions as well as accept \[{H^ + }\] ions are known as amphoteric. This means that the molecule or ion can act as both acid and base. Amphoteric can also be called as amphiprotic. Amphoterism means the molecule will act as acid in presence of basic solution and as base in presence of acidic solution. This was based on Bronsted- Lowry theory.
- Bronsted- Lowry theory is the fundamental of acid-base theory. In this theory they said that when acid and base combine with each other, acid will form conjugate base and base will form conjugate acids by exchange of \[{H^ + }\] ions. This is given by
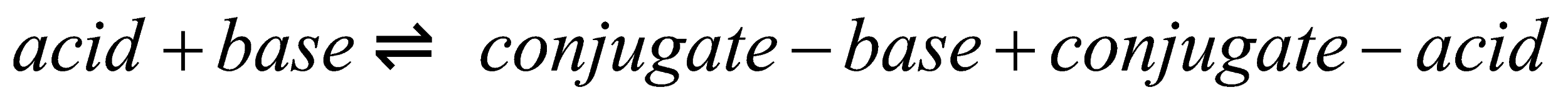
- Water is the best example for amphoteric substance. Water will act as proton donor and it forms hydronium ion \[({H_3}{O^ + })\] in the presence of hydrochloric acid. While in presence of ammonia, water will donate the proton to form hydroxide ion
\[{H_2}O + HCl{H_3}{O^ + } + C{l^ - }\]
\[{H_2}O + N{H_3}O{H^ - } + NH_4^ + \]
- Some metals oxides which react with acid and base to produce respective salt and water are called amphoteric oxides.
Metal oxides such as Zinc, aluminium, copper, beryllium, tin, lead form amphoteric oxides and hydroxides. This formation of amphoteric oxide is based on the oxidation state of the metal oxides. Amphoteric oxide i.e. ZnO reacts with HCl and NaOH to form water and salts.
\[ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) \to ZnC{l_2}(aq) + {H_2}O(l)\]
\[ZnO(s) + 2NaOH(aq) \to N{a_2}Zn{O_2}(aq) + {H_2}O(l)\]
Since all the three-element aluminium, zinc and beryllium forms amphoteric oxides.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
Bronsted-Lowry theory is the proton theory of acid and base. This theory was introduced in the year 1923 by two chemists namely Johannes Nicholas Bronsted and Thomas Martin Lowry. According to his theory any substance which can donate \[{H^ + }\] ions are called acids and any substance which can accept \[{H^ + }\] ions are called bases.
Note: Amino acid is also a good example of amphoteric substance. Amino acid group contains both acid as well as base group i.e. it has both \[ - N{H_3}\] and \[ - COOH\] groups. Here \[ - N{H_3}\] is the base group and \[ - COOH\] group is the acid group.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




