
Which of the following diarthrotic joints allows for the greatest degree of movement?
A. Ball and socket
B. Pivot
C. Hinge
D. Gliding
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the body which links the skeletal system into a functional whole.
They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement.
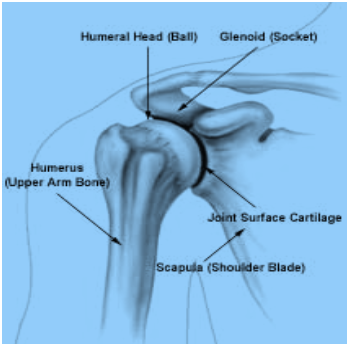
Complete answer: The ball and socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center.
The multiaxial ball and socket joints allow for flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, and circumduction. In addition, these also allow for medial (internal) and lateral (external) rotation.
Ball-and-socket joints have the greatest range of motion of all synovial joints.
Additional information: 1. A pivot joint is a synovial joint in which the ends of two bones meet one end being a central bony cylinder, the other end being a ring (or ring-like structure) made of bone and ligament.
In some joints, the cylinder rotates inside the ring.
In other joints, the ring rotates around the cylinder.
The pivot joint is also called the rotary joint or trochoid joint. It is a freely moveable joint (diarthrosis) that allows only rotary movement around a single axis.
The moving bone rotates within a ring that is formed from a second bone and adjoining ligament.
2. A hinge joint is a common class of synovial joint that includes the ankle, elbow, and knee joints. Hinge joints are formed between two or more bones where the bones can only move along one axis to flex or extend.
Hinge joints are those that allow movement along one plane.
They facilitate bending and straightening actions, such as flexing a finger.
In a hinge joint, protective cartilage covers the bones, and a thick gel called synovial fluid lubricates them, allowing them to move without rubbing against one another.
3. A gliding joint, also known as a plane joint or planar joint, is a common type of synovial joint formed between bones that meet at flat or nearly flat articular surfaces.
Gliding movements occur as relatively flat bone surfaces move past each other.
They produce very little rotational or angular movement of the bones.
The joints of the carpal and tarsal bones are examples of joints that produce gliding movements.
So, the answer is A. Ball and socket joint
Note: A freely mobile joint is classified as a diarthrosis.
Freely mobile joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion.
They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement.
Complete answer: The ball and socket joint (or spheroid joint) is a type of synovial joint in which the ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone. The distal bone is capable of motion around an indefinite number of axes, which have one common center.
The multiaxial ball and socket joints allow for flexion-extension, abduction-adduction, and circumduction. In addition, these also allow for medial (internal) and lateral (external) rotation.
Ball-and-socket joints have the greatest range of motion of all synovial joints.

Additional information: 1. A pivot joint is a synovial joint in which the ends of two bones meet one end being a central bony cylinder, the other end being a ring (or ring-like structure) made of bone and ligament.
In some joints, the cylinder rotates inside the ring.
In other joints, the ring rotates around the cylinder.
The pivot joint is also called the rotary joint or trochoid joint. It is a freely moveable joint (diarthrosis) that allows only rotary movement around a single axis.
The moving bone rotates within a ring that is formed from a second bone and adjoining ligament.
2. A hinge joint is a common class of synovial joint that includes the ankle, elbow, and knee joints. Hinge joints are formed between two or more bones where the bones can only move along one axis to flex or extend.
Hinge joints are those that allow movement along one plane.
They facilitate bending and straightening actions, such as flexing a finger.
In a hinge joint, protective cartilage covers the bones, and a thick gel called synovial fluid lubricates them, allowing them to move without rubbing against one another.
3. A gliding joint, also known as a plane joint or planar joint, is a common type of synovial joint formed between bones that meet at flat or nearly flat articular surfaces.
Gliding movements occur as relatively flat bone surfaces move past each other.
They produce very little rotational or angular movement of the bones.
The joints of the carpal and tarsal bones are examples of joints that produce gliding movements.
So, the answer is A. Ball and socket joint
Note: A freely mobile joint is classified as a diarthrosis.
Freely mobile joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




