
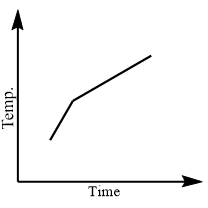
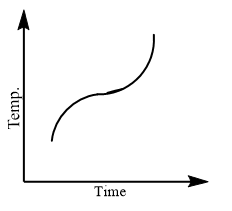
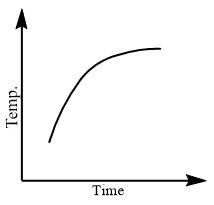
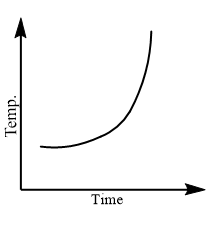
Which of the following curves would be obtained on heating solid naphthalene to a temperature which is above its melting point?
a.
b.
c.
d.




Answer
460.8k+ views
Hint: Naphthalene is the organic substance whose molecular formula is ${C_{10}}{H_8}$ . Naphthalene is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon. It is a white crystalline solid and has a characteristic odour which is observable at concentrations as low as $0.08$ ppm by mass.
Complete answer:
Naphthalene consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. Rings fused if they share two or more atoms. It is also known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. It is categorized as a benzenoid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). There are eight carbons that are not shared by the two rings carrying one hydrogen atom each. The molecule of naphthalene is planar like that of benzene but unlike benzene the carbon-carbon bonds in naphthalene are not of same length.
When naphthalene reaches the temperature just as it in solid form starts to melt, it stays at that temperature until all the solid melts to liquid state. To overcome the intermolecular forces, all thermal energy is used. When the temperature is plateaued then naphthalene exists in solid and liquid state. When all the solid converts into liquid, the temperature begins to rise until it reaches its boiling point.
Thus, option $\left( a \right)$ is correct.
Note:
By using cross-conjugation theorem, we can describe that naphthalene as an aromatic benzene unit bonded to a diene but it is not extensively conjugated to it at least in the ground state. Due to the resonance, there is bilateral symmetry in the molecule across the plane of the shared carbon pair as well as across the plane that bisects bonds.
Complete answer:
Naphthalene consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. Rings fused if they share two or more atoms. It is also known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. It is categorized as a benzenoid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH). There are eight carbons that are not shared by the two rings carrying one hydrogen atom each. The molecule of naphthalene is planar like that of benzene but unlike benzene the carbon-carbon bonds in naphthalene are not of same length.
When naphthalene reaches the temperature just as it in solid form starts to melt, it stays at that temperature until all the solid melts to liquid state. To overcome the intermolecular forces, all thermal energy is used. When the temperature is plateaued then naphthalene exists in solid and liquid state. When all the solid converts into liquid, the temperature begins to rise until it reaches its boiling point.
Thus, option $\left( a \right)$ is correct.
Note:
By using cross-conjugation theorem, we can describe that naphthalene as an aromatic benzene unit bonded to a diene but it is not extensively conjugated to it at least in the ground state. Due to the resonance, there is bilateral symmetry in the molecule across the plane of the shared carbon pair as well as across the plane that bisects bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




