
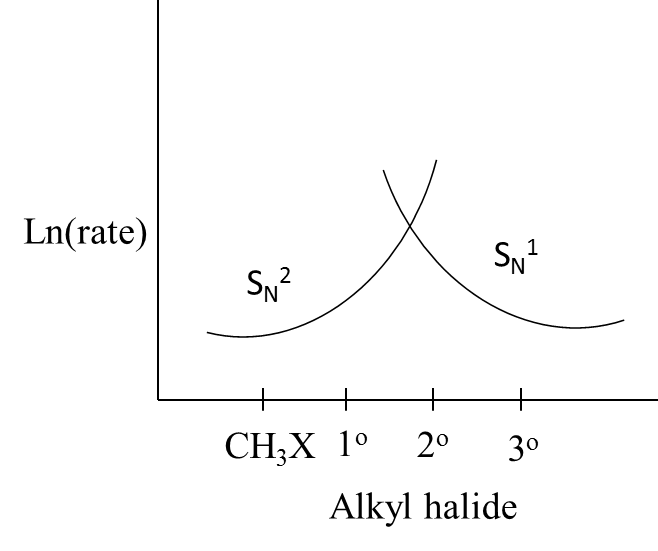
Which of the following curve correctly represents ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ and ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ ?
A.
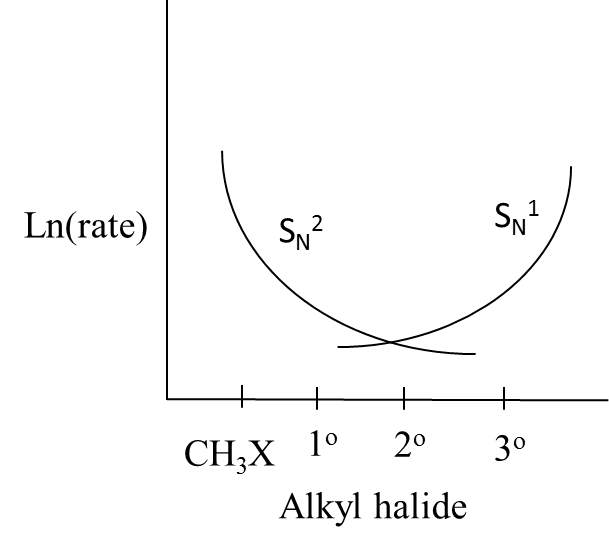
B.


Answer
548.7k+ views
Hint: SN means nucleophilic substitution reaction. Nucleophilic substitution reactions are two types. They are ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ and ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ . ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ is called unimolecular substitution reaction and ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ is called bi-molecular nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that which curves correctly explains the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ and ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reactions.
- We know that in unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions the rate of the reaction is going to depend on the concentration of the one molecule only.
- But in the case of a bi-molecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of the reaction is going to depend on the concentration of the two reactants which are involved in the reaction.
- We can say that the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ is high when the reactant contains tertiary alkyl halides.
- The order of increasing the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ reaction in case of alkyl halides is as follows.
\[C{{H}_{3}}X<{{1}^{o}}<{{2}^{o}}<{{3}^{o}}\]
- Means the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ reaction occurs easily in tertiary alkyl halides compared to simple and primary alkyl halides.
- Coming to the case of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction, the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ is high when the reactant contains primary alkyl halides.
- We can say that the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ is high when the reactant contains simple and primary alkyl halides as the reactant.
- The order of decreasing the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction in case of alkyl halides is as follows
\[C{{H}_{3}}X>{{1}^{o}}>{{2}^{o}}>{{3}^{o}}\]
- Therefore we can say that the curves in option B exactly suit the above explanation.
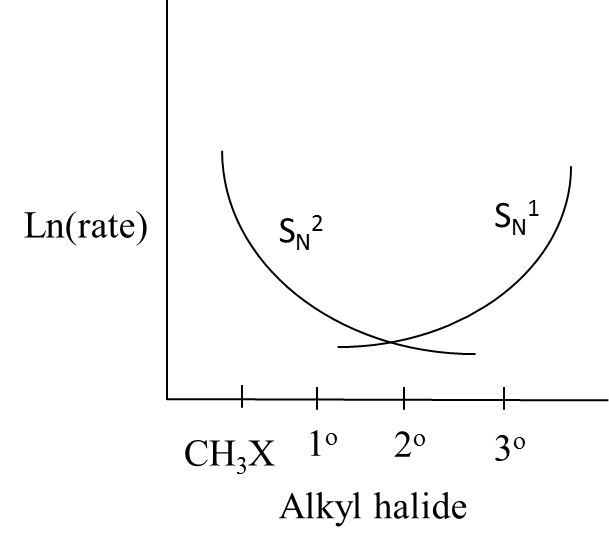
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The rate of the nucleophilic substitution reactions depends on the type of alkyl halides involved in the reaction. The reaction is going to be initiated by the nucleophile that is why the reaction is called nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the question it is given that which curves correctly explains the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ and ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reactions.
- We know that in unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions the rate of the reaction is going to depend on the concentration of the one molecule only.
- But in the case of a bi-molecular nucleophilic substitution reaction, the rate of the reaction is going to depend on the concentration of the two reactants which are involved in the reaction.
- We can say that the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ is high when the reactant contains tertiary alkyl halides.
- The order of increasing the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ reaction in case of alkyl halides is as follows.
\[C{{H}_{3}}X<{{1}^{o}}<{{2}^{o}}<{{3}^{o}}\]
- Means the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{1}$ reaction occurs easily in tertiary alkyl halides compared to simple and primary alkyl halides.
- Coming to the case of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction, the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ is high when the reactant contains primary alkyl halides.
- We can say that the rate of the ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ is high when the reactant contains simple and primary alkyl halides as the reactant.
- The order of decreasing the rate of ${{\text{S}}_{\text{N}}}\text{2}$ reaction in case of alkyl halides is as follows
\[C{{H}_{3}}X>{{1}^{o}}>{{2}^{o}}>{{3}^{o}}\]
- Therefore we can say that the curves in option B exactly suit the above explanation.

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The rate of the nucleophilic substitution reactions depends on the type of alkyl halides involved in the reaction. The reaction is going to be initiated by the nucleophile that is why the reaction is called nucleophilic substitution reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




