
Which of the following compounds show the strongest hydrogen bonding?
(A)- HF
(B)- ${{H}_{2}}O$
(C)- \[N{{H}_{3}}\]
(D)- $C{{H}_{3}}OH$
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The hydrogen bond is one of the strongest intermolecular attractions, but is weaker than a covalent or ionic bond. The greater the electronegativity of the atom attached to the hydrogen, the greater will be the strength of the hydrogen bond with another molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
-Hydrogen bonds are the result of the dipole-dipole attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as Nitrogen, Oxygen, of Fluorine atom.
-Hydrogen bonding is represented by dotted lines as recommended by the IUPAC.
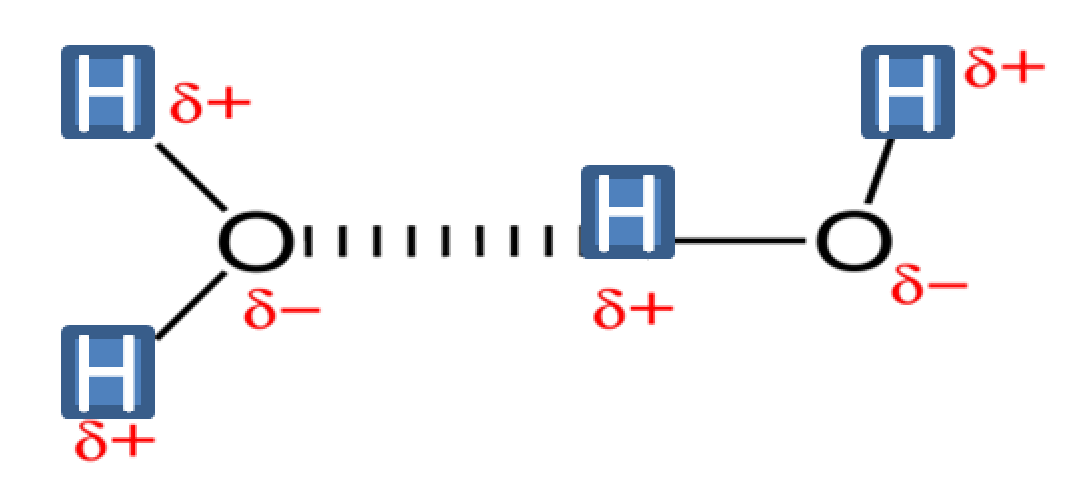
-Depending on the nature of the donor and acceptor atoms constituting the bond, hydrogen bond strengths range between 4kJ to 59kJ per mole of hydrogen bonds. This is what makes hydrogen bonding stronger than vanderwaal interactions and weaker than pure covalent or ionic bonds.
-Hydrogen bonds can be either occurring between separate molecules, i.e intermolecular or occurring among parts of the same molecule, i.e intramolecular.
-The larger the difference of electronegativity between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom will lead to a highly polar covalent bond.
-Because of the difference in electronegativity, the hydrogen gets a large partial positive charge and the electronegative atom attached bears a large partial negative charge.
-The electronegativity of Fluorine, Oxygen, and Nitrogen are 4.1, 3.5, and 3.0 respectively. Hence, fluorine bearing the higher value of electronegativity will form the strongest bond with the hydrogen atom of another molecule. So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Hydrogen bonding occurs in many inorganic molecules like DNA and proteins. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for exhibiting anomalous physical and chemical properties of compounds of N, O, and F. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water while intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids.
Complete step by step answer:
-Hydrogen bonds are the result of the dipole-dipole attraction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as Nitrogen, Oxygen, of Fluorine atom.
-Hydrogen bonding is represented by dotted lines as recommended by the IUPAC.

-Depending on the nature of the donor and acceptor atoms constituting the bond, hydrogen bond strengths range between 4kJ to 59kJ per mole of hydrogen bonds. This is what makes hydrogen bonding stronger than vanderwaal interactions and weaker than pure covalent or ionic bonds.
-Hydrogen bonds can be either occurring between separate molecules, i.e intermolecular or occurring among parts of the same molecule, i.e intramolecular.
-The larger the difference of electronegativity between the hydrogen atom and the electronegative atom will lead to a highly polar covalent bond.
-Because of the difference in electronegativity, the hydrogen gets a large partial positive charge and the electronegative atom attached bears a large partial negative charge.
-The electronegativity of Fluorine, Oxygen, and Nitrogen are 4.1, 3.5, and 3.0 respectively. Hence, fluorine bearing the higher value of electronegativity will form the strongest bond with the hydrogen atom of another molecule. So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Hydrogen bonding occurs in many inorganic molecules like DNA and proteins. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for exhibiting anomalous physical and chemical properties of compounds of N, O, and F. Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water while intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




