
Which of the following compounds is aromatic?
A.
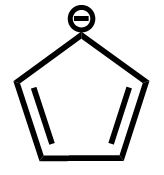
B.
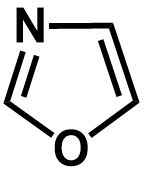
C.

D.
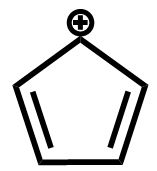




Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: Aromaticity can be determined by calculating the number of \[\pi \] electrons being delocalized in the structure and then using Huckel’s rule of aromatic compounds. The Huckel’s rule states a set of rules or parameters that must be fulfilled by an organic compound in order to be called aromatic.
Complete step by step answer:
The Huckel’s rule of aromaticity states that:
A compound is aromatic only if it contains cyclic and continuous delocalization or conjugation of \[\pi \] electrons.
The compound must be planar which means that all the carbon atoms must lie in a single plane.
The organic compound must contain \[4n + 2\] number of \[\pi \] electrons where the value of \[n\] can be any whole number.
If all these three conditions stated above are not fulfilled then the compound is not aromatic.
The first compound contains a total of four electrons which does not satisfy the \[4n + 2\] condition and is therefore not an aromatic compound.
The second compound contains a total of six electrons being delocalized in a planar ring, which makes it an aromatic compound.
The third compound has two electrons but one of the three carbon is not part of the cyclic conjugation, therefore it’s not an aromatic compound.
The fourth compound contains a total of six electrons being delocalized in a planar ring, which makes it an aromatic compound.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence, the second and the fourth compounds are aromatic which means that option (b) and (d) are correct.
Note:
The second compound contains nitrogen as well as oxygen as the members of the ring. Though the oxygen atom contains two lone pairs, it only contributes a single lone pair for the conjugation and lone pair on nitrogen does not participate in conjugation at all as it is double bonded.
Complete step by step answer:
The Huckel’s rule of aromaticity states that:
A compound is aromatic only if it contains cyclic and continuous delocalization or conjugation of \[\pi \] electrons.
The compound must be planar which means that all the carbon atoms must lie in a single plane.
The organic compound must contain \[4n + 2\] number of \[\pi \] electrons where the value of \[n\] can be any whole number.
If all these three conditions stated above are not fulfilled then the compound is not aromatic.
The first compound contains a total of four electrons which does not satisfy the \[4n + 2\] condition and is therefore not an aromatic compound.
The second compound contains a total of six electrons being delocalized in a planar ring, which makes it an aromatic compound.
The third compound has two electrons but one of the three carbon is not part of the cyclic conjugation, therefore it’s not an aromatic compound.
The fourth compound contains a total of six electrons being delocalized in a planar ring, which makes it an aromatic compound.
\[ \Rightarrow \] Hence, the second and the fourth compounds are aromatic which means that option (b) and (d) are correct.
Note:
The second compound contains nitrogen as well as oxygen as the members of the ring. Though the oxygen atom contains two lone pairs, it only contributes a single lone pair for the conjugation and lone pair on nitrogen does not participate in conjugation at all as it is double bonded.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




