
Which of the following compounds has linear shape?
(A)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$
(B)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$
(C) $C{{H}_{4}}$
(D) ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: Attempt this question finding the steric number of the carbon atom in each of the given compounds. As we know that for a compound to be linear, its hybridization must be $sp$ which is possible when steric number is equal to 2.
Formula used:
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Complete answer:
As we know that Steric Number of a molecule is used in Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory to determine the molecular geometry of that molecule i.e., it gives the electron pair arrangement for the geometry.
Below are the little hybridizations and their shape with respect to the steric number that will be required for this question:-
-Now let us check the steric number of carbon in each and every molecule by making their structure and then further calculations:-
(A)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$
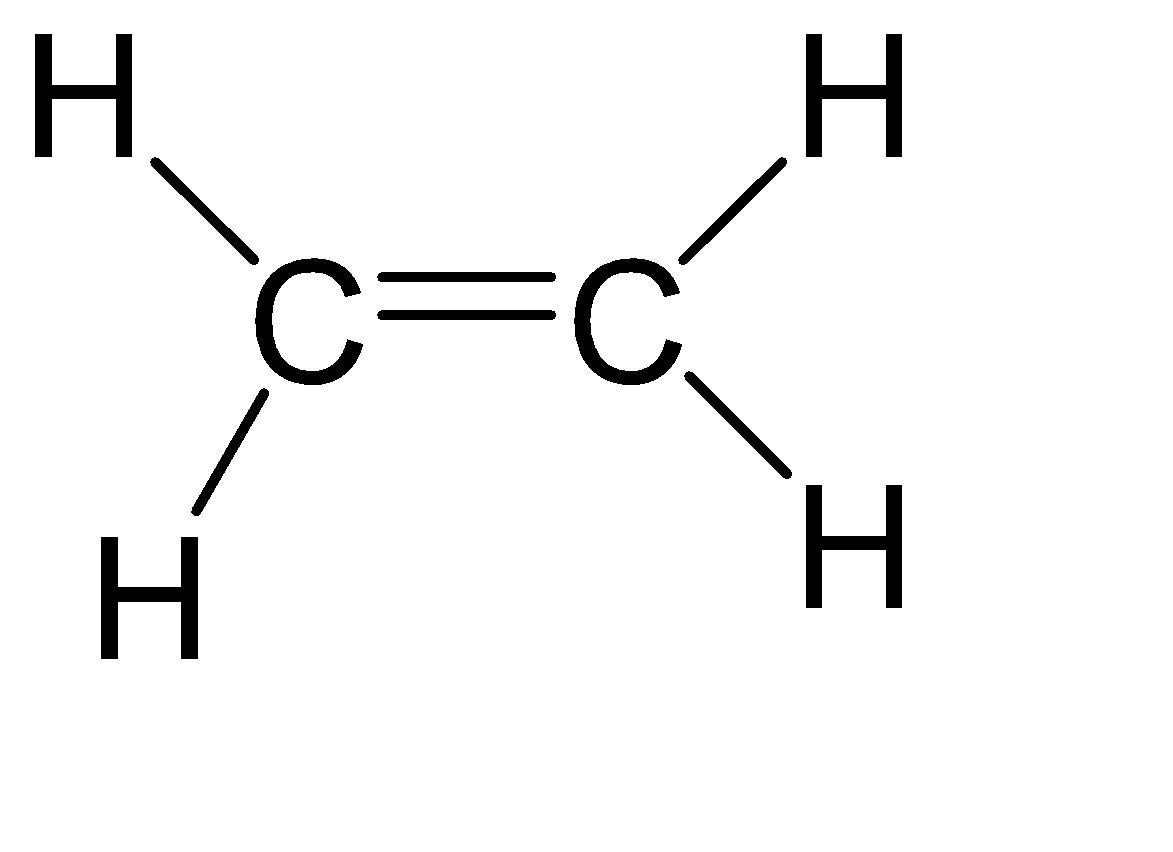
Since both carbons are the same, therefore we can calculate the steric number of any one of them.
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 3 + 0 = 3
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and hence the shape is Trigonal Planar.
(B)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$
$H-C\equiv C-H$
Since both carbons are the same, therefore we can calculate the steric number of any one of them.
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 2 + 0 = 2
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{p}$ and hence the shape is Linear.
(C) $C{{H}_{4}}$
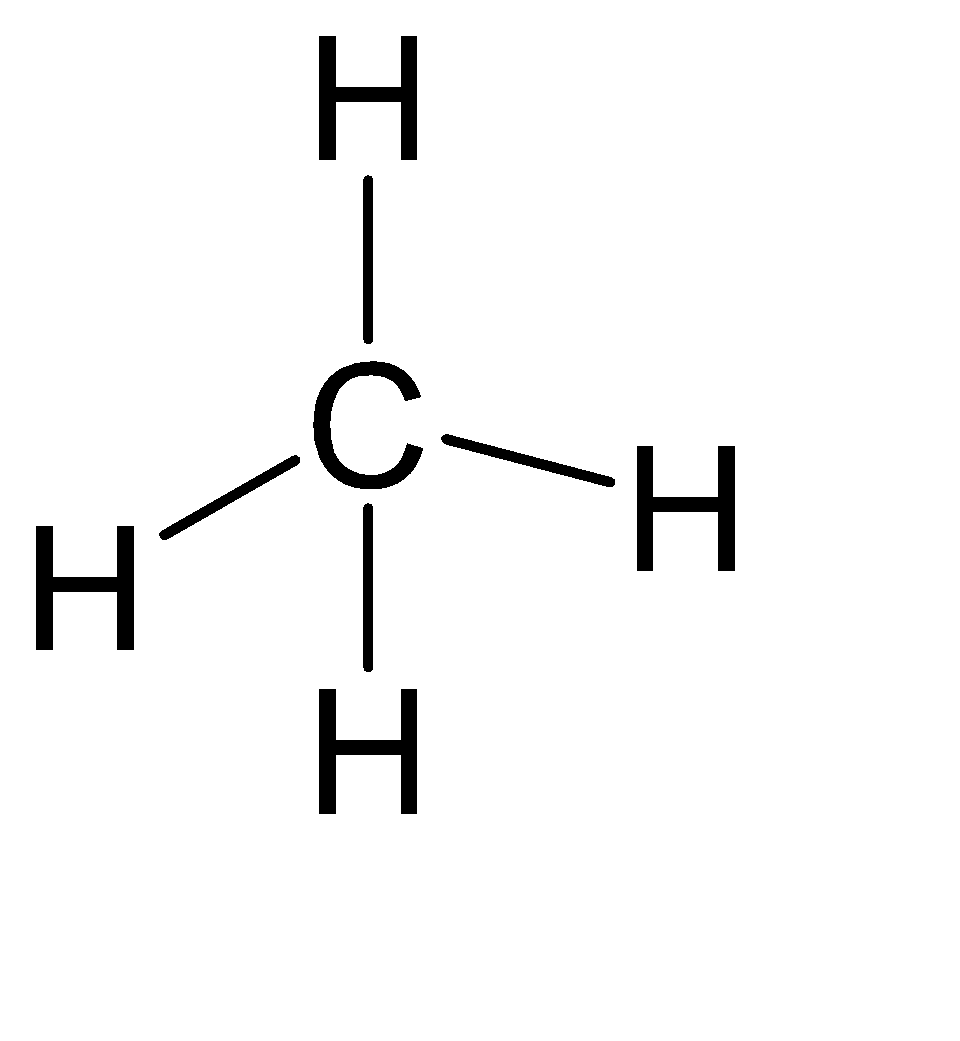
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 4 + 0 = 4
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and hence the shape is Tetrahedral.
(D) ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
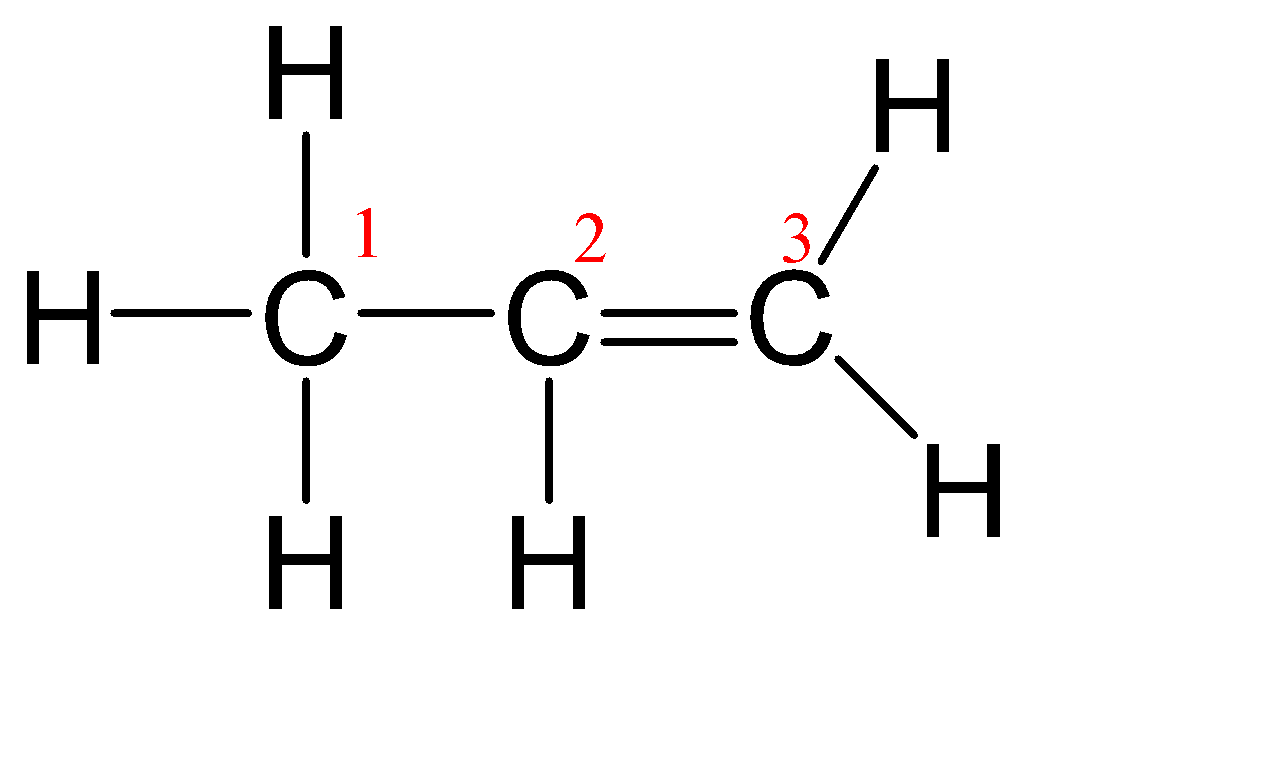
Since all the carbon have different environments so even if a single carbon has a shape other than linear then the whole molecule will not be considered as a linear molecule.
Steric number (${{C}_{1}}$ ) = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number (${{C}_{1}}$ ) = 4 + 0 = 4
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and hence the shape is Tetrahedral.
-Hence the correct answer is (B)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$
Note:
We can also calculate steric number by using the number of sigma bonds as follows:
Steric number = Number of sigma bonds around the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
-In case of${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$, there is possibility of another structure as well:-
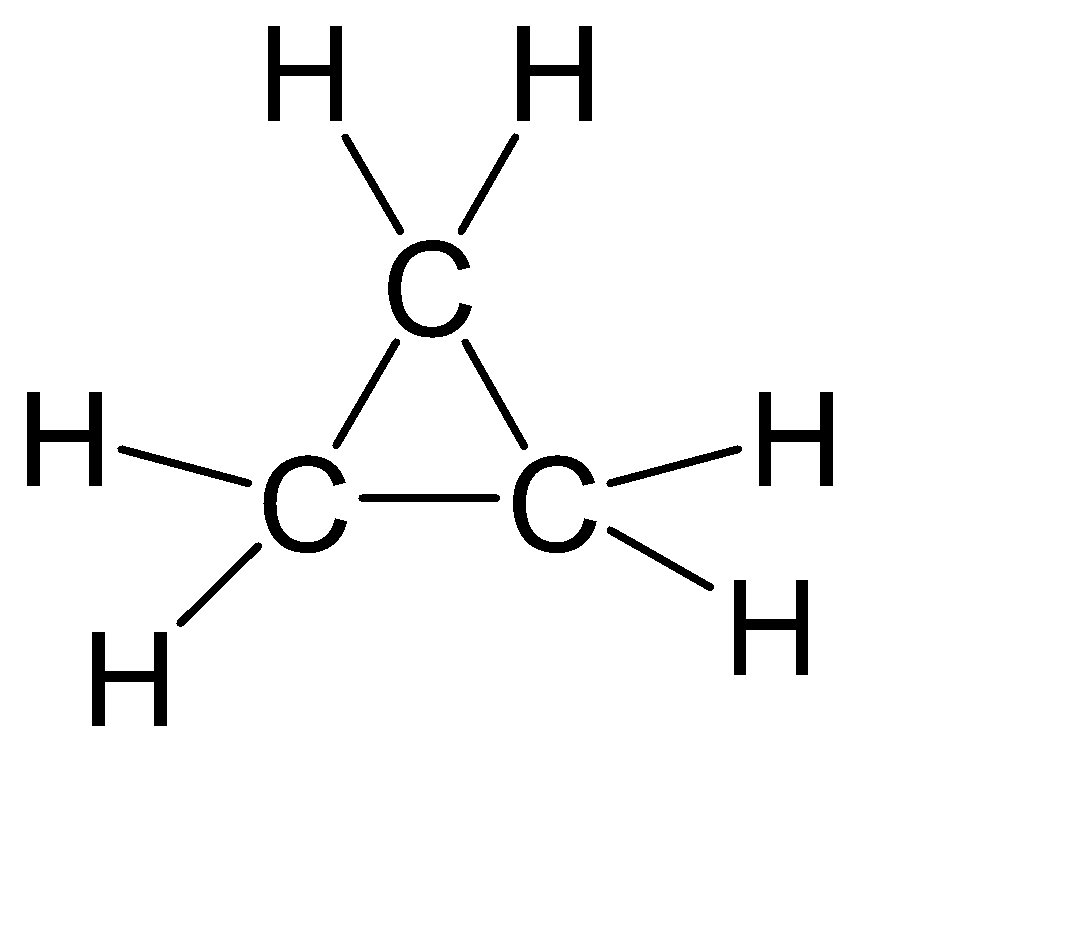
Even this structure is not linear hence the answer remains the same.
Formula used:
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Complete answer:
As we know that Steric Number of a molecule is used in Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion theory to determine the molecular geometry of that molecule i.e., it gives the electron pair arrangement for the geometry.
Below are the little hybridizations and their shape with respect to the steric number that will be required for this question:-
| Steric Number | Hybridization | Shape |
| 2 | $sp$ | Linear |
| 3 | $s{{p}^{2}}$ | Trigonal planar |
| 4 | $s{{p}^{3}}$ | Tetrahedral |
-Now let us check the steric number of carbon in each and every molecule by making their structure and then further calculations:-
(A)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{4}}$

Since both carbons are the same, therefore we can calculate the steric number of any one of them.
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 3 + 0 = 3
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{2}}$ and hence the shape is Trigonal Planar.
(B)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$
$H-C\equiv C-H$
Since both carbons are the same, therefore we can calculate the steric number of any one of them.
Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 2 + 0 = 2
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{p}$ and hence the shape is Linear.
(C) $C{{H}_{4}}$

Steric number = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number = 4 + 0 = 4
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and hence the shape is Tetrahedral.
(D) ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$
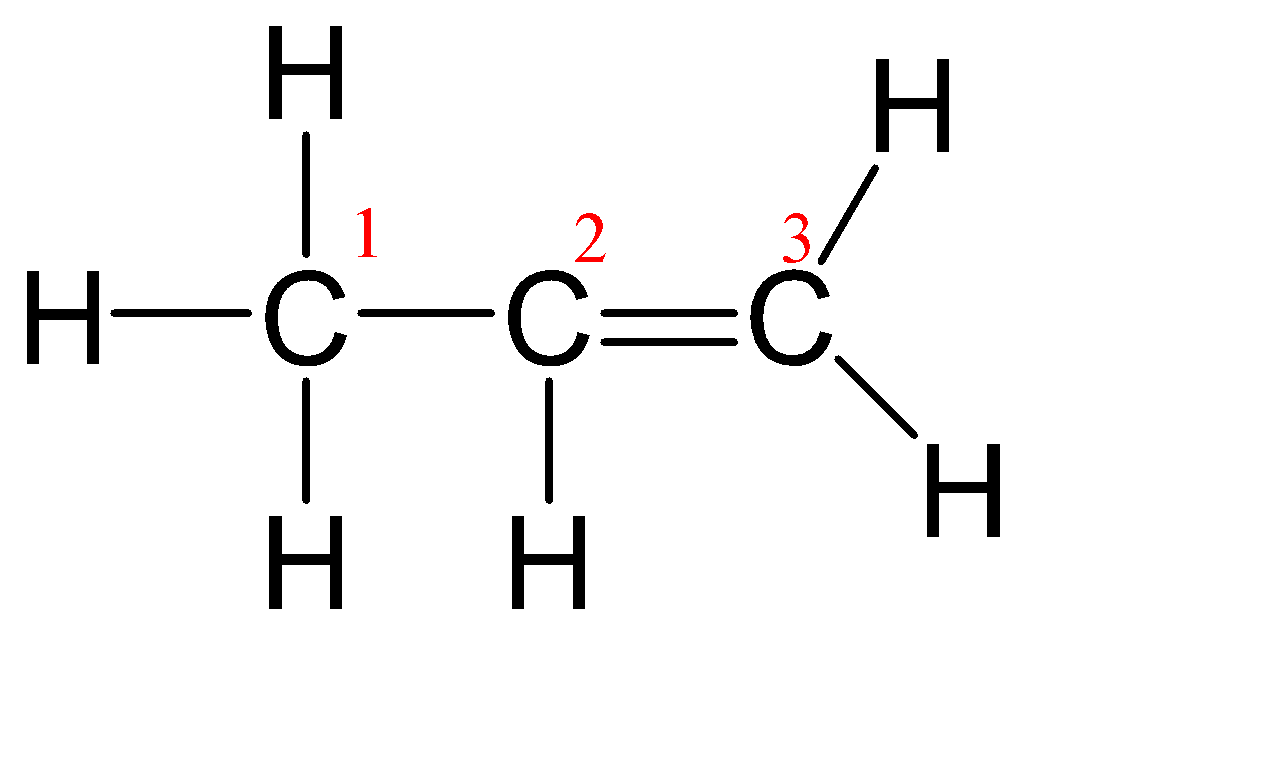
Since all the carbon have different environments so even if a single carbon has a shape other than linear then the whole molecule will not be considered as a linear molecule.
Steric number (${{C}_{1}}$ ) = Number of atoms bonded to the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
Steric number (${{C}_{1}}$ ) = 4 + 0 = 4
From the above table, we can assume that its hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$ and hence the shape is Tetrahedral.
-Hence the correct answer is (B)${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{2}}$
Note:
We can also calculate steric number by using the number of sigma bonds as follows:
Steric number = Number of sigma bonds around the central atom + number of lone pairs on the central atom.
-In case of${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{6}}$, there is possibility of another structure as well:-

Even this structure is not linear hence the answer remains the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




