
Which of the following compounds has incorrect IUPAC nomenclature? This question has multiple correct options
A. \[C{H_3}C{H_2}COO{C_2}{H_5} \leftarrow \] ethyl butanoate
B. \[C{H_3}CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)C{H_2}CHO{\text{ }} \leftarrow \] ethyl butanoate
C. \[C{H_3}CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)COC{H_2}C{H_3} \leftarrow \] 2-methyl-3-pentanone
D. \[C{H_3}CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)CH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3} \leftarrow \] 2-methyl-3-butanol
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: IUPAC names are combined with the primary prefix, root word, and primary suffix. By this, each compound can be named unique. Primary prefixes are used to indicate the origin of the compound in IUPAC nomenclature. Prefixes are used to differentiate the cyclic and acyclic molecules in IUPAC nomenclature.
Complete step by step answer:
In the IUPAC nomenclature case, the root word is the number of total carbons in the longest chain of that compound.
… and so on.
The primary suffix is used to differentiate between the saturated compounds (Alkanes) and unsaturated compounds (Alkene and Alkynes).
If there is more than one suffix. Then one of those suffixes is considered as the secondary suffix.
Example: Methanol (Alkanol), here ‘ol’ is a secondary suffix.
The primary prefixes are used to differentiate between cyclic compounds and noncyclic or chain compounds. For cyclic compound prefix s ‘cyclo’. if there are any side chains or groups are present then secondary prefixes like ‘methyl’, ‘ethyl’, ‘propyl’, ‘isopropyl’ are used.
Now according to this IUPAC nomenclature rules, in case of \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C00{C_2}{H_5}\] the IUPAC name should be, ethyl propanoate. On the other hand, the IUPAC name of \[C{H_3}CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)CH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3}\] should be 3-methyl-2-butanol.
So, the given IUPAC names of these two compounds are wrong.
Therefore, the correct options are, A and D.
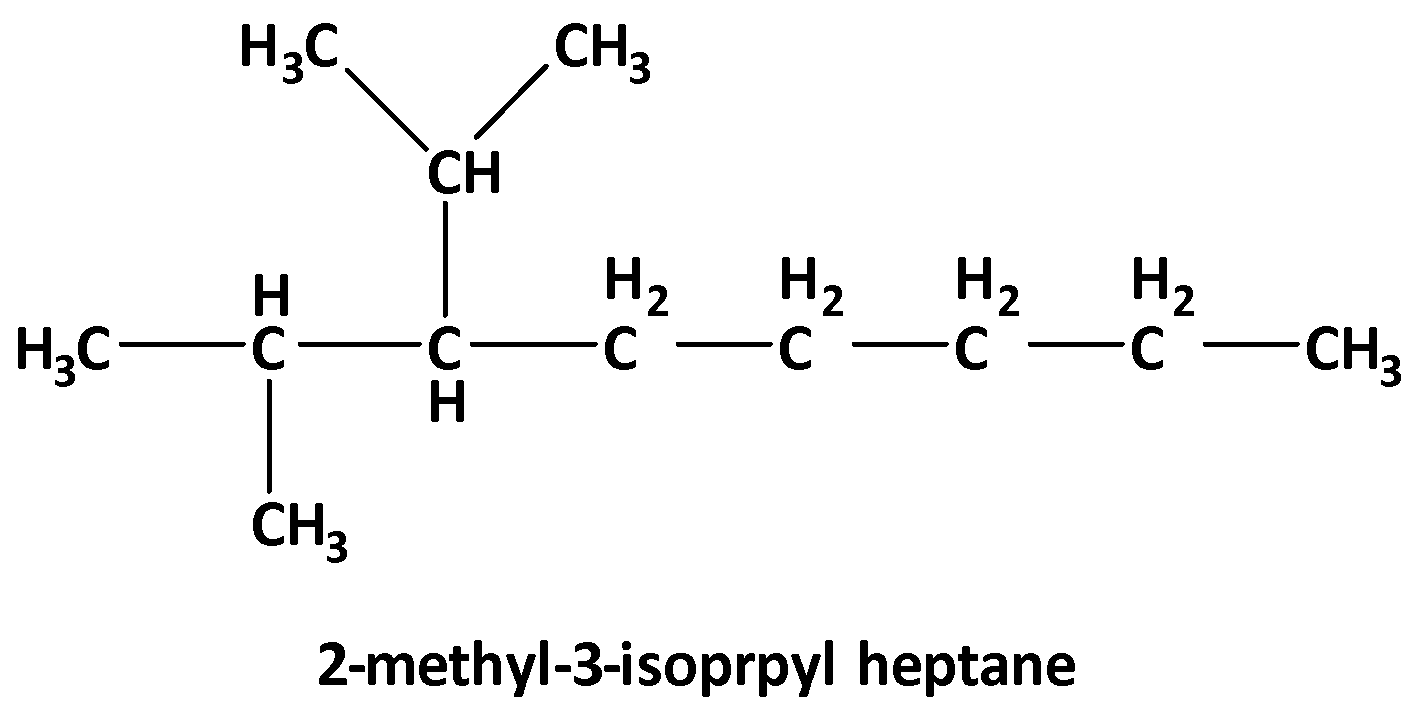
Note: Considering the IUPAC nomenclature, the structure of 2-methyl-3-isopropyl heptane is
“heptane” is for seven carbon in the longest chain, and it is from the group of alkanes that are all sigma bonds. “2-methyl” means there is a methyl group at 2 positions and “3-isopropyl” means there is an isopropyl group at 3 positions. So, the structure is as follows,
Complete step by step answer:
In the IUPAC nomenclature case, the root word is the number of total carbons in the longest chain of that compound.
| No. of carbons | Root word |
| 1 | meth |
| 2 | eth |
| 3 | prop |
| 4 | but |
| 5 | pent |
… and so on.
The primary suffix is used to differentiate between the saturated compounds (Alkanes) and unsaturated compounds (Alkene and Alkynes).
| compound | suffix |
| Alkane | ane |
| Alkene | Ene |
| Alkyne | Yne |
If there is more than one suffix. Then one of those suffixes is considered as the secondary suffix.
Example: Methanol (Alkanol), here ‘ol’ is a secondary suffix.
The primary prefixes are used to differentiate between cyclic compounds and noncyclic or chain compounds. For cyclic compound prefix s ‘cyclo’. if there are any side chains or groups are present then secondary prefixes like ‘methyl’, ‘ethyl’, ‘propyl’, ‘isopropyl’ are used.
Now according to this IUPAC nomenclature rules, in case of \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C00{C_2}{H_5}\] the IUPAC name should be, ethyl propanoate. On the other hand, the IUPAC name of \[C{H_3}CH\left( {C{H_3}} \right)CH\left( {OH} \right)C{H_3}\] should be 3-methyl-2-butanol.
So, the given IUPAC names of these two compounds are wrong.
Therefore, the correct options are, A and D.
Note: Considering the IUPAC nomenclature, the structure of 2-methyl-3-isopropyl heptane is
“heptane” is for seven carbon in the longest chain, and it is from the group of alkanes that are all sigma bonds. “2-methyl” means there is a methyl group at 2 positions and “3-isopropyl” means there is an isopropyl group at 3 positions. So, the structure is as follows,

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




