
Which of the following compounds are monobasic proton donor acids in water?
(A) $ {{\text{H}}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}},{{\text{H}}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}} $
(B) $ {{\text{H}}_{3}}B{{O}_{3}},{{\text{H}}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}} $
(C) $ {{\text{H}}_{3}}P{{O}_{3}},{{\text{H}}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}} $
(D) $ {{\text{H}}_{3}}P{{O}_{2}},HCl{{O}_{4}} $
Answer
507.3k+ views
Hint: We are given four pairs of compounds. We will study each pair and see their structure to identify their properties in water if they are monobasic, dibasic or tribasic and if they are proton donors or not.
Complete answer:
Let’s see the first pair of compounds: first is Hypophosphorous acid and second is Boric acid. The structure of both compound is given as
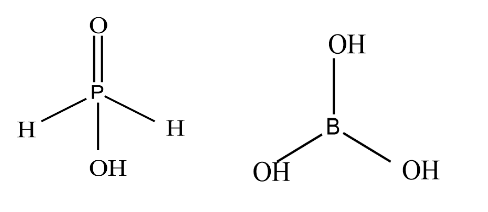
From the structure on the left side, we can say that Hypophosphorous acid is monobasic because of one hydroxyl group and it can donate protons. on the right hand from the structure of boric acid we observe that it is tribasic acid as it has three hydroxyl groups but it can act as monobasic acid as it accepts a pair of electrons it does not donate protons. So group one is not the required group.
Now for the second group of compounds we have Boric acid and Phosphorous acid we have already discussed boric acid so we will discuss only Phosphorous acid let’s see the structure
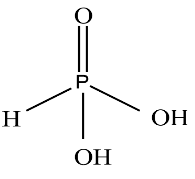
From the above structure we can see it is dibasic acid. Due to the presence of two hydroxyl groups it can donate a single proton. Due to Boric acid being unable to donate protons, group two is not the required group.
In the third group of compounds we have Hypophosphorous acid and phosphorous acid. We have already discussed their structure since Phosphorus acid is dibasic so this group is not the required group.
Let's see the last group. It has Hypophosphorous acid and Perchloric acid, we have already seen the structure of Hypophosphorous acid, it is monobasic proton donor acid. Let's see the structure of Perchloric acid.
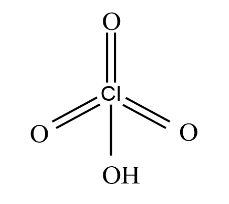
It is a monobasic acid due to the presence of one hydroxyl group and it can donate protons so this group is the required group.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
Although boric acid contains three hydroxyl groups it can act as a monobasic acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from hydroxyl ions rather than donating the proton that is why it is a monobasic Lewis acid.
Complete answer:
Let’s see the first pair of compounds: first is Hypophosphorous acid and second is Boric acid. The structure of both compound is given as

From the structure on the left side, we can say that Hypophosphorous acid is monobasic because of one hydroxyl group and it can donate protons. on the right hand from the structure of boric acid we observe that it is tribasic acid as it has three hydroxyl groups but it can act as monobasic acid as it accepts a pair of electrons it does not donate protons. So group one is not the required group.
Now for the second group of compounds we have Boric acid and Phosphorous acid we have already discussed boric acid so we will discuss only Phosphorous acid let’s see the structure

From the above structure we can see it is dibasic acid. Due to the presence of two hydroxyl groups it can donate a single proton. Due to Boric acid being unable to donate protons, group two is not the required group.
In the third group of compounds we have Hypophosphorous acid and phosphorous acid. We have already discussed their structure since Phosphorus acid is dibasic so this group is not the required group.
Let's see the last group. It has Hypophosphorous acid and Perchloric acid, we have already seen the structure of Hypophosphorous acid, it is monobasic proton donor acid. Let's see the structure of Perchloric acid.

It is a monobasic acid due to the presence of one hydroxyl group and it can donate protons so this group is the required group.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note:
Although boric acid contains three hydroxyl groups it can act as a monobasic acid because it accepts a pair of electrons from hydroxyl ions rather than donating the proton that is why it is a monobasic Lewis acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




