
Which of the following combinations are present in plant cells but not in animal cells?
(a) Cell wall and plastid
(b) Cell wall and cell membrane
(c) Plastids and the nucleus
(d) Cell membrane and cytoplasm
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint: Plants cells have a double-membrane organelle that is responsible for the processing and preservation of food and the outermost covering present outside the cell membrane and is robust, flexible, and often rigid in its texture. which is absent in the animal cells.
Complete answer:
- The cell wall is primarily composed of cellulose, long carbohydrate fibers, including hemicellulose, lignin, and pectin.
The key feature of the cell wall is:
-Protecting the cell from physical damage and invasive pathogens.
-The direction of cell growth is regulated and monitored.
-Providing strength, structural support, and preserving the cell shape.
-Functions as a storage unit by storing carbohydrates for use in plant growth, particularly in seeds.
-It allows smaller molecules to enter freely into it.
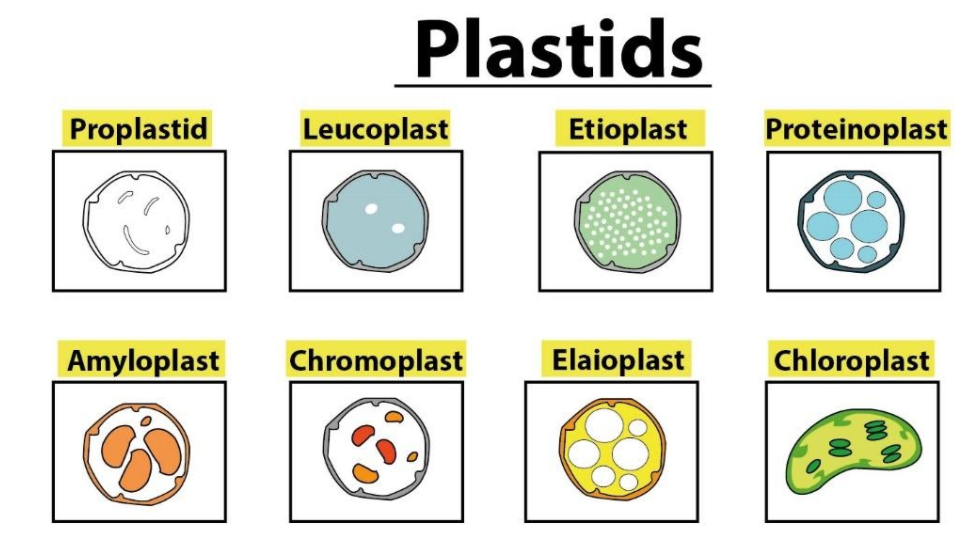
- There are various types of plastics with their unique functions. Of these, few are categorized mainly based on the presence or absence of biological pigments and their stage of development.
Chloroplast
Chromoplast
Gerontoplast
Leukoplast
So, the answer is, “Cell wall and plastid.”
Note: - Plastids also contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that may alter the color of the cells.
- Both plant and animal cells share a few different cell organelles, both of which are eukaryotes. The function of all these organelles is said to be very similar.
- Plant and animal cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysosomes. They have identical membranes, such as cytoskeletal and cytosol elements. It is also possible to have a larger plant cell than an animal cell. The animal cell standard range is between 10 and 30 micron and the plant cell range is between 10 and 100 microns.
Complete answer:
- The cell wall is primarily composed of cellulose, long carbohydrate fibers, including hemicellulose, lignin, and pectin.
The key feature of the cell wall is:
-Protecting the cell from physical damage and invasive pathogens.
-The direction of cell growth is regulated and monitored.
-Providing strength, structural support, and preserving the cell shape.
-Functions as a storage unit by storing carbohydrates for use in plant growth, particularly in seeds.
-It allows smaller molecules to enter freely into it.
- There are various types of plastics with their unique functions. Of these, few are categorized mainly based on the presence or absence of biological pigments and their stage of development.
Chloroplast
Chromoplast
Gerontoplast
Leukoplast
So, the answer is, “Cell wall and plastid.”
Note: - Plastids also contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that may alter the color of the cells.
- Both plant and animal cells share a few different cell organelles, both of which are eukaryotes. The function of all these organelles is said to be very similar.
- Plant and animal cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, nucleus, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysosomes. They have identical membranes, such as cytoskeletal and cytosol elements. It is also possible to have a larger plant cell than an animal cell. The animal cell standard range is between 10 and 30 micron and the plant cell range is between 10 and 100 microns.


Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

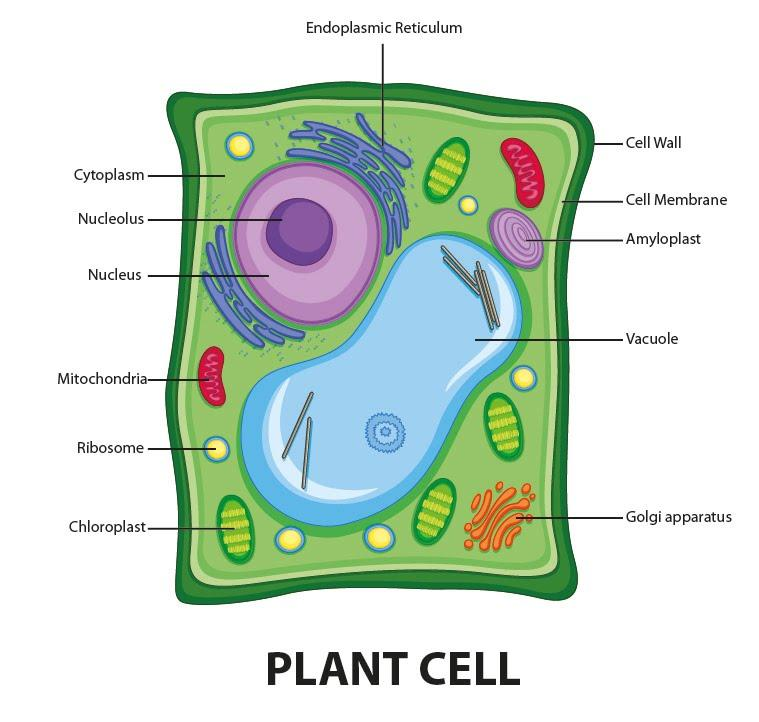
Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




