
Which of the following can be prepared effectively by Williamson ether synthesis:
A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Knowing the basic mechanism of Williamson’s ether synthesis can solve the given problem. Only one option here can be the product of the mechanism, others would have some defining factors which will stop the molecules from forming those ethers.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first study about the Williamson’s ether synthesis;
Williamson’s ether synthesis- It is an organic reaction forming an ether. It is an ${{S}_{N}}2$reaction in which an alkoxide ion (a deprotonated alcohol) is a nucleophile which is responsible to displace a halide ion from alkyl halide resulting the formation of ether. General reaction is given as,
\[R-{{O}^{-}}+R'-X\to R-O-R'+{{X}^{-}}\]
Key facts-
-As, ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is a single step reaction where the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from backside famously known as backside attack of nucleophile on alkyl halide.
-The only barrier to ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is presence of steric hindrance on alkyl halides. Thus, the molecules having steric hindrance within them won’t undergo ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction and form ether by Williamson’s ether synthesis.
-This synthesis is limited to primary and secondary alkyl halides. Tertiary halides tend to have an elimination reaction in presence of alkoxide ions.
Now, let us move towards the given illustration,
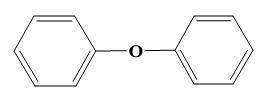
For (A)-
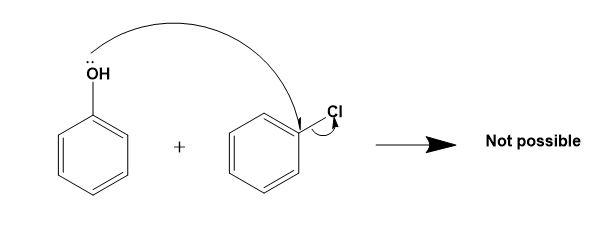
Here, the phenolic ring is already a nucleophile hence, another nucleophile cannot attack on it to form a successful ether.
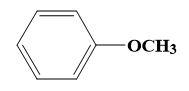
For (B)-
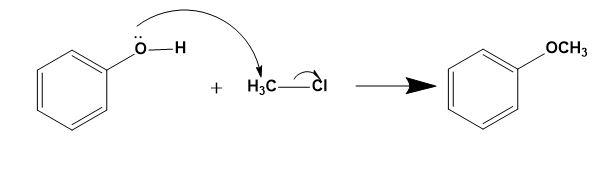
Here, formation of ether by Williamson’s ether synthesis is possible as shown above by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
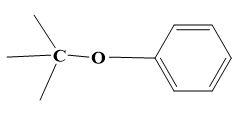
For (C)-
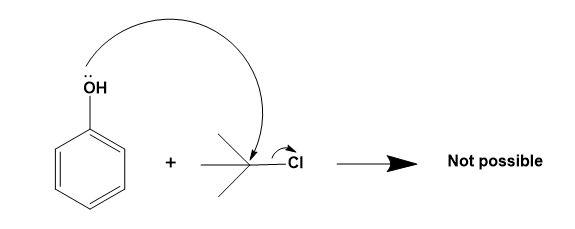
Here, formation of ether is not possible as alkyl halide has a bulky group present on it which makes it impossible from undergoing ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
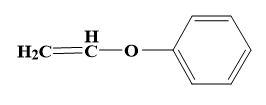
For (D)-
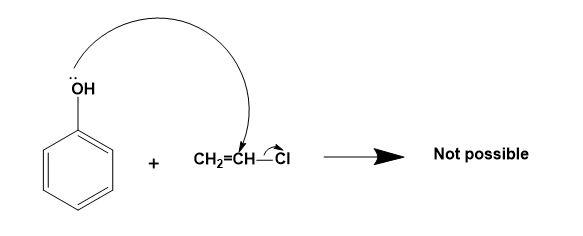
Here, the alkyl halide is a nucleophile already, so another nucleophile cannot attack the same. So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Do note that presence of bulky groups or a nucleophile within the reactants makes it hard to form an ether by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism and thus, the Williamson’s ether synthesis is not possible.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us first study about the Williamson’s ether synthesis;
Williamson’s ether synthesis- It is an organic reaction forming an ether. It is an ${{S}_{N}}2$reaction in which an alkoxide ion (a deprotonated alcohol) is a nucleophile which is responsible to displace a halide ion from alkyl halide resulting the formation of ether. General reaction is given as,
\[R-{{O}^{-}}+R'-X\to R-O-R'+{{X}^{-}}\]
Key facts-
-As, ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is a single step reaction where the nucleophile attacks the alkyl halide from backside famously known as backside attack of nucleophile on alkyl halide.
-The only barrier to ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction is presence of steric hindrance on alkyl halides. Thus, the molecules having steric hindrance within them won’t undergo ${{S}_{N}}2$ reaction and form ether by Williamson’s ether synthesis.
-This synthesis is limited to primary and secondary alkyl halides. Tertiary halides tend to have an elimination reaction in presence of alkoxide ions.
Now, let us move towards the given illustration,
For (A)-

Here, the phenolic ring is already a nucleophile hence, another nucleophile cannot attack on it to form a successful ether.
For (B)-

Here, formation of ether by Williamson’s ether synthesis is possible as shown above by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
For (C)-

Here, formation of ether is not possible as alkyl halide has a bulky group present on it which makes it impossible from undergoing ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
For (D)-

Here, the alkyl halide is a nucleophile already, so another nucleophile cannot attack the same. So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Do note that presence of bulky groups or a nucleophile within the reactants makes it hard to form an ether by ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism and thus, the Williamson’s ether synthesis is not possible.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




