
Which of the following bases is present in RNA in place of thymine?
A) Uracil
B) Adenine
C) Guanine
D) Water
Answer
511.2k+ views
Hint: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is an important biological macromolecule that is present in all biological cells and is principally involved in the synthesis of proteins, carrying the messenger instructions from DNA, which itself contains the genetic instructions required for the development and maintenance of life.
Complete answer:
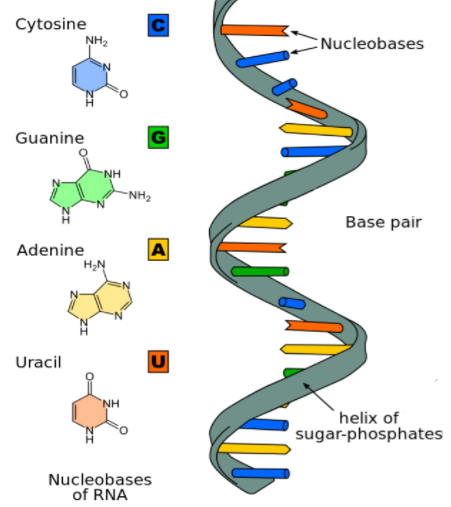
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule similar to DNA but unlike DNA, RNA is single-stranded. An RNA strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar which is ribose and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of the four bases-adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The bases are complementary to each other. Adenine is complementary with uracil and guanine to cytosine.
Different types of RNA exist in the cell:
- messenger RNA (mRNA)
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- transfer RNA (tRNA).
The cell uses RNA for a number of different tasks, mRNA called messenger RNA, is the nucleic acid information molecule that transfers information from the genome into proteins by translation. Another form of RNA is tRNA, or also called transfer RNA, and these are non-protein encoding RNA molecules that physically carry amino acids to the translation site that allows them to be assembled into chains of proteins in the process of translation. rRNA is ribosomal RNA present is ribosomes. The figure below shows the structure of RNA.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ i.e, Uracil.
Note: DNA contains thymine in place of uracil. Some of the most infamous viruses like HIV, the common cold virus, influenza and COVID-19 contain all their genetic information in RNA, with no DNA predecessor. Thus RNA is the genetic material for them. During replication, RNA viruses from double-stranded DNA in the HIV virus through reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Complete answer:
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a molecule similar to DNA but unlike DNA, RNA is single-stranded. An RNA strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar which is ribose and phosphate groups. Attached to each sugar is one of the four bases-adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The bases are complementary to each other. Adenine is complementary with uracil and guanine to cytosine.
Different types of RNA exist in the cell:
- messenger RNA (mRNA)
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- transfer RNA (tRNA).
The cell uses RNA for a number of different tasks, mRNA called messenger RNA, is the nucleic acid information molecule that transfers information from the genome into proteins by translation. Another form of RNA is tRNA, or also called transfer RNA, and these are non-protein encoding RNA molecules that physically carry amino acids to the translation site that allows them to be assembled into chains of proteins in the process of translation. rRNA is ribosomal RNA present is ribosomes. The figure below shows the structure of RNA.
Thus, the correct option is ‘A’ i.e, Uracil.

Note: DNA contains thymine in place of uracil. Some of the most infamous viruses like HIV, the common cold virus, influenza and COVID-19 contain all their genetic information in RNA, with no DNA predecessor. Thus RNA is the genetic material for them. During replication, RNA viruses from double-stranded DNA in the HIV virus through reverse transcriptase enzyme.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




