
Which of the following are isomers?
(A) Ethane and propane
(B) Ethane and ethene
(C) Ethane and ethyne
(D) n-butane and isobutane
Answer
543.6k+ views
Hint: Isomerism is a phenomenon of organic chemistry in which more than $1$ species has the same chemical formula but different structures. Those compounds who have same chemical formula but different properties and the arrangement of atoms in their molecule are called isomers
Complete step-by-step answer:Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Structural isomers are the isomers in which the arrangement of atoms is in a different order having the same molecular formulas. The difference in structures depends on the order in which the atoms are arranged.
In Chain isomerism, there is a difference in the atomic arrangement of the carbon chain of the molecule. $2$ or more compounds that have the same molecular formula with different main chains, then this isomerism is called Chain isomerism.
In Positional isomerism, there is a difference in the positions that are taken by the substituent groups or atoms. This is due to the unsaturation that occurs in the chain. When the position of the functional groups in the main chain changes, then it is called position isomerism.
The molecular formula of Ethane is \[{C_2}{H_6}\] and the molecular formula of propane is ${C_3}{H_8}$. Since, molecular formula of both compounds are different, isomerism is not possible. It is also not possible in case of Ethane and ethene and ethane and ethyne, because molecular formulae of ethene and ethyne are \[{C_2}{H_4}\] and ${C_2}{H_2}$ respectively.
In case of n-butane and iso-butane the molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$ for both Compounds. They are examples of chain isomerism. These organic compounds have $4$ carbon atoms. The rotation about the main central \[C - C\;\] bond results in $2$ different conformations for n-butane. The IUPAC name of Iso-butane is \[2 - methyl{{ }}propane\]. The isomers will be:
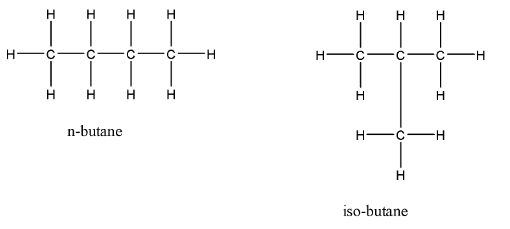
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: There are $3$ types of Structural isomerism existing namely chain isomerism, position isomerism, and functional group isomerism. Chain isomerism is called skeletal isomerism and position isomerism is also called substituent isomerism.
Complete step-by-step answer:Isomerism is of two types (a) Structural and (b) Stereo. Structural isomers are the isomers in which the arrangement of atoms is in a different order having the same molecular formulas. The difference in structures depends on the order in which the atoms are arranged.
In Chain isomerism, there is a difference in the atomic arrangement of the carbon chain of the molecule. $2$ or more compounds that have the same molecular formula with different main chains, then this isomerism is called Chain isomerism.
In Positional isomerism, there is a difference in the positions that are taken by the substituent groups or atoms. This is due to the unsaturation that occurs in the chain. When the position of the functional groups in the main chain changes, then it is called position isomerism.
The molecular formula of Ethane is \[{C_2}{H_6}\] and the molecular formula of propane is ${C_3}{H_8}$. Since, molecular formula of both compounds are different, isomerism is not possible. It is also not possible in case of Ethane and ethene and ethane and ethyne, because molecular formulae of ethene and ethyne are \[{C_2}{H_4}\] and ${C_2}{H_2}$ respectively.
In case of n-butane and iso-butane the molecular formula is ${C_4}{H_{10}}$ for both Compounds. They are examples of chain isomerism. These organic compounds have $4$ carbon atoms. The rotation about the main central \[C - C\;\] bond results in $2$ different conformations for n-butane. The IUPAC name of Iso-butane is \[2 - methyl{{ }}propane\]. The isomers will be:

Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: There are $3$ types of Structural isomerism existing namely chain isomerism, position isomerism, and functional group isomerism. Chain isomerism is called skeletal isomerism and position isomerism is also called substituent isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




